MI APC API
1. OVERVIEW¶
1.1. Module Description¶
APC (short for Audio Process Chain) is a combination of algorithms including noise reduction, equalizer and automatic gain control.
The purpose of APC is to improve audio quality. The internal algorithm concatenation process is Anr Eq/Hpf Agc. The SNR is improved through noise reduction and noise elimination. The EQ/HPF is adjusted according to the curve required by the customer, and the output is amplified or suppressed through AGC.
1.2. Keyword¶
-
AGC
AGC(Automatic Gain Control), used to control the digital output gain.
-
EQ
EQ(Equalizer) , used to gain or attenuate specific frequency bands.
-
ANR
ANR(Acoustic Noise Reduction), used to remove the continued and fixed frequency noise in the environment.
-
HPF
HPF(High-Pass Filtering)
1.3. Note¶
In order to facilitate debugging and confirm the effect of the algorithm, the user application needs to implement replacement algorithm parameter and grab audio data.
2. API REFERENCE¶
2.1. API List¶
| API name | Features |
|---|---|
| IaaApc_GetBufferSize | Get the memory size required for Apc algorithm running |
| IaaApc_Init | Initialize the Apc algorithm |
| IaaApc_Config | Configure the Apc algorithm |
| IaaApc_GetNrResult | Get the Apc algorithm Anr processing result |
| IaaApc_GetNrEqResult | Get the processing result of Anr and Eq in the Apc algorithm |
| IaaApc_Run | Apc algorithm processing |
| IaaApc_Free | Release Apc algorithm resources |
| IaaApc_Reset | Reinitialize the Apc algorithm |
| IaaApc_GetConfig | Get the Apc algorithm current configuration parameters |
| IaaAnr_GetBufferSize | Get the memory size required for Anr algorithm running |
| IaaAnr_Init | Initialize the Anr algorithm |
| IaaAnr_Config | Configure the Anr algorithm |
| IaaAnr_Run | Anr algorithm processing |
| IaaAnr_Free | Release Anr algorithm resources |
| IaaAnr_Reset | Reinitialize the Anr algorithm |
| IaaAnr_GetConfig | Get the Anr algorithm current configuration parameters |
| IaaEq_GetBufferSize | Get the memory size required for Eq algorithm running |
| IaaEq_Init | Initialize the Eq algorithm |
| IaaEq_Config | Configure the Eq algorithm |
| IaaEq_Run | Eq algorithm processing |
| IaaEq_Free | Release Eq algorithm resources |
| IaaEq_Reset | Reinitialize the Eq algorithm |
| IaaEq_GetConfig | Get the Eq algorithm current configuration parameters |
| IaaAgc_GetBufferSize | Get the memory size required for Agc algorithm running |
| IaaAgc_Init | Initialize the Agc algorithm |
| IaaAgc_Config | Configure the Agc algorithm |
| IaaAgc_Run | Agc algorithm processing |
| IaaAgc_Free | Release Agc algorithm resources |
| IaaAgc_Reset | Reinitialize the Eq algorithm |
| IaaAgc_GetConfig | Get the Agc algorithm current configuration parameters |
2.2. IaaApc_GetBufferSize¶
-
Features
Get the memory size required for Apc algorithm running.
-
Syntax
unsigned int IaaApc_GetBufferSize(AudioApcBufferConfig *apc_switch);
-
Parameters
Parameter name Description Input/output apc_switch Structure pointer for configure the Apc algorithm to enable Input -
Return value
Return value is the memory size required for Apc algorithm running.
-
Dependency
-
Header: AudioProcess.h
-
Library: libAPC_LINUX.so/ libAPC_LINUX.a
-
-
Note
The interface only returns the required memory size. The application and release of memory needs to be processed by the application.
-
Example
Please refer to IaaApc_Run example.
2.3. IaaApc_Init¶
-
Features
Initialize the Apc algorithm .
-
Syntax
APC_HANDLE IaaApc_Init(char* const working_buffer_address, AudioProcessInit *audio_process_init, AudioApcBufferConfig *apc_switch);
-
Parameters
Parameter name Description Input/output working_buffer_address Apc algorithm memory address Input audio_process_init Apc algorithm initialization structure pointer Input apc_switch Apc algorithm enable structure pointer Input -
Return value
Return value Result Not NULL Successful NULL Failed -
Dependency
-
Header: AudioProcess.h
-
Library: libAPC_LINUX.so/ libAPC_LINUX.a
-
-
Note
- In the Apc algorithm, ANR/AGC/EQ supports 8K/16K/48K sampling rate, HPF only supports 8K/16K.
-
Example
Please refer to IaaApc_Run example.
2.4. IaaApc_Config¶
-
Features
Configure the Apc algorithm.
-
Syntax
ALGO_APC_RET IaaApc_Config(APC_HANDLE handle, AudioAnrConfig *anr_config, AudioEqConfig *eq_config, AudioHpfConfig *hpf_config, AudioVadConfig *vad_config, AudioDereverbConfig *dereverb_config, AudioAgcConfig *agc_config);
-
Parameters
Parameter name Description Input/output handle Apc algorithm handle Input anr_config Configure Anr algorithm structure pointer Input eq_config Configure Eq algorithm structure pointer Input hpf_config Configure Hpf algorithm structure pointer Input vad_config Configure Vad algorithm structure pointer(stop using) Input dereverb_config Configure Dereverb algorithm structure pointer (stop using) Input agc_config Configure Agc algorithm structure pointer Input -
Return value
Return value Result 0 Successful Non-zero Failed, refer to error code -
Dependency
-
Header: AudioProcess.h
-
Library: libAPC_LINUX.so/ libAPC_LINUX.a
-
-
Example
Please refer to IaaApc_Run example.
2.5. IaaApc_GetNrResult¶
-
Features
Get the Apc algorithm Anr processing result.
-
Syntax
ALGO_APC_RET IaaApc_GetNrResult(APC_HANDLE handle, short* nr_audio_out);
-
Parameters
Parameter name Description Input/output handle Apc algorithm handle Input nr_audio_out Anr handles Output data pointer Output -
Return value
Return value Result 0 Successful Non-zero Failed, refer to error code -
Dependency
-
Header: AudioProcess.h
-
Library: libAPC_LINUX.so/ libAPC_LINUX.a
-
-
Note
- Anr in the Apc algorithm must be enabled before calling the interface to obtain data.
-
Example
Please refer to IaaApc_Run example.
2.6. IaaApc_GetNrEqResult¶
-
Features
Get the processing result of Anr and Eq in the Apc algorithm
-
Syntax
ALGO_APC_RET IaaApc_GetNrEqResult(APC_HANDLE handle,short* nr_eq_audio_out);
-
Parameters
Parameter name Description Input/output handle Aec algorithm handle Input nr_eq_audio_out Anr and Eq handle output data pointer Output -
Return value
Return value Result 0 Successful Non-zero Failed, refer to error code -
Dependency
-
Header: AudioProcess.h
-
Library: libAPC_LINUX.so/ libAPC_LINUX.a
-
-
Note
- Enable Anr and Eq in the Apc algorithm before calling this interface to obtain data.
-
Example
Please refer to IaaApc_Run example.
2.7. IaaApc_Run¶
-
Features
Apc algorithm processing.
-
Syntax
ALGO_APC_RET IaaApc_Run(APC_HANDLE handle,short* pss_audio_in); -
Parameters
Parameter name Description Input/output handle Apc algorithm handle Input pss_audio_in Input data pointer Input/output -
Return value
Return value Result 0 Successful Non-zero Failed, refer to error code -
Dependency
-
Header: AudioProcess.h
-
Library: libAPC_LINUX.so/ libAPC_LINUX.a
-
-
Note
- The data must correspond to the point_number (sampling points required for one IaaApc_Run) set when calling IaaApc_Init. The processed data will be written back to the memory pointed to by pss_audio_in.
