MI SYS API
1. SUMMARY¶
1.1. Module Description¶
MI_SYS is the foundation module for the entire MI system, and it provides the basis for the operation of other MI modules.
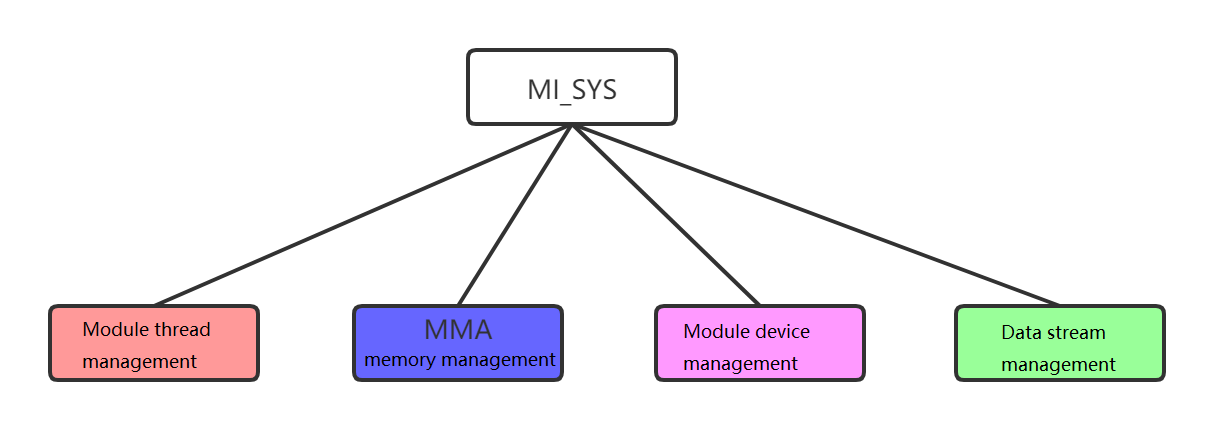
Figure 1‑1 : MI_SYS System Framework
As shown in Figure 1‑1, the main functions of the MI_SYS Overview are as follows:
-
Realize MI system initialization, MMA memory buffer pool management.
-
Provides the registration device nodes of each module, the general interface established by the proc system.
-
Provide s/he interface for each module to establish a binding relationship and manage the flow of data between the modules.
-
Provide s/he interface for each module to request MMA continuous physical memory, manage memory allocation, map virtual addresses, and reclaim memory.
-
Provides the interface of each module to establish the worker thread, manages the creation, operation, destruction of each module thread.
As shown in Figure 1‑2, the code structure of the MI_SYS is divided into four layers: the impl layer, the internal layer, the ioctl layer, and the api layer.
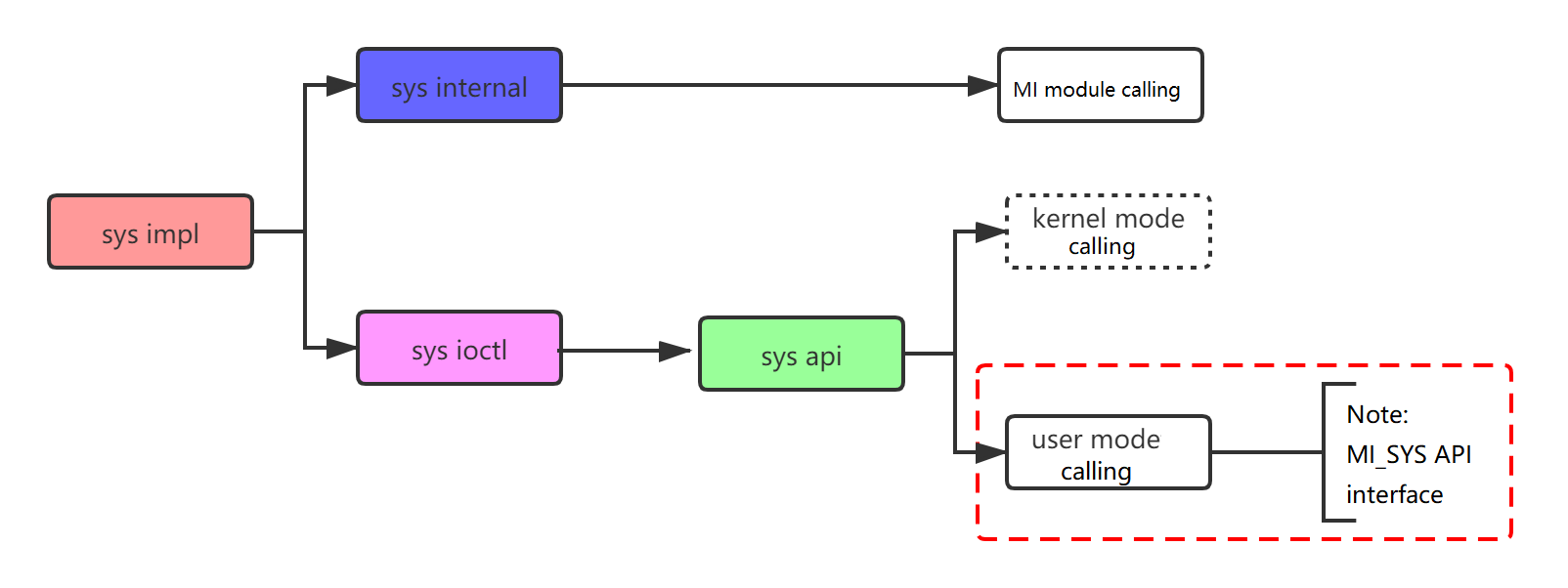
Figure 1‑2 : MI_SYS Code Structure
Sys impl layer: at the bottom of the MI_SYS, basically sys functionality is implemented here.
Sys internal layer: The Sys impl layer external interface is encapsulated in kernel mode, providing other MI modules with features such as device creation, request memory, creation of threads, and management of memory.
Sys ioctl layer: Sys impl layer external interface encapsulation, composed of the format of ioctl, provided by sys api call.
Sys api layer: The Sys api layer compiles once each in kernel mode and user mode, but is currently only open to user mode calls, i.e. the api interface that is finally open to customers. Please refer to the API interface instructions for specific functions.
Tips:
The Sys impl layer, the Sys internal layer, the Sys ioctl layer are implemented in "mi_sys.ko", the Sys api layer is implemented in "libmi_sys.so", the header file is (mi_sys.h, mi_sys_datatype.h, mi_ sys.h).
1.2. Document format constraints¶
Body: for writing the body content of the document, where the writing of the snippet needs to be written in an equal-width font.
Body and bold: For writing important content in the body of a document.
Italics: for writing in the Tips section of the document.
Italics and boldness: For writing important content in the Tips section of the document.
1.3. Keyword Description¶
ID: An abbreviation for Identity document, which means unique encoding.
MI: SStar SDK Middle Interface abbreviation, in this article, if a similar structure of "MI_SYS" appears to represent the MI SYS module, if it is a simple "MI", refers to the entire SDK.
Hex: Hex.
Kernel Mode: refers to code that works in kernel environments and has control over the hardware that operates directly, such as functions and threads in ko.
User Mode: refers to working in a User environment, such as customer applications, system calls, and so on.
APP: An abbreviation for Application, which refers primarily to an application that calls the MI API.
API: Application Interface, Application Interface.
NVR: Network Video Recorder, or Network Video Recorder.
IPC: Full name IP Camera, or webcam.
HW: Full name hardware, that is, hardware.
Dev: Full name Device, which is described in this article as the MI module device, 1.4.1 is explained in detail.
Pass: This article represents the workflow of the MI module device device, 1.4.1 is explained in detail.
Chn: Full Chanel, which represents a channel of MI module equipment, 1.4.1 is explained in detail.
Port: This article indicates that a port in the MI module device channel, 1.4.1 is explained in detail.
Additional notes:
-
Without separate instructions, the MI_SYS in this article have the same meaning as SYS, MI_DISP, and DISP, and the remaining modules have similar names.
-
All module names that appear in this article can be found in MI_ModuleId_e.
1.4. Flow frame¶
1.4.1. Relationship between Dev/Pass/Chn/Port¶
A typical MI module will have a Dev/Pass/Port three-stage structure as shown in Figure 1‑3.
-
Dev
An MI module will have one or more Devs, and in general different Devs indicate that the module device needs to invoke different HW resources or work in different working patterns. For example, VENC needs to invoke different HW resources when encoding H264/H265 and Jpeg, and Dev has to separate.
-
Chn
A Dev will have one or more Chns, which generally mean that the channel is different, and that the channel, although it shares HW resources with other Chns under Dev, is different from the data source or working pattern. For example, the source of the code flow is different, Chn is generally not the same.
-
Port
A Chn will have one or more ports, which means port, consisting of Input Port and Output Port. In general, different Ports indicate that the channel shares HW resources and data sources with other Ports under Dev and Chn, but the parameters that need to be set are different, such as different resolutions, and Port is generally different.
In general, Port is the smallest independent unit for the customer to operate the MI module because it identifies all the information: HW resources, data sources, parameter properties.
