MI AEC API
1. OVERVIEW¶
1.1. Module Description¶
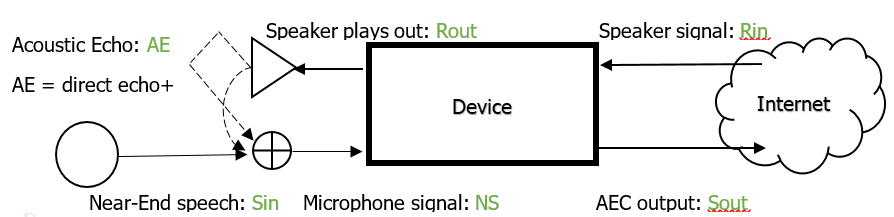
AEC (short for Acoustic Echo Cancellation) is a function used to suppress far-end echo.
Echo is common in conference systems, building intercom, security monitoring and other scenarios. When the far-end sound is played from the speaker, the microphone re-collects the sound played by the speaker and transmits it back to the far-end after a very small delay, which will cause an echo to be heard at the far-end.
1.2. Keyword¶
-
Far-end signal (Sin)
The signal source of the device speaker, or the signal from the remote.
-
Near-end signal (Rin)
The signal recorded by the microphone of the device, which may include acoustic echo and near-end talker signals.
-
Acoustic echo (AE)
The sound played from the speaker of the device is transmitted back to the microphone through a direct or indirect path, and the echo is generated. The far-end talker will hear his echo after a certain delay after speaking. This echo is claimed as an acoustic echo (AE).
-
Single talk
Only the speaker on the device side plays the far-end signal (Sin = AE + NS when NS =0)
-
Double talk
While the speaker on the device side is playing, the near-end talker also speaks into the microphone (Sin = AE + NS when NS≠0)
1.3. Note¶
In order to facilitate debugging and confirm the effect of the algorithm, the user application needs to implement replacement algorithm parameter and grab audio data.
2. API REFERENCE¶
2.1. API List¶
| API name | Features |
|---|---|
| IaaAec_GetBufferSize | Get the memory size required for Aec algorithm running |
| IaaAec_Init | Initialize the memory required for the Aec algorithm |
| IaaAec_Config | Configure Aec algorithm |
| IaaAec_Reset | Reinitialize the memory of Aec algorithm |
| IaaAec_Free | Release Aec algorithm resources |
| IaaAec_Run | Aec algorithm processing |
| IaaAec_GetLibVersion | Get the version information of the Aec algorithm |
2.2. IaaAec_GetBufferSize¶
-
Features
Get the memory size required for Aec algorithm running.
-
Syntax
unsigned int IaaAec_GetBufferSize(void); -
Return value
Return value is the memory size required for Aec algorithm running.
-
Dependency
-
Header: AudioAecProcess.h
-
Library: libAEC_LINUX.so/ libAEC_LINUX.a
-
-
Note
The interface only returns the required memory size, and the application and release of memory need to be processed by the application.
2.3. IaaAec_Init¶
-
Features
Initialize the memory required for the Aec algorithm.
-
Syntax
AEC_HANDLE IaaAec_Init (char* working_buffer_address, AudioAecInit * aec_init);
-
Parameters
Parameter Name Description Input/Output working_buffer_address Memory address used by Aec algorithm input aec_init Aec algorithm initialization structure pointer input -
Return value
Return value Result 0 Successful Non-zero Failed, refer to error code -
Dependency
-
Header: AudioAecProcess.h
-
Library: libAEC_LINUX.so / libAEC_LINUX.a
-
-
Note
- Aec algorithm only supports 8K/16K sampling rate.
2.4. IaaAec_Config¶
-
Features
Configure Aec algorithm.
-
Syntax
ALGO_AEC_RET IaaAec_Config(AEC_HANDLE handle, AudioAecConfig *aec_config);
-
Parameters
Parameter Name Description Input/Output handle Aec algorithm handle input aec_config Aec algorithm configuration parameter structure pointer input -
Return value
Return value Result 0 Successful Non-zero Failed, refer to error code -
Dependency
-
Header: AudioAecProcess.h
-
Library: libAEC_LINUX.so / libAEC_LINUX.a
-
2.5. IaaAec_Reset¶
-
Features
Reinitialize the memory of Aec algorithm.