-
Example
#include <stdio.h> #include <string.h> #include <stdlib.h> #include <sys/time.h> #include "AudioProcess.h" /* 0:Fixed input file 1:User input file */ #define IN_PARAMETER 1 float AVERAGE_RUN(int a) { static unsigned int num = 0; static float avg = 0; if(0 == num) avg = 0; num++; avg = avg + ((float)a - avg) / ((float)num); return avg; } unsigned int _OsCounterGetMs(void) { struct timeval t1; gettimeofday(&t1, NULL); unsigned int T = ((1000000 * t1.tv_sec) + t1.tv_usec) / 1000; return T; } int main(int argc, char *argv[]) { short in_output[1024]; unsigned int T0, T1; float avg = 0; char src_file[128]; char dst_file[128]; int counter = 0; unsigned int workingBufferSize; char *workingBuffer = NULL; AudioApcBufferConfig apc_switch; FILE *fpIn, * fpOut; ALGO_APC_RET ret; AudioProcessInit apc_init; AudioAnrConfig anr_config; AudioEqConfig eq_config; AudioHpfConfig hpf_config; AudioAgcConfig agc_config; APC_HANDLE handle; /****************************User change section start**********************************/ int intensity_band[6] = {3,24,40,64,80,128}; int intensity[7] = {30,30,30,30,30,30,30}; short eq_table[129]; memset(eq_table, 0, sizeof(eq_table)); short compression_ratio_input[7] = {-65,-55,-48,-25,-18,-12,0}; short compression_ratio_output[7] = {-65,-50,-27,-12,-1,-1,-1}; apc_switch.anr_enable = 1; apc_switch.eq_enable = 1; apc_switch.agc_enable = 1; apc_init.point_number = 128; apc_init.channel = 1; apc_init.sample_rate = IAA_APC_SAMPLE_RATE_16000; /******ANR Config*******/ anr_config.anr_enable = apc_switch.anr_enable; anr_config.user_mode = 2; memcpy(anr_config.anr_intensity_band, intensity_band, sizeof(intensity_band)); memcpy(anr_config.anr_intensity, intensity, sizeof(intensity)); anr_config.anr_smooth_level = 10; anr_config.anr_converge_speed = 0; /******EQ Config********/ eq_config.eq_enable = apc_switch.eq_enable; eq_config.user_mode = 1; memcpy(eq_config.eq_gain_db, eq_table, sizeof(eq_table)); /******HPF Config********/ hpf_config.hpf_enable = apc_switch.eq_enable; hpf_config.user_mode = 1; hpf_config.cutoff_frequency = AUDIO_HPF_FREQ_150; /******AGC Config********/ agc_config.agc_enable = apc_switch.agc_enable; agc_config.user_mode = 1; agc_config.gain_info.gain_max = 40; agc_config.gain_info.gain_min = -10; agc_config.gain_info.gain_init = 12; agc_config.drop_gain_max = 36; agc_config.gain_step = 1; agc_config.attack_time = 1; agc_config.release_time = 1; agc_config.noise_gate_db = -80; memcpy(agc_config.compression_ratio_input, compression_ratio_input, sizeof(compression_ratio_input)); memcpy(agc_config.compression_ratio_output, compression_ratio_output, sizeof(compression_ratio_output)); agc_config.noise_gate_attenuation_db = 0; agc_config.drop_gain_threshold = -5; /****************************User change section end***********************************/ //(1)IaaApc_GetBufferSize workingBufferSize = IaaApc_GetBufferSize(&apc_switch); workingBuffer = (char*)malloc(workingBufferSize); if(NULL == workingBuffer) { printf("malloc workingBuffer failed !\n"); return -1; } printf("malloc workingBuffer succeed !\n"); //(2)IaaApc_Init handle = IaaApc_Init(workingBuffer, &apc_init, &apc_switch); if(NULL == handle) { printf("IaaApc_Init failed !\n"); return -1; } printf("IaaApc_Init succeed !\n"); //(3)IaaApc_Config if(IaaApc_Config(handle, &anr_config, &eq_config, &hpf_config, NULL, NULL, &agc_config)) { printf("IaaApc_Config failed !\n"); return -1; } printf("IaaApc_Config succeed !\n"); #if IN_PARAMETER if(argc < 3) { printf("Please enter the correct parameters!\n"); return -1; } sscanf(argv[1], "%s", src_file); sscanf(argv[2], "%s", dst_file); #else sprintf(src_file, "%s", "./APC_AFE_16K.wav"); if(argc < 2) { printf("Please enter the correct parameters!\n"); return -1; } sscanf(argv[1], "%s", dst_file); #endif fpIn = fopen(src_file, "rb"); if(NULL == fpIn) { printf("src_file open failed !\n"); return -1; } printf("src_file open succeed !\n"); fpOut = fopen(dst_file, "wb"); if(NULL == fpOut) { printf("dst_file open failed !\n"); return -1; } printf("dst_file open succeed !\n"); #if 1 fread(in_output, sizeof(char), 44, fpIn); fwrite(in_output, sizeof(char), 44, fpOut); #endif while(fread(in_output, sizeof(short), apc_init.point_number * apc_init.channel, fpIn)) { counter++; T0 = (long)_OsCounterGetMs(); ret = IaaApc_Run(handle, in_output); T1 = (long)_OsCounterGetMs(); avg += (T1 - T0); if(counter%1000 == 999) { printf("counter = %d\n", counter); printf("current time = %f\n", (float)counter * apc_init.point_number / apc_init.sample_rate); printf("process time = %lu(ms)\t", (long)(T1 - T0)); } if(ret) { printf("Error occured in NoiseReduct\n"); break; } fwrite(in_output, sizeof(short), apc_init.point_number * apc_init.channel, fpOut); } avg /= counter; printf("AVG is %.2f ms\n", avg); IaaApc_Free(handle); free(workingBuffer); fclose(fpIn); fclose(fpOut); printf("APC end !\n"); return 0; }
2.8. IaaApc_Free¶
-
Features
Release Apc algorithm resources
-
Syntax
ALGO_APC_RET IaaApc_Free(APC_HANDLE handle); -
Parameters
Parameter name Description Input/output handle Apc algorithm handle Input -
Dependency
-
Header: AudioProcess.h
-
Library: libAPC_LINUX.so/ libAPC_LINUX.a
-
-
Example
Please refer to IaaApc_Run example.
2.9. IaaApc_Reset¶
-
Features
Reinitialize the Apc algorithm.
-
Syntax
APC_HANDLE IaaApc_Reset(char* working_buffer_address,AudioProcessInit *audio_process_init, AudioApcBufferConfig *apc_switch); -
Parameters
Parameter name Description Input/output working_buffer_address Memory address used by Apc algorithm Input audio_process_init Apc algorithm initialization structure pointer Input apc_switch Structure pointer for configure the Apc algorithm to enable Input -
Return value
Return value Result Not NULL Successful NULL Failed -
Dependency
-
Header: AudioProcess.h
-
Library: libAPC_LINUX.so/ libAPC_LINUX.a
-
-
Note
When the Apc algorithm is reinitialized and the function options are different from previous, we need to release the memory used by the original algorithm, call IaaApc_GetBufferSize again to get the memory size required by the current function options, and reapply for the corresponding size of memory for the Apc algorithm.
2.10. IaaApc_GetConfig¶
-
Features
Get the Apc algorithm current configuration parameters.