Each Port consists of InputPort and OutputPort, which are the ports for data inflows, and OutputPort, which is the port of data flowing out. It is important to note, however, that a Port does not always have input Port and OutputPort, depending on the behavior of the module. Modules like Disp only need InputPort, and output Port is needed, and it shows the results directly on the Panel. A module like Vdec, where the data can be fed directly by a user calling the Vdec interface, does not go through InputPort, so that he does not have OutputPort.
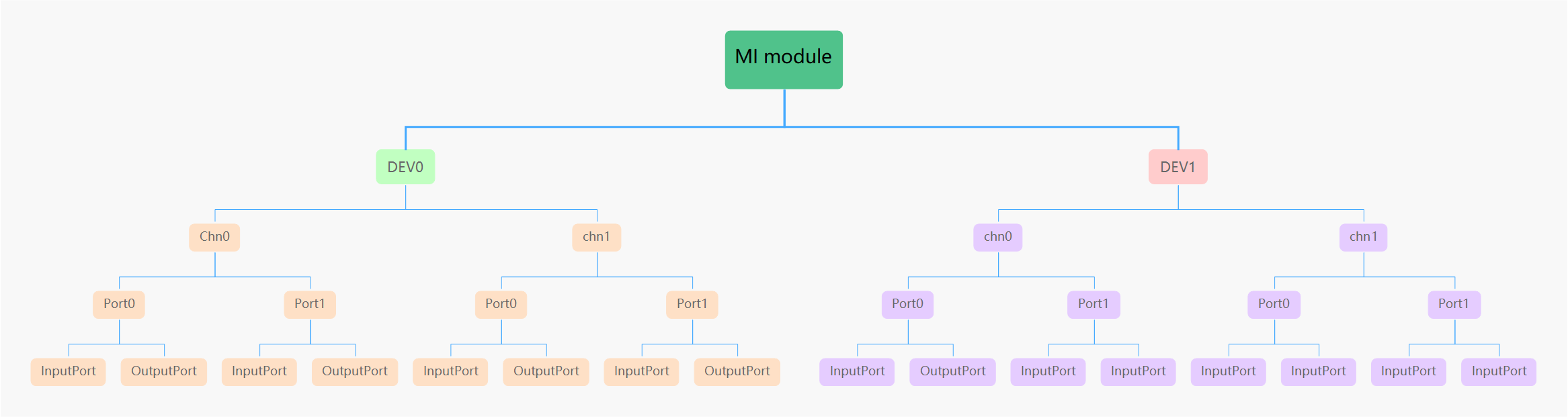
Figure 1‑3 : Three-level structure of the MI module
Tips:
1. The boundaries between Chn and Port are not always clear, if there is a difference between the interpretation of a module's API documentation and the explanation above, call the module to its API documentation.
2. InputPort/OutpuPort for a Port is usually only one or zero, with the exception of some special modules. The Vpe module, for example, has a structural relationship as shown in the figure. That is, it has one InputPort and multiple OutputPorts. This means that Vpe shares the same data source, but must have different output formats of different specifications.
- Pass
Pass is a new concept introduced MI_SYS V2.0 and above. As we said above, Dev generally corresponds to access to HW resources, which is that worker threads should have been created at this level.
However, for some complex modules, you need to use multiple sets of HW resources to complete the function in stages. These stages can work in parallel, but there is order between them, and the output of the previous stage is the input of the latter stage, at which point the process of Dev's work needs to be processed into different Pass threads.
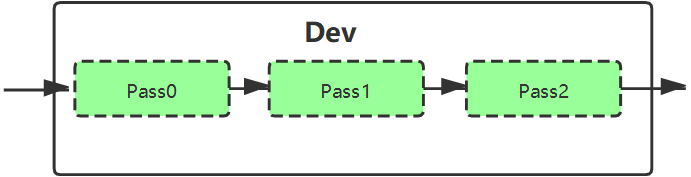
Figure 1‑4 : Relation between Pass and Dev
Tips:
-
Some modules have only one Pass, some have multiple, and one Pass is for a worker thread, and a valid execution represents the process of "one data inflow - HW processing - data outflow".
-
It is important to note that Pass and Chn/Port are not subordinate, they are a submodule belonging to Dev. Its functionality is implemented within MI, and there is no need to pay too much attention to using the API interface.
1.4.2. A typical NVR data stream¶
Figure 1‑5 is a typical NVR data flow model. The flow process is as follows:
-
Establishing a binding relationship with Vdec-Divp-Disp;
-
The user writes a stream of yards to InputPort in Vdec;
-
Vdec decoding, writing decoded data to Vdec OutpuPort requested memory, sent to the next level;
-
Divp receives the data, sends it to Divp HW for processing, writes to Divp OutputPort, and sends it to the next level;
-
Disp will receive the data displayed.

Figure 1‑5 : A typical NVR data flow model
Tips:
The data flow is the original practice, now the Vdec module has provided a separate interface to the customer, can write the data directly to Vdec's private memory, do not need to make extra copies through the interface of Ah SYS. That said, Vdec no longer needs InputPort.
1.4.3. A typical IPC data stream¶
Figure 1‑6 is a typical IPC data flow model with the following flow procedures:
-
Establishing a binding relationship with Vif-Vpe-Venc;
-
Sensor feeds the data into vif processing;
-
Vif sends the processed data to the memory requested by Output Port and sends it to the next level;
-
Vpe receives the data, feeds it into Pass0 (ISP/SCL0), Pass1 (LDC), Pass2 (SCL1) for processing, and writes the processed data to the memory requested by Output Port and sends it to the next level;
-
Venc receives the data, feeds the encoder for coding processing, and writes the encoded data to the RingPool memory area;
-
The user calls Venc's interface to retrieve the stream and feeds it into the user's business layer app.
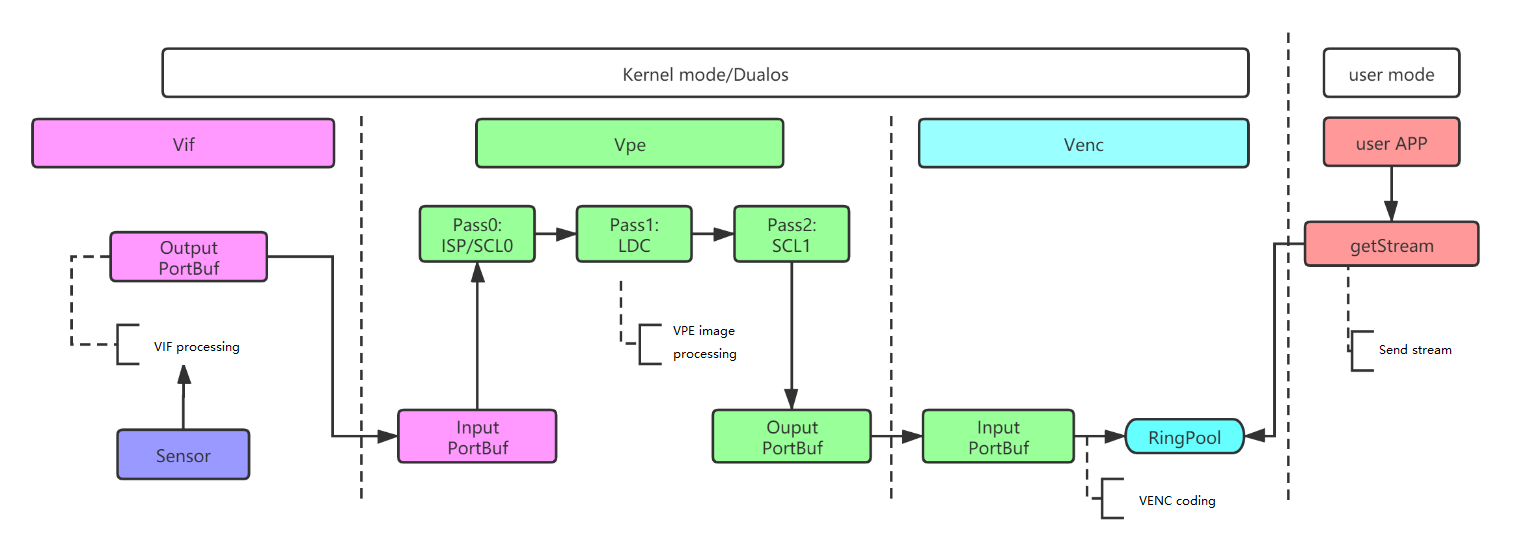
Figure 1‑6 : A typical IPC data flow model
Tips:
The flow of data between the three Passes inside Vpe is actually more complex than in the figure. But this is all MI internal processing logic, using the API without excessive attention.
2. API Reference¶
2.1. API Format Description¶
This manual uses information about the Description APIs for the nine reference domains, which are represented by Table 2-1.
Table 2‑1 : API Format Description
| Label | Function |
|---|---|
| Function | Briefly Description the main features of the API. |
| Syntax | List the header files that should be included in the call API and the prototype declaration of the API. |
| Parameters | List the parameters, parameter descriptions, and parameter properties of the API. |
| Return value | List all possible return values of the API and what it means. |
| Dependency | Lists the header files that the API contains and the library files that the API will link to when the API compiles. |
| Attention | List the things you should be aware of when using the API. |
| Example | List instances that use the API. |
| Related topics | The interface associated with the call context. |
2.2. Feature Module API List¶
As mentioned earlier, we can roughly divide the MI_SYS's API into three broad categories: system functional class, data flow class, memory management class.