-
Syntax
AEC_HANDLE IaaAec_Reset(char* working_buffer_address, AudioAecInit * aec_init);
-
Parameters
Parameter Name Description Input/Output working_buffer_address Memory address used by Aec algorithm input aec_init Aec algorithm initialization structure pointer input -
Return value
Return value Result 0 Successful Non-zero Failed, refer to error code -
Dependency
-
Header: AudioAecProcess.h
-
Library: libAEC_LINUX.so/ libAEC_LINUX.a
-
-
Note
-
Reinitialize the Aec algorithm for the same algorithm handle (same memory address) (that is, reset the sampling rate and the number of near-end and far-end channels)
-
After re-initializing the Aec algorithm, it needs to be reconfigured
-
2.6. IaaAec_Free¶
-
Features
Release Aec algorithm resources
-
Syntax
ALGO_AEC_RET IaaAec_Free(AEC_HANDLE handle); -
Parameters
Parameter Name Description Input/Output handle Aec algorithm handle input -
Return value
Return value Result 0 Successful Non-zero Failed, refer to error code -
Dependency
-
Header: AudioAecProcess.h
-
Library: libAEC_LINUX.so/ libAEC_LINUX.a
-
-
Note
Must call IaaAec_Free first, and then release the memory used by the Aec algorithm.
2.7. IaaAec_Run¶
-
Features
Aec algorithm processing
-
Syntax
ALGO_AEC_RET IaaAec_Run(AEC_HANDLE handle, short* pss_audio_near_end, short* pss_audio_far_end);
-
Parameters
Parameter Name Description Input/Output handle Algorithm handle input pss_audio_near_end Near-end data pointer input/output pss_audio_far_end Far-end data pointer input -
Return value
Return value Result 0 Successful Non-zero Failed, refer to error code -
Dependency
-
Header: AudioAecProcess.h
-
Library: libAEC_LINUX.so/ libAEC_LINUX.a
-
-
Note
-
The amount of near-end and far-end data must correspond to the point_number (the number of sampling points required for one IaaAec_Run) when calling IaaAec_Init.
-
The result after AEC is output by pss_audio_near_end
-
-
Example
#include <stdio.h> #include <string.h> #include <sys/time.h> #include <stdlib.h> #include "AudioAecProcess.h" /* 0:Fixed input file 1:User input file */ #define IN_PARAMETER 1 float AVERAGE_RUN(int a) { static unsigned int num = 0; static float avg = 0; if(0 == num) avg = 0; num++; avg = avg + ((float)a - avg) / ((float)num); return avg; } unsigned int _OsCounterGetMs(void) { struct timeval t1; gettimeofday(&t1, NULL); unsigned int T = ((1000000 * t1.tv_sec) + t1.tv_usec) / 1000; return T; } int main(int argc, char *argv[]) { short in_output[1024]; short input_far[1024]; char src_file1[128] = {0}; char src_file2[128] = {0}; char dst_file[128] = {0}; unsigned int workingBufferSize; char *workingBuffer = NULL; int counter = 0; ALGO_AEC_RET ret; int tempSize; unsigned int T0, T1; float avg; FILE *fpInFar, *fpOut, *fpInNear; AudioAecInit aec_init; AudioAecConfig aec_config; AEC_HANDLE handle; /*********************User change section start*******************/ unsigned int supMode_band[6] = {20,40,60,80,100,120}; unsigned int supMode[7] = {4,4,4,4,4,4,4}; aec_init.point_number = 128; aec_init.nearend_channel = 1; aec_init.farend_channel = 1; aec_init.sample_rate = IAA_AEC_SAMPLE_RATE_16000; aec_config.delay_sample = 0; aec_config.comfort_noise_enable = IAA_AEC_FALSE; /*********************User change section end*******************/ memcpy(&(aec_config.suppression_mode_freq[0]), supMode_band, sizeof(supMode_band)); memcpy(&(aec_config.suppression_mode_intensity[0]), supMode, sizeof(supMode)); //(1)IaaAec_GetBufferSize workingBufferSize = IaaAec_GetBufferSize(); workingBuffer = (char*)malloc(workingBufferSize); if(NULL == workingBuffer) { printf("workingBuffer malloc failed !\n"); return -1; } printf("workingBuffer malloc success !\n"); //(2)IaaAec_Init handle = IaaAec_Init(workingBuffer, &aec_init); if (NULL == handle) { printf("AEC init failed !\r\n"); return -1; } printf("AEC init success !\r\n"); //(3)IaaAec_Config ret = IaaAec_Config(handle, &aec_config); if(ret) { printf("IaaAec_Config failed !\n"); return -1; } printf("IaaAec_Config succeed !\n"); #if IN_PARAMETER if(argc < 4) { printf("Please enter the correct parameters!