-
Syntax
ALGO_APC_RET IaaApc_GetConfig(APC_HANDLE handle, AudioProcessInit *audio_process_init, AudioAnrConfig *anr_config, AudioEqConfig *eq_config, AudioHpfConfig *hpf_config, AudioVadConfig *vad_config, AudioDereverbConfig *dereverb_config, AudioAgcConfig *agc_config);
-
Parameters
Parameter name Description Input/output handle Apc algorithm handle Input audio_process_init Apc algorithm initialization structure pointer Output anr_config The current Anr configuration parameters in the Apc algorithm Output eq_config The current Eq configuration parameters in the Apc algorithm Output hpf_config The current Hpf configuration parameters in the Apc algorithm Output vad_config The current Vad configuration parameters in the Apc algorithm(stop using) Output dereverb_config The current Dereverb configuration parameters in the Apc algorithm(stop using) Output agc_config The current Agc configuration parameters in the Apc algorithm Output -
Return value
Return value Result 0 Successful Non-zero Failed, refer to error code -
Dependency
-
Header: AudioProcess.h
-
Library: libAPC_LINUX.so/ libAPC_LINUX.a
-
-
Example
Please refer to IaaApc_Run example.
2.11. IaaAnr_GetBufferSize¶
-
Features
Get the memory size required for Anr algorithm running.
-
Syntax
unsigned int IaaAnr_GetBufferSize(void); -
Return value
Return value is the memory size required for Anr algorithm running.
-
Dependency
-
Header: AudioProcess.h
-
Library: libAPC_LINUX.so/ libAPC_LINUX.a
-
-
Note
The interface only returns the required memory size. The application and release of memory needs to be processed by the application.。
-
Example
Please refer to IaaAnr_Run example.
2.12. IaaAnr_Init¶
-
Features
Initialize the Anr algorithm.
-
Syntax
ANR_HANDLE IaaAnr_Init(char* working_buffer_address, AudioProcessInit *anr_init); -
Parameters
Parameter name Description Input/output working_buffer_address Anr algorithm memory address Input anr_init Anr algorithm initialization structure pointer Input -
Return value
Return value Result Not NULL Successful NULL Failed -
Dependency
-
Header: AudioProcess.h
-
Library: libAPC_LINUX.so/ libAPC_LINUX.a
-
-
Note
- ANR supports 8K/16K/48K sampling rate.
-
Example
Please refer to IaaAnr_Run example.
2.13. IaaAnr_Config¶
-
Features
Configure the Anr algorithm.
-
Syntax
ALGO_APC_RET IaaAnr_Config(ANR_HANDLE handle, AudioAnrConfig *anr_config);
-
Parameters
Parameter name Description Input/output handle Anr algorithm handle Input anr_config Configure Anr algorithm structure pointer Input -
Return value
Return value Result 0 Successful Non-zero Failed, refer to error code -
Dependency
-
Header: AudioProcess.h
-
Library: libAPC_LINUX.so/ libAPC_LINUX.a
-
-
Example
Please refer to IaaAnr_Run example.
2.14. IaaAnr_Run¶
-
Features
Anr algorithm processing.
-
Syntax
ALGO_APC_RET IaaAnr_Run(ANR_HANDLE handle, short* pss_audio_in); -
Parameters
Parameter name Description Input/output handle Anr algorithm handle Input pss_audio_in Input data pointer Input/output -
Return value
Return value Result 0 Successful Non-zero Failed, refer to error code -
Dependency
-
Header: AudioProcess.h
-
Library: libAPC_LINUX.so/ libAPC_LINUX.a
-
-
Note
- The data must correspond to the point_number (sampling points required for one IaaAnr_Run) set when calling IaaAnr_Init. The processed data will be written back to the memory pointed to by pss_audio_in.
-
Example
#include <stdio.h> #include <string.h> #include <stdlib.h> #include <sys/time.h> #include "AudioProcess.h" /* 0:Fixed input file 1:User input file */ #define IN_PARAMETER 1 int main(int argc, char *argv[]) { short in_output[1024]; unsigned int workingBufferSize; char *workingBuffer = NULL; ANR_HANDLE handle; AudioProcessInit anr_init, anr_get_init; AudioAnrConfig anr_config, anr_get_config; ALGO_APC_RET ret; int tempSize; FILE* fpIn; //input file FILE* fpOut; //output file char src_file[128] = {0}; char dst_file[128] = {0}; /*********************User change section start*******************/ int intensity_band[6] = {3,24,40,64,80,128}; int intensity[7] = {30,30,30,30,30,30,30}; anr_init.point_number = 128; anr_init.channel = 1; anr_init.sample_rate = IAA_APC_SAMPLE_RATE_16000; anr_config.anr_enable = 1; anr_config.user_mode = 2; anr_config.anr_smooth_level = 10; anr_config.anr_converge_speed = 0; /*********************User change section end*******************/ memcpy(anr_config.anr_intensity_band, intensity_band, sizeof(intensity_band)); memcpy(anr_config.anr_intensity, intensity, sizeof(intensity)); //(1)IaaAnr_GetBufferSize workingBufferSize = IaaAnr_GetBufferSize(); workingBuffer = (char *)malloc(workingBufferSize); if(NULL == workingBuffer) { printf("malloc workingBuffer failed !\n"); return -1; } printf("malloc workingBuffer succeed !\n"); //(2)IaaAnr_Init handle = IaaAnr_Init(workingBuffer, &anr_init); if(NULL == handle) { printf("IaaAnr_Init failed !\n"); return -1; } printf("IaaAnr_Init succeed !\n"); //(3)IaaAnr_Config ret = IaaAnr_Config(handle, &anr_config); if(ret) { printf("IaaAnr_Config failed !\n"); return -1; } printf("IaaAnr_Config succeed !\n"); //(4)IaaAnr_GetConfig ret = IaaAnr_GetConfig(handle, &anr_get_init, &anr_get_config); if(ret) { printf("IaaAnr_GetConfig failed !\n"); return -1; } printf("IaaAnr_GetConfig succeed !\n"); printf("anr_get_config.user_mode = %d, ...\n", anr_get_config.user_mode); #if IN_PARAMETER if(argc < 3) { printf("Please enter the correct parameters!\n"); return -1; } sscanf(argv[1], "%s", src_file); sscanf(argv[2], "%s", dst_file); #else sprintf(src_file, "%s", "./APC_AFE_16K.wav"); if(argc < 2) { printf("Please enter the correct parameters!\n"); return -1; } sscanf(argv[1], "%s", dst_file); #endif fpIn = fopen(src_file, "rb"); if(NULL == fpIn) { printf("fopen in_file failed !\n"); return -1; } printf("fopen in_file success !\n"); fpOut = fopen(dst_file, "wb"); if(NULL == fpOut) { printf("fopen out_file failed !\n"); return -1; } printf("fopen out_file success !\n"); #if 1 fread(in_output, sizeof(char), 44, fpIn); fwrite(in_output, sizeof(char), 44, fpOut); #endif tempSize = anr_init.point_number * anr_init.channel; while(tempSize == fread(in_output, sizeof(short), tempSize, fpIn)) { //(5)IaaAnr_Run ret = IaaAnr_Run(handle, in_output); if(ret) { printf("IaaAnr_Run failed !\n"); return -1; } fwrite(in_output, sizeof(short), tempSize, fpOut); } printf("Break:needBytes =%d \t nBytesRead = %d\n", anr_init.point_number * anr_init.channel, tempSize); //(6)IaaAnr_Free IaaAnr_Free(handle); free(workingBuffer); fclose(fpIn); fclose(fpOut); printf("APC_ANR end !\n"); return 0; }
2.15. IaaAnr_Free¶
-
Features
Release Anr algorithm resources.
-
Syntax
ALGO_APC_RET IaaAnr_Free(ANR_HANDLE handle); -
Parameters
Parameter name Description Input/output handle Anr algorithm handle Input -
Dependency
-
Header: AudioProcess.h
-
Library: libAPC_LINUX.so/ libAPC_LINUX.a
-
-
Example
Please refer to IaaAnr_Run example.
2.16. IaaAnr_Reset¶
-
Features
Reinitialize the Anr algorithm.