Table 2‑2 : API List
| API Name | Function |
|---|---|
| System functional class | |
| MI_SYS_Init | Initialize the MI_SYS system |
| MI_SYS_Exit | Destructing MI_SYS System |
| MI_SYS_GetVersion | Get the system version number of MI |
| MI_SYS_GetCurPts | Get the current timestamp of the MI system |
| MI_SYS_InitPtsBase | Initializing MI System Baseline Timestamp |
| MI_SYS_SyncPts | Synchronized MI system timestamp |
| MI_SYS_SetReg | Set the value of the register, debug with |
| MI_SYS_GetReg | Get the value of the register, debug with |
| MI_SYS_ReadUuid | Get Chip's Unique ID |
| MI_SYS_EnableChnOutputPortLowLatency | Enable or disable output port low latency |
| MI_SYS_InitDev | Initialize sys device |
| MI_SYS_DeInitDev | De-initialize sys device |
| MI_SYS_SetGlobalFlag | Set global flag bit value |
| Data stream class | |
| MI_SYS_BindChnPort | Binding of the data source Output port to the recipient Input port |
| MI_SYS_BindChnPort2 | Binding from the output port of the data source to the recipient Input port, requiring a working mode to be specified |
| MI_SYS_UnBind_ChnPort | The de-binding of the data source Output port to the recipient Input port |
| MI_SYS_GetBindbyDest | Query the corresponding source Output port for the data recipient Input port |
| MI_SYS_ChnInputPortGetBuf | Get the buf of channel input Port |
| MI_SYS_ChnInputPortPutBuf | Add the buf of the channel input Port to the pending queue |
| MI_SYS_ChnOutputPortGetBuf | Get the buf of the channel output Port |
| MI_SYS_ChnOutputPortPutBuf | Release channel outputPort's buf |
| MI_SYS_ChnInputPortGetBufPa | The buf object corresponding to the allocation channel input port, which only returns MIU physical address |
| MI_SYS_ChnInputPortPutBufPa | Add the buf object corresponding to the channel input port to the pending queue, which needs to be used in pair with the function MI_SYS_ChnInputPortGetBufPa |
| MI_SYS_ChnOutputPortGetBufPa | The buf object corresponding to the allocation channel ouput port, which only returns MIU physical address |
| MI_SYS_ChnOutputPortPutBufPa | Release channel output port corresponding to the buf object, which needs to be used in pair with the function MI_SYS_ChnOutputPortGetBufPa |
| MI_SYS_SetChnOutputPortDepth | Set the depth of the channel OutputPort |
| MI_SYS_ChnPortInjectBuf | Inject output Port Buf data into module channel inputPort Port |
| MI_SYS_GetFd | Get the file Description character of the current channel wait event |
| MI_SYS_CloseFd | File Description character to close the current channel |
| MI_SYS_DupBuf | Duplicate buf object |
| Memory management classes | |
| MI_SYS_SetChnMMAConf | Set the MMA pool name for the default allocation of memory for the module device channel Output port |
| MI_SYS_GetChnMMAConf | Get the MMA pool name of the module device channel Output port's default allocated memory |
| MI_SYS_ConfDevPubPools | Configure and initialize the module's public buffer pool |
| MI_SYS_ReleaseDevPubPools | Release module public buffer pool |
| MI_SYS_ConfGloPubPools | Configure and initialize the MI system-wide default VB cache pool |
| MI_SYS_ReleaseGloPubPools | Release MI System Default VB Cache Pool |
| MI_SYS_MMA_Alloc | Application requests physical continuous memory from MMA memory management pool |
| MI_SYS_MMA_Free | Memory allocated to the MMA memory management pool in the user state |
| MI_SYS_Mmap | Mapping physical memory to CPU virtual addresses |
| MI_SYS_FlushInvCache | Flush cache CPU virtual address |
| MI_SYS_Munmap | Unmapping physical memory to virtual addresses |
| MI_SYS_MemsetPa | Fill the entire physical memory with the DMA hardware module. |
| MI_SYS_MemcpyPa | Copy the source memory data to the target memory via the DMA hardware module |
| MI_SYS_BufFillPa | Fill some of the physical memory with the DMA hardware module |
| MI_SYS_BufBlitPa | Copy parts of the source memory data to parts of the target memory through the DMA hardware module. |
| MI_SYS_ConfigPrivateMMAPool | Configure private MMA Heap for mold fast |
| MI_SYS_PrivateDevChnHeapAlloc | Request memory from module channel private MMA Pool |
| MI_SYS_PrivateDevChnHeapFree | Free memory from module channel private MMA pool |
| MI_SYS_Va2Pa | Turn CPU virtual address pointer to Physical address |
2.3. System functional class API¶
2.3.1. MI_SYS_Init¶
-
Function
MI_SYS_Init ialization, the MI_SYS module provides basic support for other MI modules in the system and needs to be initialized earlier than other MI modules in the system, otherwise other stream types within the module will fail when initialization.
-
Syntax
MI_S32 MI_SYS_Init(void); -
Return
-
0 Successful.
-
!0 Failed, please refer to the error code.
-
-
Dependency
-
Head file: mi_sys_datatype.h, mi_sys.h
-
Library files: libmi_sys.a / libmi_sys.so
-
-
Note
-
MI_SYS_Init need to be called earlier than other MI modules in the Init function.
-
The MI_SYS_Init can be repeatedly called, but must be used in pairs with the MI_SYS_Exit or an error will be reported.
-
The system needs to configure the configuration parameters of the MMA memory heap within the kernel boot parameters.
-
-
Sample
MI_SYS_Init Sample
MI_S32 ST_Sys_Init(void) { MI_SYS_Version_t stVersion; MI_U64 u64Pts = 0; STCHECKRESULT(MI_SYS_Init()); memset(&stVersion, 0x0, sizeof(MI_SYS_Version_t)); STCHECKRESULT(MI_SYS_GetVersion(&stVersion)); ST_INFO("u8Version:%s\n", stVersion.u8Version); STCHECKRESULT(MI_SYS_GetCurPts(&u64Pts)); ST_INFO("u64Pts:0x%llx\n", u64Pts); u64Pts = 0xF1237890F1237890; STCHECKRESULT(MI_SYS_InitPtsBase(u64Pts)); u64Pts = 0xE1237890E1237890; STCHECKRESULT(MI_SYS_SyncPts(u64Pts)); return MI_SUCCESS; } MI_S32 ST_Sys_Exit(void) { STCHECKRESULT(MI_SYS_Exit()); return MI_SUCCESS; }
Tips:
This example is intended for: MI_SYS_Init / MI_SYS_Exit / MI_SYS_GetVersion / MI_SYS_GetCurPts / MI_SYS_InitPtsBase / MI_SYS_SyncPts / MI_SYS_ReadUuid .
-
Related topics
2.3.2. MI_SYS_Exit¶
-
Function
MI_SYS_Init ialization, before calling MI_SYS_Exit, you need to make sure that all other modules in the system have been deinitialized and that all VBPOOL has been Destroyed or the MI_SYS_Exit will return to failure.
-
Syntax
MI_S32 MI_SYS_Exit (void); -
Return
-
0 Successful.
-
!0 Failed, please refer to the error code.
-
-
Dependency
-
Head file: mi_sys_datatype.h, mi_sys.h
-
Library files: libmi_sys.a / libmi_sys.so
-
-
Note
-
MI_SYS_Exit Before calling, make sure that all other modules in the system have been deinitialized.
-
MI_SYS_Exit Before calling, you need to make sure that all created VBPOOL in the system has been successfully destroyed.
-
-
Sample
Reference MI_SYS_Init Sample.
-
Related topics
2.3.3. MI_SYS_GetVersion¶
-
Function
Get the system version number of MI.
-
Syntax
MI_S32 MI_SYS_GetVersion (MI_SYS_Version_t *pstVersion); -
Parameters
Parameter Name Description Input/Output pstVersion System version number returns data structure pointer Output -
Return
-
0 Successful.
-
!0 Failed, please refer to the error code.
-
-
Dependency
-
Head file: mi_sys_datatype.h, mi_sys.h
-
Library files: libmi_sys.a / libmi_sys.so
-
-
Sample
Reference MI_SYS_Init Sample.
2.3.4. MI_SYS_GetCurPts¶
-
Function
Get the current timestamp of the MI system.
-
Syntax
MI_S32 MI_SYS_GetCurPts (MI_U64 *pu64Pts); -
Parameters
Parameter Name Description Input/Output pu64Pts The system's current timestamp returns address Output -
Return
-
0 Successful.
-
!0 Failed, please refer to the error code.
-
-
Dependency
-
Head file: mi_sys_datatype.h, mi_sys.h
-
Library files: libmi_sys.a / libmi_sys.so
-
-
Sample
Reference MI_SYS_Init Sample.