\n"); return -1; } sscanf(argv[1], "%s", src_file1); sscanf(argv[2], "%s", src_file2); sscanf(argv[3], "%s", dst_file); #else sprintf(src_file1, "%s", "./farend.wav"); sprintf(src_file2, "%s", "./nearend.wav"); if(argc < 2) { printf("Please enter the correct parameters!\n"); return -1; } sscanf(argv[1], "%s", dst_file); #endif fpInFar = fopen(src_file1, "rb"); if(NULL == fpInFar) { printf("src_file1 open failed !\n"); return -1; } printf("src_file1 open succeed !\n"); fpInNear = fopen(src_file2, "rb"); if(NULL == fpInNear) { printf("src_file2 open failed !\n"); return -1; } printf("src_file2 open succeed !\n"); fpOut = fopen(dst_file, "wb"); if(NULL == fpOut) { printf("dst_file open failed !\n"); return -1; } printf("dst_file open succeed !\n"); #if 1 fread(in_output, sizeof(char), 44, fpInNear); // Remove the 44 bytes header fwrite(in_output, sizeof(char), 44, fpOut); // New file add header fread(input_far, sizeof(char), 44, fpInFar); // Remove the 44 bytes header #endif tempSize = aec_init.point_number * aec_init.nearend_channel; while(fread(in_output, sizeof(short), tempSize, fpInNear)) { tempSize = aec_init.point_number * aec_init.farend_channel; fread(input_far, sizeof(short), tempSize, fpInFar); counter++; T0 = (long)_OsCounterGetMs(); //(4)IaaAec_Run ret = IaaAec_Run(handle, in_output, input_far); T1 = (long)_OsCounterGetMs(); avg = AVERAGE_RUN(T1 - T0); if(0 == counter % 100) { printf("counter = %d\n", counter); printf("current time = %f\n", (float)counter * aec_init.point_number / aec_init.sample_rate); printf("process time = %lu(ms)\t", (long)(T1 - T0)); printf("AVG is %.2f ms\n", avg); } if(ret < 0) { printf("IaaAec_Run failed !\n"); break; } tempSize = aec_init.point_number * aec_init.nearend_channel; fwrite(in_output, sizeof(short), tempSize, fpOut); } //(5)IaaAec_Free IaaAec_Free(handle); fclose(fpInFar); fclose(fpInNear); fclose(fpOut); free(workingBuffer); printf("AEC end !\n"); return 0; }
2.8. IaaAec_GetLibVersion¶
-
Features
Get the version information of the Aec algorithm.
-
Syntax
ALGO_AEC_RET IaaAec_GetLibVersion(unsigned short *ver_year, unsigned short *ver_date, unsigned short *ver_time);
-
Parameters
Parameter Name Description Input/Output ver_year Year when Aec Algorithm Library was built output ver_date Date when Aec Algorithm Library was built output ver_time Date when Aec Algorithm Library was built output -
Return value
Return value Result 0 Successful Non-zero Failed, refer to error code -
Dependency
-
Header: AudioAecProcess.h
-
Library: libAEC_LINUX.so/ libAEC_LINUX.a
-
3. AEC DATA TYPE¶
3.1. AEC data type list¶
The AEC module related data types are defined as follows:
| DATA TYPE | Description |
|---|---|
| AudioAecInit | The initialization parameter structure of the Aec algorithm |
| AudioAecConfig | the configuration parameter structure of the Aec algorithm |
| IAA_AEC_SAMPLE_RATE | AEC algorithm supported sampling rate type |
| IAA_AEC_BOOL | The Boolean type used internally in the Aec algorithm |
| AEC_HANDLE | The handle type of the Aec algorithm |
3.2. AudioAecInit¶
-
Description
Define the initialization parameter structure of the Aec algorithm.
-
Definition
typedef struct { unsigned int point_number; unsigned int nearend_channel; unsigned int farend_channel; IAA_AEC_SAMPLE_RATE sample_rate; }AudioAecInit;
-
Member
Member name Description point_number The number of sampling points processed by the Aec algorithm once nearend_channel The near-end channel number ( the microphone channel number) farend_channel The far-end channel number (the speaker channel number) sample_rate Sampling rate processed by Aec algorithm -
Related data types and interfaces
3.3. AudioAecConfig¶
-
Description
Define the configuration parameter structure of the Aec algorithm
-
Definition
typedef struct { IAA_AEC_BOOL comfort_noise_enable; short delay_sample; unsigned int suppression_mode_freq[6]; unsigned int suppression_mode_intensity[7]; }AudioAecConfig;
-
Member
Member name Description comfort_noise_enable Add comfort noise after AEC to avoid the muting part of the paragraph after echo cancellation, which makes users feel disconnected.