-
Syntax
ANR_HANDLE IaaAnr_Reset(char* working_buffer_address, AudioProcessInit *anr_init);
-
Parameters
Parameter name Description Input/output working_buffer_address Memory address used by Anr algorithm Input anr_init Anr algorithm initialization structure pointer Input -
Return value
Return value Result Not NULL Successful NULL Failed -
Dependency
-
Header: AudioProcess.h
-
Library: libAPC_LINUX.so/ libAPC_LINUX.a
-
2.17. IaaAnr_GetConfig¶
-
Features
Get the Anr algorithm current configuration parameters.
-
Syntax
ALGO_APC_RET IaaAnr_GetConfig(ANR_HANDLE handle, AudioProcessInit *anr_init, AudioAnrConfig *anr_config);
-
Parameters
Parameter name Description Input/output handle Anr algorithm handle Input anr_init Anr algorithm initialization structure pointer Output anr_config Anr algorithm in the current configuration parameters Output -
Return value
Return value Result 0 Successful Non-zero Failed, refer to error code -
Dependency
-
Header: AudioProcess.h
-
Library: libAPC_LINUX.so/ libAPC_LINUX.a
-
-
Example
Please refer to IaaAnr_Run example.
2.18. IaaEq_GetBufferSize¶
-
Features
Get the memory size required for Anr algorithm running.
-
Syntax
unsigned int IaaEq_GetBufferSize(void); -
Return value
Return value is the memory size required for Eq algorithm running.
-
Dependency
-
Header: AudioProcess.h
-
Library: libAPC_LINUX.so/ libAPC_LINUX.a
-
-
Note
The interface only returns the required memory size. The application and release of memory needs to be processed by the application.。
-
Example
Please refer to IaaEq_Run example.
2.19. IaaEq_Init¶
-
Features
Initialize the Eq algorithm.
-
Syntax
EQ_HANDLE IaaEq_Init(char* working_buffer_address, AudioProcessInit *eq_init);
-
Parameters
Parameter name Description Input/output working_buffer_address Eq algorithm memory address Input eq_init Eq algorithm initialization structure pointer Input -
Return value
Return value Result Not NULL Successful NULL Failed -
Dependency
-
Header: AudioProcess.h
-
Library: libAPC_LINUX.so/ libAPC_LINUX.a
-
-
Note
- Eq algorithm supports 8K/16K/48K sampling Rate,Hpf only supports 8K/16K.
-
Example
Please refer to IaaEq_Run example.
2.20. IaaEq_Config¶
-
Features
Configure the Eq algorithm.
-
Syntax
ALGO_APC_RET IaaEq_Config(EQ_HANDLE handle, AudioHpfConfig *hpf_config, AudioEqConfig *eq_config);
-
Parameters
Parameter name Description Input/output handle Eq algorithm handle Input hpf_config Configure Hpf algorithm structure pointer Input eq_config Configure Eq algorithm structure pointer Input -
Return value
Return value Result 0 Successful Non-zero Failed, refer to error code -
Dependency
-
Header: AudioProcess.h
-
Library: libAPC_LINUX.so/ libAPC_LINUX.a
-
-
Example
Please refer to IaaEq_Run example.
2.21. IaaEq_Run¶
-
Features
Eq algorithm processing.
-
Syntax
ALGO_APC_RET IaaEq_Run(EQ_HANDLE handle, short* pss_audio_in); -
Parameters
Parameter name Description Input/output handle Eq algorithm handle Input pss_audio_in Input data pointer Input/output -
Return value
Return value Result 0 Successful Non-zero Failed, refer to error code -
Dependency
-
Header: AudioProcess.h
-
Library: libAPC_LINUX.so/ libAPC_LINUX.a
-
-
Note
- he data must correspond to the point_number (sampling points required for one IaaEq_Run) set when calling IaaEq_Init. The processed data will be written back to the memory pointed to by pss_audio_in.
-
Example
#include <stdio.h> #include <string.h> #include <stdlib.h> #include <sys/time.h> #include "AudioProcess.h" /* 0:Fixed input file 1:User input file */ #define IN_PARAMETER 1 int main(int argc, char *argv[]) { short in_output[1024]; unsigned int workingBufferSize; char *workingBuffer = NULL; EQ_HANDLE handle; AudioProcessInit eq_init, eq_get_init; AudioHpfConfig hpf_config, hpf_get_config; AudioEqConfig eq_config, eq_get_config; ALGO_APC_RET ret; int tempSize; FILE* fpIn; //input file FILE* fpOut; //output file char src_file[128] = {0}; char dst_file[128] = {0}; /*********************User change section start*******************/ short eq_table[129]; memset(eq_table, 0, sizeof(eq_table)); eq_init.point_number = 128; eq_init.channel = 1; eq_init.sample_rate = IAA_APC_SAMPLE_RATE_16000; hpf_config.hpf_enable = 1; hpf_config.user_mode = 1; hpf_config.cutoff_frequency = AUDIO_HPF_FREQ_150; eq_config.eq_enable = 1; eq_config.user_mode = 1; /*********************User change section end*******************/ memcpy(eq_config.eq_gain_db, eq_table, sizeof(eq_table)); //(1)IaaEq_GetBufferSize workingBufferSize = IaaEq_GetBufferSize(); workingBuffer = (char *)malloc(workingBufferSize); if(NULL == workingBuffer) { printf("malloc workingBuffer failed !\n"); return -1; } printf("malloc workingBuffer succeed !\n"); //(2)IaaEq_Init handle = IaaEq_Init(workingBuffer, &eq_init); if(NULL == handle) { printf("IaaEq_Init failed !\n"); return -1; } printf("IaaEq_Init succeed !\n"); //(3)IaaEq_Config ret = IaaEq_Config(handle, &hpf_config, &eq_config); if(ret) { printf("IaaEq_Config failed !\n"); return -1; } printf("IaaEq_Config succeed !\n"); //(4)IaaEq_GetConfig ret = IaaEq_GetConfig(handle, &eq_get_init, &hpf_get_config, &eq_get_config); if(ret) { printf("IaaEq_GetConfig failed !\n"); return -1; } printf("IaaEq_GetConfig succeed !\n"); printf("eq_get_config.user_mode = %d, ...\n", eq_get_config.user_mode); #if IN_PARAMETER if(argc < 3) { printf("Please enter the correct parameters!\n"); return -1; } sscanf(argv[1], "%s", src_file); sscanf(argv[2], "%s", dst_file); #else sprintf(src_file, "%s", "./APC_AFE_16K.wav"); if(argc < 2) { printf("Please enter the correct parameters!\n"); return -1; } sscanf(argv[1], "%s", dst_file); #endif fpIn = fopen(src_file, "rb"); if(NULL == fpIn) { printf("fopen in_file failed !\n"); return -1; } printf("fopen in_file success !\n"); fpOut = fopen(dst_file, "wb"); if(NULL == fpOut) { printf("fopen out_file failed !\n"); return -1; } printf("fopen out_file success !\n"); #if 1 fread(in_output, sizeof(char), 44, fpIn); fwrite(in_output, sizeof(char), 44, fpOut); #endif tempSize = eq_init.point_number * eq_init.channel; while(tempSize == fread(in_output, sizeof(short), tempSize, fpIn)) { //(5)IaaEq_Run ret = IaaEq_Run(handle, in_output); if(ret) { printf("IaaEq_Run failed !\n"); return -1; } fwrite(in_output, sizeof(short), tempSize, fpOut); } printf("Break:needBytes =%d \t nBytesRead = %d\n", eq_init.point_number * eq_init.channel, tempSize); //(6)IaaEq_Free IaaEq_Free(handle); free(workingBuffer); fclose(fpIn); fclose(fpOut); printf("APC_EQ end !\n"); return 0; }
2.22. IaaEq_Free¶
-
Features
Release Eq algorithm resources.