2.3.5. MI_SYS_InitPtsBase¶
-
Function
Initializing MI System Baseline Timestamp.
-
Syntax
MI_S32 MI_SYS_InitPtsBase (MI_U64 u64PtsBase); -
Parameters
Parameter Name Description Input/Output u64PtsBase Set system timestamp baseline Input -
Return
-
0 Successful.
-
!0 Failed, please refer to the error code.
-
-
Dependency
-
Head file: mi_sys_datatype.h, mi_sys.h
-
Library files: libmi_sys.a / libmi_sys.so
-
-
Sample
Reference MI_SYS_Init Sample.
2.3.6. MI_SYS_SyncPts¶
-
Function
Synchronized MI system timestamp.
-
Syntax
MI_S32 MI_SYS_SyncPts (MI_U64 u64Pts); -
Parameters
Parameter Name Description Input/Output u64Pts Fine-tuned system timestamp baseline Input -
Return
-
0 Successful.
-
!0 Failed, please refer to the error code.
-
-
Dependency
-
Head file: mi_sys_datatype.h, mi_sys.h
-
Library files: libmi_sys.a / libmi_sys.so
-
-
Sample
Reference MI_SYS_Init Sample.
2.3.7. MI_SYS_SetReg¶
-
Function
Set the value of the register.
-
Syntax
MI_S32 MI_SYS_SetReg (MI_U32 u32RegAddr, MI_U16 u16Value,MI_U16 u16Mask); -
Parameters
Parameter Name Description Input/Output u32RegAddr Register Bus Address Input u16Value 16bit register value to be written Input u16Mask This time the Mask mask ingests the bar for the register value Input -
Return
-
0 Successful.
-
!0 Failed, please refer to the error code.
-
-
Dependency
-
Head file: mi_sys_datatype.h, mi_sys.h
-
Library files: libmi_sys.a / libmi_sys.so
-
2.3.8. MI_SYS_GetReg¶
-
Function
Get the value of the register, debug with.
-
Syntax
MI_S32 MI_SYS_GetReg (MI_U32 u32RegAddr, MI_U16 *pu16Value); -
Parameters
Parameter Name Description Input/Output u32RegAddr Register Bus Address Input pu16Value To read back to 16bit register value return address Output -
Return
-
0 Successful.
-
!0 Failed, please refer to the error code.
-
-
Dependency
-
Head file: mi_sys_datatype.h, mi_sys.h
-
Library files: libmi_sys.a / libmi_sys.so
-
2.3.9. MI_SYS_ReadUuid¶
-
Function
Get Chip's Unique ID.
-
Syntax
MI_S32 MI_SYS_ReadUuid (MI_U64 *u64Uuid); -
Parameters
Parameter Name Description Input/Output u64Uuid Get a pointer to the chip unique ID value Output -
Return
-
0 Successful.
-
!0 Failed, please refer to the error code.
-
-
Dependency
-
Head file: mi_sys_datatype.h, mi_sys.h
-
Library files: libmi_sys.a / libmi_sys.so
-
-
Sample
Reference MI_SYS_Init Sample.
2.3.10. MI_SYS_EnableChnOutputPortLowLatency¶
-
Function
Enable or disable output port low latency.
-
Syntax
MI_S32 MI_SYS_EnableChnOutputPortLowLatency(MI_SYS_ChnPort_t *pstChnPort,MI_BOOL bEnable , MI_U32 u32Param); -
Parameters
Parameter Name Parameter meaning Input/Output pstChnPort A pointer to the output port of the module channel Input bEnable TRUE: enable; FALSE: disable Input u32Param Low Latency parameter, which is determined by specific modules. For VPE, it is used for configuring the line count. The buffer of frame is sent to user or backward once the count of lines is written, instead of waiting for the whole frame done. Input -
Return
-
0 Successful.
-
!0 Failed, please refer to the error code.
-
-
Dependency
-
Head file: mi_sys_datatype.h, mi_sys.h
-
Library files: libmi_sys.a / libmi_sys.so
-
-
Note
When bEnable is true, u32Param must be greater than 0; otherwise the setting is invalid.
-
Sample
MI_SYS_ChnPort_t stChnPort; stChnPort.eModId = E_MI_MODULE_ID_VPE; stChnPort.u32DevId = 0; stChnPort.u32ChnId = 0; stChnPort.u32PortId = 0; MI_SYS_EnableChnOutputPortLowLatency(&stChnPort,TRUE , 100); MI_SYS_EnableChnOutputPortLowLatency(&stChnPort,FALSE , 0);
2.3.11. MI_SYS_InitDev¶
-
Function
MI_SYS_Init ialization, the MI_SYS module provides basic support for other MI modules in the system and needs to be initialized earlier than other MI modules in the system, otherwise other stream types within the module will fail when initialization.
-
Syntax
MI_S32 MI_SYS_InitDev(MI_SYS_InitParam_t *pstInitParam); -
Parameters
Parameter Name Description Input/Output pstInitParam Initialization Parameter Input -
Return
-
0 Successful.
-
!0 Failed, please refer to the error code.
-
-
Dependency
-
Head file: mi_sys_datatype.h, mi_sys.h
-
Library files: libmi_sys.a / libmi_sys.so
-
-
Note
-
MI_SYS_Init need to be called earlier than other MI modules in the Init function.
-
The system needs to configure the configuration parameters of the MMA memory heap within the kernel boot parameters.
-
pstInitParam is not used now, the null value can be passed in.
-
This interface is recommended in version 2.17 or above, use to replace the original MI_SYS_Init interface.
-
-
Related topics
2.3.12. MI_SYS_DeInitDev¶
-
Function
MI_SYS initialization, before calling MI_SYS_DeInitDev, you need to make sure that all other modules in the system have been deinitialized and that all VBPOOL has been Destroyed or the MI_SYS_DeInit will return to failure.
-
Syntax
MI_S32 MI_SYS_DeInitDev(void); -
Return
-
0 Successful.
-
!0 Failed, please refer to the error code.
-
-
Dependency
-
Head file: mi_sys_datatype.h, mi_sys.h
-
Library files: libmi_sys.a / libmi_sys.so
-
-
Note
-
This interface should be called after device has been initialized; otherwise a failed message will be returned.
-
This interface does not support multiple calls under the same process, otherwise a failed message will be returned.
-
MI_SYS_DeInitDev Before calling, make sure that all other modules in the system have been deinitialized.
-
This interface is recommended in Version 2.17 and above, use to replace the original MI_SYS_Exit interface
-
-
Related topics
2.3.13. MI_SYS_SetGlobalFlag¶
-
Function
Set the global flag bit value, currently supports setting the IR flag bit value.
-
Syntax
MI_S32 MI_SYS_SetGlobalFlag(MI_SYS_GlobalFlagParam_t *pstGlobalFlagParam); -
Parameters
Parameter Name Description Input/Output pstGlobalFlagParam Set global Flag parameter Input -
Return
-
0 Successful.
-
!0 Failed, please refer to the error code.
-
-
Dependency
-
Head file: mi_sys_datatype.h、mi_sys.h
-
Library files: libmi_sys.a / libmi_sys.so
-
2.4. Data flow class API¶
2.4.1. MI_SYS_BindChnPort¶
-
Function
Binding of the data source Output port to the data receiver Input port.
-
Syntax
MI_S32 MI_SYS_BindChnPort( *pstSrcChnPort, *pstDstChnPort, ,MI_U32 u32SrcFrmrate, MI_U32 u32DstFrmrate); -
Parameters
Parameter Name Parameter meaning Input/Output pstSrcChnPort Source port configuration information data structure pointer Input pstDstChnPort Target port configuration information data structure pointer Input u32SrcFrmrate Frame rate of source port configuration Input u32DstFrmrate Frame rate of target port configuration Input -
Return
-
0 Successful.
-
!0 Failed, please refer to the error code.
-
-
Dependency
-
Head file: mi_sys_datatype.h, mi_sys.h
-
Library files: libmi_sys.a / libmi_sys.so
-
-
Note
-
The source port must be a channel Output port.
-
The destination port must be a channel Input port.
-
The source and destination ports must not have been bound before.
-
This interface only supports binding modules in E_MI_SYS_BIND_TYPE_FRAME_BASE mode, not recommended in version 2.0 or above, please use MI_SYS_BindChnPort2 instead.
-
-
Sample
MI_SYS_ChnPort_t stSrcChnPort; MI_SYS_ChnPort_t stDstChnPort; MI_U32 u32SrcFrmrate; MI_U32 u32DstFrmrate; stSrcChnPort.eModId = E_MI_MODULE_ID_VPE; stSrcChnPort.u32DevId = 0; stSrcChnPort.u32ChnId = 0; stSrcChnPort.u32PortId = 0; stDstChnPort.eModId = E_MI_MODULE_ID_VENC; stDstChnPort.u32DevId = 0; stDstChnPort.u32ChnId = 0; stDstChnPort.u32PortId = 0; u32SrcFrmrate = 30; u32DstFrmrate = 30; MI_SYS_BindChnPort(&stSrcChnPort, &stDstChnPort, u32SrcFrmrate, u32DstFrmrate);
-
Related topics
2.4.2. MI_SYS_BindChnPort2¶
-
Function
Binding of the data source Output port to the data receiver Input port requires additional operating mode.