If noise reduction is turned on after AEC, it is recommended to turn on comfort noise to help NR converge noise.delay_sample Echo delay samples between left and right channels When Stereo cost down is turned on, you can set the sample delay number according to the relative position of the microphone, reducing the amount of calculation required for the dual-channel.
Default value : 0
Unit : the number of samples
Value ranges: -9-9suppression_mode_freq The frequency band division of AEC processing divides the highest frequency that can be resolved by different sampling rates into 128 equal parts. Setting six values, which can cut out seven segments to set different AEC intensities.
Value ranges: 1-127suppression_mode_intensity Set seven intensities respectively in the seven paragraphs cut by the suppression_mode_freq.
Value ranges: 0-25 -
Note
-
comfort_noise_enable
After enabling the parameter, the AEC algorithm will add some comfort noise when there is no sound. This function can be enabled when you require a stable noise floor or when AEC is too clean that causes the NR convergence time is too long.
-
delay_sample
Due to the placement of the microphone and the speaker, the distance between the microphones, etc., the time points when the left and right channels receive the echo are not consistent, and the echo delay between the two channels is different.
This value indicates how many sampling points the left channel receives the echo earlier than the right channel. You can adjust this value to align the left and right channel data. When setting, please use the left channel as a reference. For example, the echo of the left channel is 4 samples faster than the right, s16DelaySample is set to 4, otherwise it is set to -4.
-
suppression_mode_freq
This array divides the highest frequency of the current sampling rate into 7 frequency bands for processing. The following is the conversion formula of array elements and frequency range: (residual\ Echo\ Frequency\ Range/(sampleRate/2) \times pointNumber(128), The array requires that each element must be greater than the previous element.
-
suppression_mode_intensity
This array represents the echo cancellation intensity of each frequency band, and each element corresponds to the 7 frequency bands divided by u32AecSupfreq. The greater the intensity, the more details are eliminated and the more unnatural the sound.
-
-
Related data types and interfaces
3.4. IAA_AEC_SAMPLE_RATE¶
-
Description
AEC algorithm supported sampling rate type.
-
Definition
typedef enum { IAA_AEC_SAMPLE_RATE_8000 = 8000 , IAA_AEC_SAMPLE_RATE_16000 = 16000 , }IAA_AEC_SAMPLE_RATE;
-
Member
Member name Description IAA_AEC_SAMPLE_RATE_8000 8K sampling rate IAA_AEC_SAMPLE_RATE_16000 16K sampling rate -
Related data types and interfaces
3.5. IAA_AEC_BOOL¶
-
Description
Define the Boolean type used internally in the Aec algorithm.
-
Definition
typedef enum { IAA_AEC_TRUE = 1, IAA_AEC_FALSE = 0, }IAA_AEC_BOOL;
-
Member
Member name Description IAA_AEC_TRUE True IAA_AEC_FALSE False -
Related data types and interfaces
3.6. AEC_HANDLE¶
-
Description
Define the handle type of the Aec algorithm.
-
Definition
typedef void* AEC_HANDLE; -
Related data types and interfaces
4. ERROR CODE¶
AEC API error codes are shown as follow:
| Error code | Definition | Description |
|---|---|---|
| 0x00000000 | ALGO_AEC_RET_SUCCESS | AEC runs successfully |
| 0x10000401 | ALGO_AEC_RET_INIT_ERROR | AEC isn`t initialized |
| 0x10000402 | ALGO_AEC_RET_INVALID_HANDLE | HANDLE is invalid |
| 0x10000403 | ALGO_AEC_RET_INVALID_SAMPLE_RATE | Sampling frequency doesn`t support |
| 0x10000404 | ALGO_AEC_RET_INVALID_POINT_NUMBER | Points per frame doesn`t support |
| 0x10000405 | ALGO_AEC_RET_INVALID_CHANNEL | Channel number doesn`t support |
| 0x10000406 | ALGO_AEC_RET_INVALID_SUP_BAND | AEC rejection band parameter setting is invalid |
| 0x10000407 | ALGO_AEC_RET_INVALID_SUP_MODE | AEC rejection intensity parameter setting is invalid |
| 0x10000408 | ALGO_AEC_RET_INVALID_COMFORT_NOISE | AEC comfort noise parameter setting is invalid |
| 0x10000409 | ALGO_AEC_RET_INVALID_DELAY_SAMPLE | AEC delay sample number setting is invalid |
| 0x10000410 | ALGO_AEC_RET_API_CONFLICT | Other APIs are running |
| 0x10000411 | ALGO_AEC_RET_INVALID_CALLING | Incorrect order of calling API |