-
Syntax
ALGO_APC_RET IaaEq_Free(EQ_HANDLE handle); -
Parameters
Parameter name Description Input/output handle Eq algorithm handle Input -
Dependency
-
Header: AudioProcess.h
-
Library: libAPC_LINUX.so/ libAPC_LINUX.a
-
-
Example
Please refer to IaaEq_Run example.
2.23. IaaEq_Reset¶
-
Features
Reinitialize the Eq algorithm.
-
Syntax
EQ_HANDLE IaaEq_Reset(char* working_buffer_address, AudioProcessInit *eq_init);
-
Parameters
Parameter name Description Input/output working_buffer_address Memory address used by Eq algorithm Input eq_init Eq algorithm initialization structure pointer Input -
Return value
Return value Result Not NULL Successful NULL Failed -
Dependency
-
Header: AudioProcess.h
-
Library: libAPC_LINUX.so/ libAPC_LINUX.a
-
2.24. IaaEq_GetConfig¶
-
Features
Get the Eq algorithm current configuration parameters.
-
Syntax
ALGO_APC_RET IaaEq_GetConfig(EQ_HANDLE handle, AudioProcessInit *eq_init, AudioHpfConfig *hpf_config, AudioEqConfig *eq_config);
-
Parameters
Parameter name Description Input/output handle Eq algorithm handle Input eq_init Eq algorithm initialization structure pointer Output hpf_config Hpf algorithm in the current configuration parameters Output eq_config Eq algorithm in the current configuration parameters Output -
Return value
Return value Result 0 Successful Non-zero Failed, refer to error code -
Dependency
-
Header: AudioProcess.h
-
Library: libAPC_LINUX.so/ libAPC_LINUX.a
-
-
Example
Please refer to IaaEq_Run example
2.25. IaaAgc_GetBufferSize¶
-
Features
Get the memory size required for Agc algorithm running.
-
Syntax
unsigned int IaaAgc_GetBufferSize(void); -
Return value
Return value is the memory size required for Agc algorithm running.
-
Dependency
-
Header: AudioProcess.h
-
Library: libAPC_LINUX.so/ libAPC_LINUX.a
-
-
Note
The interface only returns the required memory size. The application and release of memory needs to be processed by the application.。
-
Example
Please refer to IaaAgc_Run example.
2.26. IaaAgc_Init¶
-
Features
Initialize the Agc algorithm.
-
Syntax
AGC_HANDLE IaaAgc_Init(char* working_buffer_address, AudioProcessInit *agc_init);
-
Parameters
Parameter name Description Input/output working_buffer_address Agc algorithm memory address Input agc_init Agc algorithm initialization structure pointer Input -
Return value
Return value Result Not NULL Successful NULL Failed -
Dependency
-
Header: AudioProcess.h
-
Library: libAPC_LINUX.so/ libAPC_LINUX.a
-
-
Note
- AGC supports 8K/16K/48K sampling rate.
-
Example
Please refer to IaaAgc_Run example.
2.27. IaaAgc_Config¶
-
Features
Configure the Agc algorithm.
-
Syntax
ALGO_APC_RET IaaAgc_Config(AGC_HANDLE handle, AudioAgcConfig *agc_config);
-
Parameters
Parameter name Description Input/output handle Agc algorithm handle Input agc_config Configure Agc algorithm structure pointer Input -
Return value
Return value Result 0 Successful Non-zero Failed, refer to error code -
Dependency
-
Header: AudioProcess.h
-
Library: libAPC_LINUX.so/ libAPC_LINUX.a
-
-
Example
Please refer to IaaAgc_Run example.
2.28. IaaAgc_Run¶
-
Features
Agc algorithm processing.
-
Syntax
ALGO_APC_RET IaaAgc_Run(AGC_HANDLE handle, short* pss_audio_in); -
Parameters
Parameter name Description Input/output handle Agc algorithm handle Input pss_audio_in Input data pointer Input/output -
Return value
Return value Result 0 Successful Non-zero Failed, refer to error code -
Dependency
-
Header: AudioProcess.h
-
Library: libAPC_LINUX.so/ libAPC_LINUX.a
-
-
Note
- The data must correspond to the point_number (sampling points required for one IaaAgc_Run) set when calling IaaAgc_Init. The processed data will be written back to the memory pointed to by pss_audio_in.
-
Example
#include <stdio.h> #include <string.h> #include <stdlib.h> #include <sys/time.h> #include "AudioProcess.h" /* 0:Fixed input file 1:User input file */ #define IN_PARAMETER 1 int main(int argc, char *argv[]) { short in_output[1024]; unsigned int workingBufferSize; char *workingBuffer = NULL; AGC_HANDLE handle; AudioProcessInit agc_init, agc_get_init; AudioAgcConfig agc_config, agc_get_config; ALGO_APC_RET ret; int tempSize; FILE* fpIn; //input file FILE* fpOut; //output file char src_file[128] = {0}; char dst_file[128] = {0}; /*********************User change section start*******************/ short compression_ratio_input[7] = {-65,-55,-48,-25,-18,-12,0}; short compression_ratio_output[7] = {-65,-50,-27,-12,-1,-1,-1}; agc_init.point_number = 128; agc_init.channel = 1; agc_init.sample_rate = IAA_APC_SAMPLE_RATE_16000; agc_config.agc_enable = 1; agc_config.user_mode = 1; agc_config.gain_info.gain_max = 40; agc_config.gain_info.gain_min = -10; agc_config.gain_info.gain_init = 12; agc_config.drop_gain_max = 36; agc_config.gain_step = 1; agc_config.attack_time = 1; agc_config.release_time = 1; agc_config.noise_gate_db = -80; agc_config.noise_gate_attenuation_db = 0; agc_config.drop_gain_threshold = -5; /*********************User change section end*******************/ memcpy(agc_config.compression_ratio_input, compression_ratio_input, sizeof(compression_ratio_input)); memcpy(agc_config.compression_ratio_output, compression_ratio_output, sizeof(compression_ratio_output)); //(1)IaaAgc_GetBufferSize workingBufferSize = IaaAgc_GetBufferSize(); workingBuffer = (char *)malloc(workingBufferSize); if(NULL == workingBuffer) { printf("malloc workingBuffer failed !\n"); return -1; } printf("malloc workingBuffer succeed !\n"); //(2)IaaAgc_Init handle = IaaAgc_Init(workingBuffer, &agc_init); if(NULL == handle) { printf("IaaAgc_Init failed !\n"); return -1; } printf("IaaAgc_Init succeed !\n"); //(3)IaaAgc_Config ret = IaaAgc_Config(handle, &agc_config); if(ret) { printf("IaaAgc_Config failed !\n"); return -1; } printf("IaaAgc_Config succeed !\n"); //(4)IaaAgc_GetConfig ret = IaaAgc_GetConfig(handle, &agc_get_init, &agc_get_config); if(ret) { printf("IaaAgc_GetConfig failed !\n"); return -1; } printf("IaaAgc_GetConfig succeed !\n"); printf("agc_get_config.user_mode = %d, ...\n", agc_get_config.user_mode); #if IN_PARAMETER if(argc < 3) { printf("Please enter the correct parameters!\n"); return -1; } sscanf(argv[1], "%s", src_file); sscanf(argv[2], "%s", dst_file); #else sprintf(src_file, "%s", "./APC_AFE_16K.wav"); if(argc < 2) { printf("Please enter the correct parameters!\n"); return -1; } sscanf(argv[1], "%s", dst_file); #endif fpIn = fopen(src_file, "rb"); if(NULL == fpIn) { printf("fopen in_file failed !\n"); return -1; } printf("fopen in_file success !\n"); fpOut = fopen(dst_file, "wb"); if(NULL == fpOut) { printf("fopen out_file failed !\n"); return -1; } printf("fopen out_file success !\n"); #if 1 fread(in_output, sizeof(char), 44, fpIn); fwrite(in_output, sizeof(char), 44, fpOut); #endif tempSize = agc_init.point_number * agc_init.channel; while(tempSize == fread(in_output, sizeof(short), tempSize, fpIn)) { //(5)IaaAgc_Run ret = IaaAgc_Run(handle, in_output); if(ret) { printf("IaaAnr_Run failed !\n"); return -1; } fwrite(in_output, sizeof(short), tempSize, fpOut); } printf("Break:needBytes =%d \t nBytesRead = %d\n", agc_init.point_number * agc_init.channel, tempSize); //(6)IaaAgc_Free IaaAgc_Free(handle); free(workingBuffer); fclose(fpIn); fclose(fpOut); printf("APC_AGC end !\n"); return 0; }
2.29. IaaAgc_Free¶
-
Features
Release Agc algorithm resources.