-
Syntax
MI_S32 MI_SYS_BindChnPort2(MI_SYS_ChnPort_t *pstSrcChnPort, MI_SYS_ChnPort_t *pstDstChnPort,MI_U32 u32SrcFrmrate, MI_U32 u32DstFrmrate, MI_SYS_BindType_e eBindType, MI_U32 u32BindParam);
-
Parameters
Parameter Name Parameter meaning Input/Output pstSrcChnPort The source port configures the information data structure pointer. Input pstDstChnPort The destination port configures the information data structure pointer. Input u32SrcFrmrate Frame rate of source port configuration Input u32DstFrmrate Frame rate of target port configuration Input eBindType The operating mode of the source port connected to the destination port, refer to the MI_SYS_BindType_e Input u32BindParam Additional parameters to be brought in by different working modes. Input -
Return
-
0 Successful.
-
!0 Failed, please refer to the error code.
-
-
Dependency
-
Head file: mi_sys_datatype.h, mi_sys.h
-
Library files: libmi_sys.a / libmi_sys.so
-
-
Note
-
The source port must be a channel Output port.
-
The destination port must be a channel Input port.
-
The source and destination ports must not have been previously bound
-
Older versions of MI SYS do not provide this interface if not found, do not need to be set.
-
Various eBindType usage scenarios are as follows:
eBindType Applicable Scenario E_MI_SYS_BIND_TYPE_SW_LOW_LATENCY u32 Bind Param represents low latency value, unit ms E_MI_SYS_BIND_TYPE_HW_RING u32 Bind Param represents ring buffer depth, currently only vpe and venc (h264/h265) support this model, only all the way E_MI_SYS_BIND_TYPE_REALTIME u32 Bind Param unused, jpe imi will go this way, only support all the way E_MI_SYS_BIND_TYPE_FRAME_BASE u32 Bind Param unused, default is to walk this frame mode
-
-
Sample
MI_SYS_ChnPort_t stSrcChnPort; MI_SYS_ChnPort_t stDstChnPort; MI_U32 u32SrcFrmrate; MI_U32 u32DstFrmrate; MI_SYS_BindType_e eBindType; MI_U32 u32BindParam; // a. When the type of connection between vpe and venc is E_MI_SYS_BIND_TYPE_FRAME_BASE, the code is as follows: stSrcChnPort.eModId = E_MI_MODULE_ID_VPE; stSrcChnPort.u32DevId = 0; stSrcChnPort.u32ChnId = 0; stSrcChnPort.u32PortId = 0; stDstChnPort.eModId = E_MI_MODULE_ID_VENC; stDstChnPort.u32DevId = 0; stDstChnPort.u32ChnId = 0; stDstChnPort.u32PortId = 0; u32SrcFrmrate = 30; u32DstFrmrate = 30; eBindType = E_MI_SYS_BIND_TYPE_FRAME_BASE; u32BindParam = 0; STCHECKRESULT(MI_SYS_BindChnPort2(&stSrcChnPort, &stDstChnPort, u32SrcFrmrate, u32DstFrmrate, eBindType, u32BindParam)); //b. When the type of connection between vpe and venc is E_MI_SYS_BIND_TYPE_REALTIME, the code is as follows: stSrcChnPort.eModId = E_MI_MODULE_ID_VPE; stSrcChnPort.u32DevId = 0; stSrcChnPort.u32ChnId = 0; stSrcChnPort.u32PortId = 0; stDstChnPort.eModId = E_MI_MODULE_ID_VENC; stDstChnPort.u32DevId = 1; stDstChnPort.u32ChnId = 0; stDstChnPort.u32PortId = 0; u32SrcFrmrate = 30; u32DstFrmrate = 30; eBindType = E_MI_SYS_BIND_TYPE_REALTIME; u32BindParam = 0; STCHECKRESULT(MI_SYS_BindChnPort2(&stSrcChnPort, &stDstChnPort, u32SrcFrmrate, u32DstFrmrate, eBindType, u32BindParam)); //c. When the type of connection between vpe and venc is E_MI_SYS_BIND_TYPE_HW_RING, the code is as follows: tSrcChnPort.eModId = E_MI_MODULE_ID_VPE; stSrcChnPort.u32DevId = 0; stSrcChnPort.u32ChnId = 0; stSrcChnPort.u32PortId = 0; stDstChnPort.eModId = E_MI_MODULE_ID_VENC; stDstChnPort.u32DevId = 0; stDstChnPort.u32ChnId = 0; stDstChnPort.u32PortId = 0; u32SrcFrmrate = 30; u32DstFrmrate = 30; eBindType = E_MI_SYS_BIND_TYPE_HW_RING; u32BindParam = 1080; //Suppose vpe output resolution is 1920*1080, and ring buffer depth is 1080 STCHECKRESULT(MI_SYS_BindChnPort2(&stSrcChnPort, &stDstChnPort, u32SrcFrmrate u32DstFrmrate, eBindType, u32BindParam));
-
Related topics
2.4.3. MI_SYS_UnBind_ChnPort¶
-
Function
Debinding between the data source Output port to the data receiver Input port.
-
Syntax
MI_S32 MI_SYS_UnBindChnPort( *pstSrcChnPort, *pstDstChnPort); -
Parameters
Parameter Name Description Input/Output pstSrcChnPort The source port configures the information data structure pointer. Input pstDstChnPort The destination port configures the information data structure pointer. Input -
Return
-
0 Successful.
-
!0 Failed, please refer to the error code.
-
-
Dependency
-
Head file: mi_sys_datatype.h, mi_sys.h
-
Library files: libmi_sys.a / libmi_sys.so
-
-
Note
-
The source port must be a channel Output port.
-
The destination port must be a channel Input port.
-
The source and destination ports must have been bound before
-
-
Related topics
2.4.4. MI_SYS_GetBindbyDest¶
-
Function
Query the corresponding source Output port for the data recipient Input port.
-
Syntax
MI_S32 MI_SYS_GetBindbyDest ( *pstDstChnPort, *pstSrcChnPort); -
Parameters
Parameter Name Description Input/Output pstDstChnPort The destination port configures the information data structure pointer. Input pstDstChnPort The source port configures the information data structure pointer. Output -
Return
-
0 Successful.
-
!0 Failed, please refer to the error code.
-
-
Dependency
-
Head file: mi_sys_datatype.h, mi_sys.h
-
Library files: libmi_sys.a / libmi_sys.so
-
-
Note
-
The destination port must be a channel Input port.
-
The target port must have been bound before
-
2.4.5. MI_SYS_ChnInputPortGetBuf¶
-
Function
The buf object corresponding to the allocation channel input port.
-
Syntax
MI_S32 MI_SYS_ChnInputPortGetBuf (MI_SYS_ChnPort_t *pstChnPort,MI_SYS_BufConf_t *pstBufConf, MI_SYS_BufInfo_t *pstBufInfo, MI_SYS_BUF_HANDLE *phHandle , MI_S32 s32TimeOutMs); -
Parameters
Parameter Name Description Input/Output pstChnPort A pointer to the input port of the module channel Input pstBufConf Memory configuration information to be allocated Input pstPortBuf Return buf pointer Output phHandle Get the Idr handle of intput Port Buf Output s32TimeOutMs Number of milliseconds waiting for timeout Output -
Return
-
0 Successful.
-
!0 Failed, please refer to the error code.
-
-
Dependency
-
Head file: mi_sys_datatype.h, mi_sys.h
-
Library files: libmi_sys.a / libmi_sys.so
-
-
Sample
MI_SYS_ChnInputPortGetBuf Call Sample
MI_SYS_ChnPort_t stVpeChnInput; MI_SYS_BUF_HANDLE hHandle = 0; MI_SYS_BufConf_t stBufConf; MI_SYS_BufInfo_t stBufInfo; struct timeval stTv; MI_U16 u16Width = 1920, u16Height = 1080; FILE *fp = NULL; memset(&stVpeChnInput, 0x0, sizeof(MI_SYS_ChnPort_t)); memset(&stBufConf, 0x0, sizeof(MI_SYS_BufConf_t)); memset(&stBufInfo, 0x0, sizeof(MI_SYS_BufInfo_t)); stVpeChnInput.eModId = E_MI_MODULE_ID_VPE; stVpeChnInput.u32DevId = 0; stVpeChnInput.u32ChnId = 0; stVpeChnInput.u32PortId = 0; fp = fopen("/mnt/vpeport0_1920x1080_pixel0_737.raw","rb"); if(fp == NULL) { printf("file %s open fail\n", "/mnt/vpeport0_1920x1080_pixel0_737.raw"); return 0; } while(1) { stBufConf.eBufType = E_MI_SYS_BUFDATA_FRAME; gettimeofday(&stTv, NULL); stBufConf.u64TargetPts = stTv.tv_sec*1000000 + stTv.tv_usec; stBufConf.stFrameCfg.eFormat = E_MI_SYS_PIXEL_FRAME_YUV422_YUYV; stBufConf.stFrameCfg.eFrameScanMode = E_MI_SYS_FRAME_SCAN_MODE_PROGRESSIVE; stBufConf.stFrameCfg.u16Width = u16Width; stBufConf.stFrameCfg.u16Height = u16Height; if(MI_SUCCESS == MI_SYS_ChnInputPortGetBuf(&stVpeChnInput,&stBufConf,&stBufInfo,&hHandle,0)) { if(fread(stBufInfo.stFrameData.pVirAddr[0], u16Width*u16Height*2, 1, fp) <= 0) { fseek(fp, 0, SEEK_SET); } MI_SYS_ChnInputPortPutBuf(hHandle,&stBufInfo, FALSE); } }
-
Related topics
2.4.6. MI_SYS_ChnInputPortPutBuf¶
-
Function
Add the buf object corresponding to the channel input port to the pending queue.
-
Syntax
MI_S32 MI_SYS_ChnInputPortPutBuf (MI_SYS_BUF_HANDLE hHandle ,MI_SYS_BufInfo_t *pstPortBuf, MI_BOOL bDropBuf); -
Parameters
Parameter Name Description Input/Output hHandle Current buf's Idr Handle Input pstPortBuf Buf pointer to be submitted Input bDropBuf Direct waiver of modifications to buf does not submit Input -
Return
-
0 Successful.
-
!0 Failed, please refer to the error code.
-
-
Dependency
-
Head file: mi_sys_datatype.h, mi_sys.h
-
Library files: libmi_sys.a / libmi_sys.so
-
-
Sample
Reference MI_SYS_ChnInputPortGetBuf Call Sample.
-
Related topics
2.4.7. MI_SYS_ChnOutputPortGetBuf¶
-
Function
The buf object corresponding to the allocation channel input port.
-
Syntax
MI_S32 MI_SYS_ChnOutputPortGetBuf (MI_SYS_ChnPort_t *pstChnPort, MI_SYS_BufInfo_t MI_SYS_BufInfo_t *pstBufInfo , MI_SYS_BUF_HANDLE *phHandle); -
Parameters
Parameter Name Description Input/Output pstChnPort A pointer to the input port of the module channel Input pstBufInfo Return buf pointer Output phHandle Get the Idr handle of outputPort Buf Output -
Return
-
0 Successful.
-
!0 Failed, please refer to the error code.
-
-
Dependency
-
Head file: mi_sys_datatype.h, mi_sys.h
-
Library files: libmi_sys.a / libmi_sys.so
-
-
Sample
MI_SYS_ChnOutputPortGetBuf Sample
MI_SYS_ChnPort_t stChnPort; MI_SYS_BufInfo_t stBufInfo; MI_SYS_BUF_HANDLE stBufHandle; MI_S32 s32Ret = MI_SUCCESS; MI_S32 s32Fd = 0; fd_set read_fds; struct timeval TimeoutVal; char szFileName[128]; int fd = 0; MI_U32 u32GetFramesCount = 0; MI_BOOL _bWriteFile = TRUE; stChnPort.eModId = E_MI_MODULE_ID_DIVP; stChnPort.u32DevId = 0; stChnPort.u32ChnId = DIVP_CHN_FOR_VDF; stChnPort.u32PortId = 0; s32Ret = MI_SYS_GetFd(&stChnPort, &s32Fd); if(MI_SUCCESS != s32Ret) { ST_ERR("MI_SYS_GetFd 0, error, %X\n", s32Ret); return NULL; } s32Ret = MI_SYS_SetChnOutputPortDepth(&stChnPort, 2, 3); if (MI_SUCCESS != s32Ret) { ST_ERR("MI_SYS_SetChnOutputPortDepth err:%x, chn:%d,port:%d\n", s32Ret, stChnPort.u32ChnId, stChnPort.u32PortId); return NULL; } sprintf(szFileName, "divp%d.es", stChnPort.u32ChnId); printf("start to record %s\n", szFileName); fd = open(szFileName, O_RDWR | O_ CREAT | O_TRUNC, S_IRUSR | S_IWUSR | S_IRGRP | S_IROTH); if (fd < 0) { ST_ERR("create %s fail\n", szFileName); } while (1) { FD_ZERO(&read_fds); FD_SET(s32Fd, &read_fds); TimeoutVal.tv_sec = 1; TimeoutVal.tv_usec = 0; s32Ret = select(s32Fd + 1, &read_fds, NULL, NULL, &TimeoutVal); if(s32Ret < 0) { ST_ERR("select failed!\n"); // usleep(10 * 1000); continue; } else if(s32Ret == 0) { ST_ERR("get divp frame time out\n"); //usleep(10 * 1000); continue; } else { if(FD_ISSET(s32Fd, &read_fds)) { s32Ret = MI_SYS_ChnOutputPortGetBuf(&stChnPort, &stBufInfo, &stBufHandle); if(MI_SUCCESS != s32Ret) { //ST_ERR("MI_SYS_ChnOutputPortGetBuf err, %x\n", s32Ret); continue; } // save one Frame YUV data if (fd > 0) { if(_bWriteFile) { write(fd, stBufInfo.stFrameData.pVirAddr[0], stBufInfo.stFrameData.u16Height * stBufInfo.stFrameData.u32Stride[0] + stBufInfo.stFrameData.u16Height * stBufInfo.stFrameData.u32Stride[1] /2); } } ++u32GetFramesCount; printf("channelId[%u] u32GetFramesCount[%u]\n", stChnPort.u32ChnId, u32GetFramesCount); MI_SYS_ChnOutputPortPutBuf(stBufHandle); } } } if (fd > 0) { close(fd); fd = -1; } MI_SYS_SetChnOutputPortDepth(&stChnPort, 0, 3); printf("exit record\n"); return NULL;
-
Related topics
2.4.8. MI_SYS_ChnOutputPortPutBuf¶
-
Function
Release channel output port corresponding to buf object.
-
Syntax
MI_S32 MI_SYS_ChnOutputPortPutBuf (MI_SYS_BUF_HANDLE hBufHandle); -
Parameters
Parameter Name Description Input/Output hBufHandle Idr handle for buf to be submitted Input -
Return
-
0 Successful.
-
!0 Failed, please refer to the error code.
-
-
Dependency
-
Head file: mi_sys_datatype.h, mi_sys.h
-
Library files: libmi_sys.a / libmi_sys.so
-
-
Sample
Reference MI_SYS_ChnOutputPortGetBuf Sample.
-
Related topics
2.4.9. MI_SYS_ChnInputPortGetBufPa¶
-
Function
The buf object corresponding to the allocation channel input port, which only returns MIU physical address.
-
Syntax
MI_S32 MI_SYS_ChnInputPortGetBufPa (MI_SYS_ChnPort_t *pstChnPort,MI_SYS_BufConf_t *pstBufConf, MI_SYS_BufInfo_t *pstBufInfo, MI_SYS_BUF_HANDLE *phHandle , MI_S32 s32TimeOutMs); -
Parameters
Parameter Name Description Input/Output pstChnPort A pointer to the input port of the module channel Input pstBufConf Configuration information of the memory to be allocated Input pstPortBuf Return buf pointer Output phHandle Get the Idr handle of intput Port Buf Output s32TimeOutMs Time in milliseconds before timeout Output -
Return
-
0 Successful.
-
!0 Failed, please refer to the error code.
-
-
Dependency
-
Head file: mi_sys_datatype.h, mi_sys.h
-
Library files: libmi_sys.a / libmi_sys.so
-
-
Sample
MI_SYS_ChnInputPortGetBufPa Call Sample
MI_SYS_ChnPort_t stVpeChnInput; MI_SYS_BUF_HANDLE hHandle = 0; MI_SYS_BufConf_t stBufConf; MI_SYS_BufInfo_t stBufInfo; struct timeval stTv; MI_U16 u16Width = 1920, u16Height = 1080; FILE *fp = NULL; void *pVirAddr = NULL; memset(&stVpeChnInput, 0x0, sizeof(MI_SYS_ChnPort_t)); memset(&stBufConf, 0x0, sizeof(MI_SYS_BufConf_t)); memset(&stBufInfo, 0x0, sizeof(MI_SYS_BufInfo_t)); stVpeChnInput.eModId = E_MI_MODULE_ID_VPE; stVpeChnInput.u32DevId = 0; stVpeChnInput.u32ChnId = 0; stVpeChnInput.u32PortId = 0; fp = fopen("/mnt/vpeport0_1920x1080_pixel0_737.raw", "rb"); if (fp == NULL) { printf("file %s open fail\n", "/mnt/vpeport0_1920x1080_pixel0_737.raw"); return 0; } while (1) { stBufConf.eBufType = E_MI_SYS_BUFDATA_FRAME; gettimeofday(&stTv, NULL); stBufConf.u64TargetPts = stTv.tv_sec * 1000000 + stTv.tv_usec; stBufConf.stFrameCfg.eFormat = E_MI_SYS_PIXEL_FRAME_YUV422_YUYV; stBufConf.stFrameCfg.eFrameScanMode = E_MI_SYS_FRAME_SCAN_MODE_PROGRESSIVE; stBufConf.stFrameCfg.u16Width = u16Width; stBufConf.stFrameCfg.u16Height = u16Height; if (MI_SUCCESS == MI_SYS_ChnInputPortGetBuf(&stVpeChnInput, &stBufConf, &stBufInfo, &hHandle, 0)) { pVirAddr = MI_SYS_Mmap(stBufInfo.stFrameData.phyAddr[0], stBufInfo.stFrameData.u32BufSize, &pVirAddr, TRUE); assert(pVirAddr); if (fread(pVirAddr, u16Width * u16Height * 2, 1, fp) <= 0) { fseek(fp, 0, SEEK_SET); } MI_SYS_Munmap(pVirAddr, stBufInfo.stFrameData.u32BufSize); MI_SYS_ChnInputPortPutBuf(hHandle, &stBufInfo, FALSE); } }
-
Related topics
2.4.10. MI_SYS_ChnInputPortPutBufPa¶
-
Function
Add the buf object corresponding to the channel input port to the pending queue, which needs to be used in pair with the function MI_SYS_ChnInputPortGetBufPa.