-
Syntax
ALGO_APC_RET IaaAgc_Free(AGC_HANDLE handle); -
Parameters
Parameter name Description Input/output handle Agc algorithm handle Input -
Dependency
-
Header: AudioProcess.h
-
Library: libAPC_LINUX.so/ libAPC_LINUX.a
-
-
Example
Please refer to IaaAgc_Run example.
2.30. IaaAgc_Reset¶
-
Features
Reinitialize the Eq algorithm.
-
Syntax
AGC_HANDLE IaaAgc_Reset(char* working_buffer_address, AudioProcessInit *agc_init);
-
Parameters
Parameter name Description Input/output working_buffer_address Memory address used by Agc algorithm Input agc_init Agc algorithm initialization structure pointer Input -
Return value
Return value Result Not NULL Successful NULL Failed -
Dependency
-
Header: AudioProcess.h
-
Library: libAPC_LINUX.so/ libAPC_LINUX.a
-
2.31. IaaAgc_GetConfig¶
-
Features
Get the Agc algorithm current configuration parameters.
-
Syntax
ALGO_APC_RET IaaAgc_GetConfig(AGC_HANDLE handle, AudioProcessInit *agc_init, AudioAgcConfig *agc_config);
-
Parameters
Parameter name Description Input/output handle Agc algorithm handle Input agc_init Agc algorithm initialization structure pointer Output agc_config Agc algorithm in the current configuration parameters Output -
Return value
Return value Result 0 Successful Non-zero Failed, refer to error code -
Dependency
-
Header: AudioProcess.h
-
Library: libAPC_LINUX.so/ libAPC_LINUX.a
-
-
Example
Please refer to IaaAgc_Run example.
3. APC DATA TYPE¶
3.1. APC data type list¶
| Data type | Definition |
|---|---|
| AudioApcBufferConfig | The buffer configuration parameter structure type of the Apc algorithm |
| AudioProcessInit | Apc algorithm initialization parameter structure type |
| APC_HANDLE | Apc algorithm handle type |
| AudioAnrConfig | The Anr configuration parameter structure type of the Apc algorithm |
| AudioEqConfig | The Eq configuration parameter structure type of the Apc algorithm |
| AudioHpfConfig | The Hpf configuration parameter structure type of the Apc algorithm |
| AudioAgcConfig | The Agc configuration parameter structure type of the Apc algorithm |
| AgcGainInfo | Agc gain parameter structure type in Apc algorithm |
| IAA_APC_SAMPLE_RATE | Define the sampling rate type in the Apc algorithm |
| NR_CONVERGE_SPEED | Anr algorithm convergence speed type |
| IAA_HPF_FREQ | Hpf algorithm cut-off frequency type |
| ANR_HANDLE | Anr algorithm handle type |
| EQ_HANDLE | Eq algorithm handle type |
| AGC_HANDLE | Agc algorithm handle type |
3.2. AudioApcBufferConfig¶
-
Description
Define the buffer configuration parameter structure type of the Apc algorithm.
-
Definition
typedef struct{ unsigned int anr_enable; unsigned int eq_enable; unsigned int dr_enable; unsigned int vad_enable; unsigned int agc_enable; }AudioApcBufferConfig;
-
Member
Member name Description anr_enable The Anr enable option in the Apc algorithm is used to assist in calculating the memory size required for Apc algorithm running. eq_enable The Eq enable option in the Apc algorithm is used to assist in calculating the memory size required for Apc algorithm running. dr_enable Algorithm is being developed vad_enable Vad algorithm has established a separate module, Vad is currently disabled in APC, it is recommended to close agc_enable The Agc enable option in the Apc algorithm is used to assist in calculating the memory size required for Apc algorithm running. -
Related data types and interfaces
3.3. AudioProcessInit¶
-
Description
Define Apc(Anr/Eq/Hpf/Agc) algorithm initialization parameter structure type.
-
Definition
typedef struct { unsigned int point_number; unsigned int channel; IAA_APC_SAMPLE_RATE sample_rate; }AudioProcessInit;
-
Member
Member name Description point_number The amount of data processed by the algorithm once (that is, how many sampling points are in a frame), the value is 128 or 256, and how many short values need to be given to Apc is determined by chip. Value range: 128 or 256 channel The channel numbers of data. If it is a dual channel, the data given to Apc in each frame is twice the point_number. sample_rate Data sampling frequency -
Related data types and interfaces
3.4. APC_HANDLE¶
-
Description
Apc algorithm handle type.
-
Definition
typedef void* APC_HANDLE; -
Related data types and interfaces
3.5. AudioAnrConfig¶
-
Description
Define the Anr configuration parameter structure type of the Apc algorithm.
-
Definition
typedef struct{ unsigned int anr_enable; unsigned int user_mode; int anr_intensity_band[6]; int anr_intensity[7]; unsigned int anr_smooth_level; NR_CONVERGE_SPEED anr_converge_speed; }AudioAnrConfig;
-
Member
Member name Description anr_enable Whether to enable Anr algorithm user_mode Anr algorithm running mode anr_intensity_band ANR frequency range Range [1,127]; step size 1 anr_intensity ANR intensity, the larger the value, the higher the ANR intensity, but at the same time it will also bring about the loss/damage of details. The recommended value is 10. Range [0,30]; step size 1 anr_smooth_level Frequency domain smoothness Recommended value:10 Range [0,10]; step size 1 anr_converge_speed Noise convergence speed Recommended value: mid Range [low; mid; high] -
Note
-
When anr_enable is FALSE, other Anr parameters will not work;
-
user_mode specifies the running mode of Anr. 0, means that the Anr algorithm does not use other Anr parameters at all, but uses the internal settings of the Anr algorithm; 1 or 2 means that the Anr parameters under the application are completely used.
-
anr_intensity_band, ANR frequency range, the latter element must be greater than or equal to the first element.
For example: u32NrIntensityBand[0]= 10, then: u32NrIntensityBand[1] must be greater than or equal to 10.
The highest frequency corresponding to the current sampling rate is divided into 128 parts on average, and the frequency range corresponds to how many parts form a frequency band.
For example: the current sampling rate is 16K, the corresponding maximum frequency is 8K, each one is 8000 / 128 ≈ 62.5Hz. Under the setting of {4,6,36, 49,50,51}, the ANR frequency range is {0~4 * 62.5Hz, 4~6 * 62.5Hz, 6~36 * 62.5Hz, 36~49 * 62.5Hz, 49~50 * 62.5Hz, 50~51 * 62.5Hz, 51-127 * 62.5Hz} = {0~250Hz, 250~375Hz, 375~2250Hz, 2250~3062.5Hz, 3062.5~3125Hz, 3125~3187.5Hz, 3187.5Hz~8000Hz},anr_intensity is the ANR intensity, According to the frequency band division of anr_intensity_band, different parameters are set for the noise situation of each frequency band.
-
anr_smooth_level, the smoothness of Anr algorithm the frequency domain procession, avoid excessively large suppression gaps between adjacent frequencies during noise estimation, resulting in sound damage.