-
Syntax
MI_S32 MI_SYS_ChnInputPortPutBufPa (MI_SYS_BUF_HANDLE hHandle ,MI_SYS_BufInfo_t *pstPortBuf, MI_BOOL bDropBuf);
-
Parameters
Parameter Name Description Input/Output hHandle Current buf's Idr Handle Input pstPortBuf Buf pointer to be submitted Input bDropBuf Drop direct waiver of modifications to buf Input -
Return
-
0 Successful.
-
!0 Failed, please refer to the error code.
-
-
Dependency
-
Head file: mi_sys_datatype.h, mi_sys.h
-
Library files: libmi_sys.a / libmi_sys.so
-
-
Sample
Please refer to MI_SYS_ChnInputPortGetBufPa Call Sample.
-
Related topics
2.4.11. MI_SYS_ChnOutputPortGetBufPa¶
-
Function
The buf object corresponding to the allocation channel ouput port, which only returns MIU physical address.
-
Syntax
MI_S32 MI_SYS_ChnOutputPortGetBufPa ( *pstChnPort, MI_SYS_BufInfo_t *pstBufInfo , MI_SYS_BUF_HANDLE *phHandle);
-
Parameters
Parameter Name Description Input/Output pstChnPort A pointer to the input port of the module channel Input pstBufInfo Return buf pointer Output phHandle Get the Idr handle of outputPort Buf Output -
Return
-
0 Successful.
-
!0 Failed, please refer to the error code.
-
-
Dependency
-
Head file: mi_sys_datatype.h, mi_sys.h
-
Library files: libmi_sys.a / libmi_sys.so
-
-
Sample
MI_SYS_ChnOutputPortGetBufPa Sample
MI_SYS_ChnPort_t stChnPort; MI_SYS_BufInfo_t stBufInfo; MI_SYS_BUF_HANDLE stBufHandle; MI_S32 s32Ret = MI_SUCCESS; MI_S32 s32Fd = 0; fd_set read_fds; struct timeval TimeoutVal; char szFileName[128]; int fd = 0; MI_U32 u32GetFramesCount = 0; MI_BOOL _bWriteFile = TRUE; void *pVirAddr = NULL; stChnPort.eModId = E_MI_MODULE_ID_DIVP; stChnPort.u32DevId = 0; stChnPort.u32ChnId = DIVP_CHN_FOR_VDF; stChnPort.u32PortId = 0; s32Ret = MI_SYS_GetFd(&stChnPort, &s32Fd); if (MI_SUCCESS != s32Ret) { ST_ERR("MI_SYS_GetFd 0, error, %X\n", s32Ret); return NULL; } s32Ret = MI_SYS_SetChnOutputPortDepth(&stChnPort, 2, 3); if (MI_SUCCESS != s32Ret) { ST_ERR("MI_SYS_SetChnOutputPortDepth err:%x, chn:%d,port:%d\n", s32Ret, stChnPort.u32ChnId, stChnPort.u32PortId); return NULL; } sprintf(szFileName, "divp%d.es", stChnPort.u32ChnId); printf("start to record %s\n", szFileName); fd = open(szFileName, O_RDWR | O_CREAT | O_TRUNC, S_IRUSR | S_IWUSR | S_IRGRP | S_IROTH); if (fd < 0) { ST_ERR("create %s fail\n", szFileName); } while (1) { FD_ZERO(&read_fds); FD_SET(s32Fd, &read_fds); TimeoutVal.tv_sec = 1; TimeoutVal.tv_usec = 0; s32Ret = select(s32Fd + 1, &read_fds, NULL, NULL, &TimeoutVal); if (s32Ret < 0) { ST_ERR("select failed!\n"); // usleep(10 * 1000); continue; } else if (s32Ret == 0) { ST_ERR("get divp frame time out\n"); //usleep(10 * 1000); continue; } else { if (FD_ISSET(s32Fd, &read_fds)) { s32Ret = MI_SYS_ChnOutputPortGetBuf(&stChnPort, &stBufInfo, &stBufHandle); if (MI_SUCCESS != s32Ret) { //ST_ERR("MI_SYS_ChnOutputPortGetBuf err, %x\n", s32Ret); continue; } pVirAddr = MI_SYS_Mmap(stBufInfo.stFrameData.phyAddr[0], stBufInfo.stFrameData.u32BufSize, &pVirAddr, TRUE); assert(pVirAddr); // save one Frame YUV data if (fd > 0) { if (_bWriteFile) { write(fd, pVirAddr, stBufInfo.stFrameData.u16Height * stBufInfo.stFrameData.u32Stride[0] + stBufInfo.stFrameData.u16Height * stBufInfo.stFrameData.u32Stride[1] / 2); } } ++u32GetFramesCount; printf("channelId[%u] u32GetFramesCount[%u]\n", stChnPort.u32ChnId, u32GetFramesCount); MI_SYS_Munmap(pVirAddr, stBufInfo.stFrameData.u32BufSize); MI_SYS_ChnOutputPortPutBuf(stBufHandle); } } } if (fd > 0) { close(fd); fd = -1; } MI_SYS_SetChnOutputPortDepth(&stChnPort, 0, 3); printf("exit record\n"); return NULL;
-
Related topics
2.4.12. MI_SYS_ChnOutputPortPutBufPa¶
-
Function
Release channel output port corresponding to the buf object, which needs to be used in pair with the function MI_SYS_ChnOutputPortGetBufPa.
-
Syntax
MI_S32 MI_SYS_ChnOutputPortPutBufPa (MI_SYS_BUF_HANDLE hBufHandle); -
Parameters
Parameter Name Description Input/Output hBufHandle Idr handle for buf to be submitted Input -
Return
-
0 Successful.
-
!0 Failed, please refer to the error code.
-
-
Dependency
-
Head file: mi_sys_datatype.h, mi_sys.h
-
Library files: libmi_sys.a / libmi_sys.so
-
-
Sample
Please refer to MI_SYS_ChnOutputPortGetBufPa Sample.
-
Related topics
2.4.13. MI_SYS_SetChnOutputPortDepth¶
-
Function
Set the number of system bufs corresponding to the channel output port and the number of bufs that users can get.
-
Syntax
MI_S32 MI_SYS_SetChnOutputPortDepth(MI_SYS_ChnPort_t *pstChnPort, MI_U32 u32UserFrameDepth, MI_U32 u32BufQueueDepth);
-
Parameters
Parameter Name Description Input/Output pstChnPort A pointer to the output port of the module channel Input u32UserFrameDepth Set the maximum number of buf that the output user can get Input u32BufQueueDepth Set the maximum number of buf for this output system Input -
Return
-
0 Successful.
-
!0 Failed, please refer to the error code.
-
-
Dependency
-
Head file: mi_sys_datatype.h, mi_sys.h
-
Library files: libmi_sys.a / libmi_sys.so
-
-
Note
If you have finished using OutputPortBuf (no more call MI_SYS_ChnOutputPortGetBuf / MI_SYS_ChnOutputPortPutBuf), you can set u32UserFrameTou to 0 so that the speed of the underlying call is not affected.
-
Sample
Reference MI_SYS_ChnOutputPortGetBuf Sample.
2.4.14. MI_SYS_ChnPortInjectBuf¶
-
Function
Plug the acquired output Port buf into the specified input Port Buf Queue.
-
Syntax
MI_S32 MI_SYS_ChnPortInjectBuf(MI_SYS_BUF_HANDLE hHandle ,MI_SYS_ChnPort_t *pstChnInputPort); -
Parameters
| Parameter Name | Description | Input/Output |
|---|---|---|
| pstChnPort | A pointer to the input port of the module channel | Input |
| hHandle | Get the Idr handle of outputPort Buf | Output |
-
Return
-
0 Successful.
-
!0 Failed, please refer to the error code.
-
-
Dependency
-
Head file: mi_sys_datatype.h, mi_sys.h
-
Library files: libmi_sys.a / libmi_sys.so
-
-
Sample
Reference MI_SYS_ChnOutputPortGetBuf Sample.