-
anr_converge_speed,Anr algorithm convergence speed, noise update speed, the faster the setting, the faster the ANR will converge, but the details will be lost/damaged.
-
-
Related data types and interfaces
3.6. AudioEqConfig¶
-
Description
Define the Eq configuration parameter structure type of the Apc algorithm.
-
Definition
typedef struct{ unsigned int eq_enable; unsigned int user_mode; short eq_gain_db[129]; }AudioEqConfig;
-
Member
Member name Description eq_enable Whether to enable Eq algorithm user_mode Eq algorithm running mode eq_gain_db Eq algorithm gain adjustment value, divide the frequency range of the current sampling rate into 129 frequency ranges for adjustment. Unit: 1dB Range [-50,20]; step size 1 -
Note
-
When eq_enable is FALSE, other Eq parameters will not work;
-
user_mode specifies the running mode of Eq. 0, means Eq uses the preset parameters which are all 0, without any gain or attenuation; 1 means that the Eq parameters under the application are completely used.
-
eq_gain_db is the table for gain adjustment, divide the frequency range of the current sampling rate into 129 frequency ranges for adjustment. For example: the current sampling rate is 16K, the corresponding highest frequency is 8K, 8000 / 129 ≈ 62Hz, the frequency range of a single adjustment is 62Hz, and 0-8K is divided into {0-1 * 62Hz,1-2 * 62Hz,2-3 * 62Hz,…,128-129 * 62Hz} = {0-62Hz,62-124Hz,124-186Hz,…,7938-8000Hz}, each segment corresponds to a gain value.
-
-
Related data types and interfaces
3.7. AudioHpfConfig¶
-
Description
Define the Hpf configuration parameter structure type of the Apc algorithm.
-
Definition
typedef struct{ unsigned int hpf_enable; unsigned int user_mode; IAA_HPF_FREQ cutoff_frequency; }AudioHpfConfig;
-
Member
Member name Description hpf_enable Whether to enable Hpf algorithm user_mode Hpf algorithm running mode cutoff_frequency Hpf cutoff frequency Range: [80,120,150] -
Note
-
When hpf_enable is FALSE, other Hpf parameters will not work;
-
user_mode specifies the running mode of Hpf. 0, means Eq uses the preset parameters, without any gain or attenuation; 1 means that the Hpf parameters under the application are completely used.
-
cutoff_frequency is the cutoff frequency of Hpf, signals below this frequency will be filtered out.
-
-
Related data types and interfaces
3.8. AudioAgcConfig¶
-
Description
Define the Agc configuration parameter structure type of the Apc algorithm.
-
Definition
typedef struct { unsigned int agc_enable; unsigned int user_mode; //gain setting AgcGainInfo gain_info; unsigned int drop_gain_max; //attack time, release time unsigned int attack_time; unsigned int release_time; //target level short compression_ratio_input[7]; short compression_ratio_output[7]; int drop_gain_threshold; // noise gate int noise_gate_db; unsigned int noise_gate_attenuation_db; unsigned int gain_step; }AudioAgcConfig;
-
Member
Member name Description agc_enable Whether to enable Agc algorithm user_mode Agc algorithm running mode gain_info The Agc algorithm gain information, which defines the maximum, minimum and initial values of the AGC gain drop_gain_max The maximum value of instantaneous gain drop, prevent output saturation. If the output plus the current Gain exceeds the dB value set by drop_gain_threshold, Agc will instantly reduce the Gain to prevent the peak value of the current signal from exceeding drop_gain_threshold. Range: [0,60]; Step size: 1 Note:This value only represents the range that can be lowered, but the specific value that can be lowered depends on the minimum value of the AGC gain. attack_time Time step for gain reduction, take 4 milliseconds as 1 unit, if set to 2, it will judge whether to increase Gain every 8 milliseconds. Range: [1,20]; step size: 1 release_time Time step for gain increase, take 4 milliseconds as 1 unit, if set to 2, it will judge whether to increase Gain every 8 milliseconds Range: [1,20]; step size: 1 compression_ratio_input Use with compression_ratio_output, realize the curve with multiple slopes through multiple turning points to get the relationship between input power level and output power level. Range: [-80,0]dBFS; step size: 1 compression_ratio_output Use with compression_ratio_input, realize the curve with multiple slopes through multiple turning points to get the relationship between input power level and output power level. Range: [-80,0]dBFS; step size: 1 drop_gain_threshold Attenuation threshold, When the signal peak amplitude exceeds this value, it will attenuate instantly, and the attenuation amplitude is limited by drop_gain_max and gain_info. Range: [-80,0]dB; step size: 1 noise_gate_db Noise threshold, when the signal is less than this value, treat it as noise. Case1: If you set noise_gate_db from -80 to 0, the current gain value will converge to 0 according to the release/attack time. Case2: If you set noise_gate_db from 1 to 80, when the signal is less than this value, the Gain value will not be changed, and keep the Gain value of the previous frame Range: [-80,80] ; step size: 1 noise_gate_attenuation_db When the noise threshold is effective, it is input source attenuation percentage. Range: [0,100] ; step size: 1 gain_step The speed of applying gain is 0.5dB as a unit. If it is set to 1, then ±0.5dB is applied per frame according to requirements. The higher the value, the faster the speed of increasing and decreasing the volume. Range: [1,10] ; step size: 1 -
Note
-
When agc_enable is FALSE, other Agc parameters will not work;
-
user_mode specifies the running mode of Agc. 0, means that the Agc algorithm does not use other Agc parameters at all, but uses the internal settings of the Agc algorithm; 1 means that the Agc parameters under the application are completely used.
-
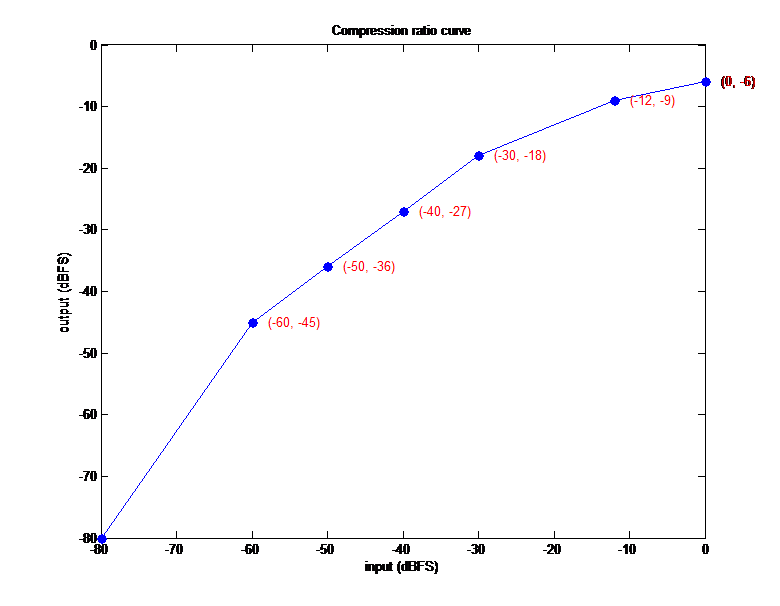
Compression ratio Curve defines the relationship between InputOutput energy. By setting seven points, six different slope transitions can be obtained. For example, the parameters are set as follows:
compression_ratio_input[7] = {-80, -60, -50,-40,-30,-12,0}
compression_ratio_output[7] = {-80, -45, -36, -27, -18, -9, -6}
The curve is shown in the figure below.
If you don’t need so many different slopes, you can set the last compression ratio parameter to 0, as follows:
compression_ratio_input[7] = {-70, -60, -30, 0,0,0,0};
compression_ratio_output[7] = {-60, -50, -10, -3, 0,0,0};
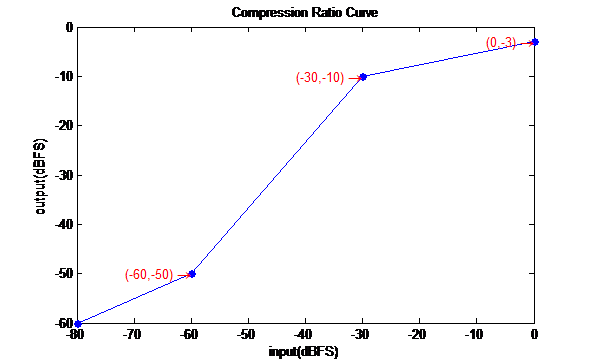
-
There are two modes for the noise gate setting, which can converge Gain to 0 or keep it unchanged. Convergence to 0 can prevent signals smaller than the noise gate from being amplified, maintain noise stability, and maintain the Gain value unchanged to avoid the "breathing phenomenon" where the beginning and end of the voice disappear.
-
-
Related data types and interfaces
3.9. AgcGainInfo¶
-
Description
Define Agc gain parameter structure type in Apc algorithm.
-
Definition
typedef struct { int gain_max; //gain maximum int gain_min; //gain minimum int gain_init; //default gain (initial gain) }AgcGainInfo;
-
Member
Member name Description gain_max Maximum gain Range: [0,60]; step size: 1 gain_min Minimum gain Range: [-20,30] ; step size: 1 gain_init Gain initial value Range: [-20,60] ; step size: 1 -
Related data types and interfaces
3.10. IAA_APC_SAMPLE_RATE¶
-
Description
Define the sampling rate type in the Apc algorithm.
-
Definition
typedef enum { IAA_APC_SAMPLE_RATE_8000 = 8000 , IAA_APC_SAMPLE_RATE_16000 = 16000 , IAA_APC_SAMPLE_RATE_48000 = 48000 , }IAA_APC_SAMPLE_RATE;
-
Member
Member name Description IAA_APC_SAMPLE_RATE_8000 8K sampling rate IAA_APC_SAMPLE_RATE_16000 16K sampling rate IAA_APC_SAMPLE_RATE_48000 48K sampling rate -
Related data types and interfaces
3.11. NR_CONVERGE_SPEED¶
-
Description
Define Anr algorithm convergence speed type.
-
Definition
typedef enum { NR_SPEED_LOW, NR_SPEED_MID, NR_SPEED_HIGH } NR_CONVERGE_SPEED;
-
Member
Member name Description NR_SPEED_LOW Low speed NR_SPEED_MID Medium speed NR_SPEED_HIGH High speed -
Note
- Low/medium/high NR convergence speed represents 3/2/1 frame update once noise suppression
-
Related data types and interfaces
3.12. IAA_HPF_FREQ¶
-
Description
Define Hpf algorithm cut-off frequency type.
-
Definition
typedef enum { AUDIO_HPF_FREQ_80 , /* 80Hz*/ AUDIO_HPF_FREQ_120, /*120Hz*/ AUDIO_HPF_FREQ_150, /*150Hz*/ AUDIO_HPF_FREQ_BUTT, }IAA_HPF_FREQ;
-
Member
Member name Description AUDIO_HPF_FREQ_80 80Hz AUDIO_HPF_FREQ_120 120Hz AUDIO_HPF_FREQ_150 150Hz AUDIO_HPF_FREQ_BUTT -
Related data types and interfaces
3.13. ANR_HANDLE¶
-
Description
Define Anr algorithm handle type.
-
Definition
typedef void* ANR_HANDLE; -
Related data types and interfaces
3.14. EQ_HANDLE¶
-
Description
Define Eq algorithm handle type.
-
Definition
typedef void* EQ_HANDLE; -
Related data types and interfaces
3.15. AGC_HANDLE¶
-
Description
Define Agc algorithm handle type.
-
Definition
typedef void* AGC_HANDLE;
-
Related data types and interfaces
4. Error code¶
APC API error codes are shown as follow:
| Error code | Definition | Description |
|---|---|---|
| 0x00000000 | ALGO_APC_RET_SUCCESS | APC run successful |
| 0x10000501 | ALGO_APC_RET_INIT_ERROR | APC not initialized |
| 0x10000502 | ALGO_APC_RET_INVALID_HANDLE | HANDLE invalid |
| 0x10000503 | ALGO_APC_RET_INVALID_SAMPLE_RATE | Sampling frequency is not supported |
| 0x10000504 | ALGO_APC_RET_INVALID_POINT_NUMBER | Points per frame not supported |
| 0x10000505 | ALGO_APC_RET_INVALID_CHANNEL | Channel number doesn`t support |
| 0x10000506 | ALGO_APC_ANR_RET_INVALID_ENABLE | ANR switch parameter setting is invalid |
| 0x10000507 | ALGO_APC_ANR_RET_INVALID_MODE | ANR mode parameter setting is invalid |
| 0x10000508 | ALGO_APC_ANR_RET_INVALID_INTENSITY | ANR intensive parameter setting is invalid |
| 0x10000509 | ALGO_APC_ANR_RET_INVALID_SMOOTH_LEVEL | ANR smoothing parameter setting is invalid |
| 0x10000510 | ALGO_APC_ANR_RET_INVALID_COVERGE_SPEED | ANR convergence rate parameter setting is invalid |
| 0x10000511 | ALGO_APC_EQ_RET_INVALID_ENABLE | EQ switch parameter setting is invalid |
| 0x10000512 | ALGO_APC_EQ_RET_INVALID_MODE | EQ mode parameter setting is invalid |
| 0x10000513 | ALGO_APC_EQ_RET_INVALID_TABLE | EQ parameter setting is invalid |
| 0x10000514 | ALGO_APC_HPF_RET_INVALID_ENABLE | HPF switch parameter setting is invalid |
| 0x10000515 | ALGO_APC_HPF_RET_INVALID_MODE | HPF mode parameter setting is invalid |
| 0x10000516 | ALGO_APC_HPF_RET_INVALID_TABLE | HPF parameter setting is invalid |
| 0x10000517 | ALGO_APC_AGC_RET_INVALID_ENABLE | AGC switch parameter setting is invalid |
| 0x10000518 | ALGO_APC_AGC_RET_INVALID_MODE | AGC mode parameter setting is invalid |
| 0x10000519 | ALGO_APC_AGC_RET_INVALID_COMPRESSION_RATIO | AGC compression curve parameter setting is invalid |
| 0x10000520 | ALGO_APC_AGC_RET_INVALID_DROP_GAIN_MAX | AGC anti-saturation parameter setting is invalid |
| 0x10000521 | ALGO_APC_AGC_RET_INVALID_GAIN_STEP | AGC gain step parameter setting is invalid |
| 0x10000522 | ALGO_APC_AGC_RET_INVALID_RELEASE_TIME | AGC recovery time parameter setting is invalid |
| 0x10000523 | ALGO_APC_AGC_RET_INVALID_ATTACK_TIME | AGC subtracted time parameter setting is invalid |
| 0x10000524 | ALGO_APC_AGC_RET_INVALID_NOISE_GATE | AGC noise threshold parameter setting is invalid |
| 0x10000525 | ALGO_APC_AGC_RET_INVALID_NOISE_ATTENU | AGC noise attenuation setting is invalid |
| 0x10000526 | ALGO_APC_AGC_RET_INVALID_DROP_GAIN_LEVEL | AGC anti-saturation threshold parameter setting is invalid |
| 0x10000527 | ALGO_APC_AGC_RET_INVALID_GAIN_INFO | AGC gain control parameter setting is invalid |
| 0x10000528 | ALGO_APC_RET_API_CONFLICT | Other APIs are running |
| 0x10000529 | ALGO_APC_RET_INVALID_CALLING | Incorrect order of calling API |
| 0x10000530 | ALGO_APC_RET_FAILED | Parameter setting error |