-
Related topics
2.4.15. MI_SYS_GetFd¶
-
Function
Get the file Description Number for the current output Port wait ing-up event.
-
Syntax
MI_S32 MI_SYS_GetFd(MI_SYS_ChnPort_t *pstChnPort, MI_S32 *ps32Fd); -
Parameters
Parameter Name Description Input/Output pstChnPort Port information structure pointer Input ps32Fd File Description for waiting for event Output -
Return
-
0 Successful.
-
!0 Failed, please refer to the error code.
-
-
Dependency
-
Head file: mi_sys_datatype.h, mi_sys.h
-
Library files: libmi_sys.a / libmi_sys.so
-
-
Note
-
Need to be used in pairs with MI_SYS_CloseFd.
-
It is recommended to use the fd s select method to extract the data, so that the MI_SYS only wake up the thread when the corresponding port port port has data, the efficiency is more efficient than the use of while and sleep loop to take data.
-
-
Sample
Reference MI_SYS_ChnOutputPortGetBuf Sample.
-
Related topics
2.4.16. MI_SYS_CloseFd¶
-
Function
File Description Number to close the current channel
-
Syntax
MI_S32 MI_SYS_CloseFd(MI_S32 s32ChnPortFd); -
Parameters
Parameter Name Description Input/Output s32ChnPortFd File Description Members for waiting for event Input -
Return
-
0 Successful.
-
!0 Failed, please refer to the error code.
-
-
Dependency
-
Head file: mi_sys_datatype.h, mi_sys.h
-
Library files: libmi_sys.a / libmi_sys.so
-
-
Sample
Reference MI_SYS_ChnOutputPortGetBuf Sample.
-
Related topics
2.4.17. MI_SYS_DupBuf¶
-
Function
Duplicate buf object.
-
Syntax
MI_S32 MI_SYS_DupBuf (MI_SYS_BUF_HANDLE srcBufHandle , MI_SYS_BUF_HANDLE *pDupTargetBufHandle); -
Parameters
Parameter Name Description Input/Output srcBufHandle Source buf object Input pDupTargetBufHandle Return buf object pointer Output -
Return
-
0 Successful.
-
!0 Failed, please refer to the error code.
-
-
Dependency
-
Head file: mi_sys_datatype.h, mi_sys.h
-
Library files: libmi_sys.a / libmi_sys.so
-
-
Sample
MI_SYS_ChnOutputPortGetBuf Sample
int test0() { MI_SYS_ChnPort_t stChnPort; MI_SYS_BufInfo_t stBufInfo; MI_SYS_BUF_HANDLE bufHandle ,DupTargetBufHandle; MI_S32 s32Ret; stChnPort.eModId = E_MI_MODULE_ID_VPE; stChnPort.u32DevId = 0; stChnPort.u32ChnId = 0; stChnPort.u32PortId = 0; s32Ret = MI_SYS_ChnOutputPortGetBuf (&stChnPort,&stBufInfo,&bufHandle); if(s32Ret != MI_SUCCESS) return 0; s32Ret = MI_SYS_DupBuf(bufHandle, &DupTargetBufHandle); if(s32Ret != MI_SUCCESS) { MI_SYS_ChnOutputPortPutBuf(bufHandle); return 0; } stChnPort.eModId = E_MI_MODULE_ID_DIVP; stChnPort.u32DevId = 0; stChnPort.u32ChnId = 0; stChnPort.u32PortId = 0; MI_SYS_ChnPortInjectBuf(DupTargetBufHandle , &stChnPort); *************************** continue to use the stBufInfo *************************** MI_SYS_ChnOutputPortPutBuf(bufHandle); return 1; } int test1() { MI_SYS_ChnPort_t stChnPort; MI_SYS_BufInfo_t stBufInfo; MI_SYS_BufConf_t stBufConf; MI_SYS_BUF_HANDLE bufHandle ,DupTargetBufHandle; MI_S32 s32Ret; stChnPort.eModId = E_MI_MODULE_ID_DIVP; stChnPort.u32DevId = 0; stChnPort.u32ChnId = 0; stChnPort.u32PortId = 0; memset(&stBufConf , 0 , sizeof(stBufConf)); stBufConf.eBufType = E_MI_SYS_BUFDATA_FRAME; stBufConf.stFrameCfg.eFormat = E_MI_SYS_PIXEL_FRAME_YUV_SEMIPLANAR_422; stBufConf.stFrameCfg.u16Height = 1080; stBufConf.stFrameCfg.u16Width = 1920; stBufConf.stFrameCfg.eFrameScanMode = E_MI_SYS_FRAME_SCAN_MODE_PROGRESSIVE; s32Ret = MI_SYS_ChnInputPortGetBuf (&stChnPort,&stBufConf,&stBufInfo,&bufHandle ,0); if(s32Ret != MI_SUCCESS) return 0; *************************** Fill stBufInfo *************************** s32Ret = MI_SYS_DupBuf(bufHandle, &DupTargetBufHandle); if(s32Ret != MI_SUCCESS) { MI_SYS_ChnInputPortPutBuf(bufHandle); return 0; } MI_SYS_ChnInputPortPutBuf(DupTargetBufHandle , &stBufInfo , FALSE); *************************** continue to use the stBufInfo *************************** MI_SYS_ChnInputPortPutBuf(bufHandle); return 1; }
-
Related topics
2.5. Memory Management Class API¶
2.5.1. MI_SYS_SetChnMMAConf¶
-
Function
Set the MMA pool name of the module device channel Output default allocation memory.
-
Syntax
MI_S32 MI_SYS_SetChnMMAConf (MI_ModuleId_e eModId, MI_U32 u32DevId, MI_U32 u32ChnId, MI_U8 *pu8MMAHeapName); -
Parameters
Parameter Name Description Input/Output eModId Module ID to be configured Input u32DevId Device ID to be configured Input u32ChnId Channel number to be configured Input pu8MMAHeapName MMA heap name Input -
Return
-
0 Successful.
-
!0 Failed, please refer to the error code.
-
-
Dependency
-
Head file: mi_sys_datatype.h, mi_sys.h
-
Library files: libmi_sys.a / libmi_sys.so
-
-
Sample
MI_ModuleId_e eVifModeId = E_MI_MODULE_ID_VIF; MI_VIF_DEV vifDev = 0; MI_VIF_CHN vifChn = 0; MI_SYS_SetChnMMAConf(eVifModeId, vifDev, vifChn, "mma_heap_name0");
2.5.2. MI_SYS_GetChnMMAConf¶
-
Function
Get the MMA pool name of the module device channel Output port's default allocated memory.
-
Syntax
MI_S32 MI_SYS_GetChnMMAConf (MI_ModuleId_e eModId, MI_U32 u32DevId, MI_U32 u32ChnId, void *data, MI_U32 u32Length); -
Parameters
Parameter Name Description Input/Output eModId Module ID to be configured Input u32DevId Device ID to be configured Input u32ChnId Channel number to be configured Input pu8MMAHeapName MMA heap name Input -
Return
-
0 Successful.
-
!0 Failed, please refer to the error code.
-
-
Dependency
-
Head file: mi_sys_datatype.h, mi_sys.h
-
Library files: libmi_sys.a / libmi_sys.so
-
-
Related topics
2.5.3. MI_SYS_ConfDevPubPools¶
-
Function
Configure and initialize the module's public buffer pool.
-
Syntax
MI_S32 MI_SYS_ConfDevPubPools(MI_ModuleId_e eModule, MI_U32 u32DevId, MI_VB_PoolListConf_t stPoolListConf); -
Parameters
Parameter Name Description Input/Output eModule Target module ID Input u32DevId Dev ID Input stPoolListConf Module public buffer pool queue configuration Input -
Return
-
0 Successful.
-
!0 Failed, please refer to the error code.
-
-
Dependency
-
Head file: mi_sys_datatype.h, mi_sys.h
-
Library files: libmi_sys.a / libmi_sys.so
-
-
Note
Version 2.0 and above is not on by default, recommended MI_SYS_ConfigPrivateMMAPool.
2.5.4. MI_SYS_ReleaseDevPubPools¶
-
Function
Free the global public buffer pool.
-
Syntax
MI_S32 MI_SYS_ReleaseDevPubPools(MI_ModuleId_e eModule, MI_U32 u32DevId); -
Parameters
Parameter Name Description Input/Output eModule Target module ID Input u32DevId Dev ID Input -
Return
-
0 Successful.
-
!0 Failed, please refer to the error code.
-
-
Dependency
-
Head file: mi_sys_datatype.h, mi_sys.h
-
Library files: libmi_sys.a / libmi_sys.so
-
-
Sample
Version 2.0 and above is not on by default, recommended MI_SYS_ConfigPrivateMMAPool.
2.5.5. MI_SYS_ConfGloPubPools¶
-
Function
Configure and initialize the system's global public buffer pool.
-
Syntax
MI_S32 MI_SYS_ConfGloPubPools(MI_VB_PoolListConf_t stPoolListConf); -
Parameters
Parameter Name Description Input/Output stPoolListConf Module public buffer pool queue configuration Input -
Return
-
0 Successful.
-
!0 Failed, please refer to the error code.
-
-
Dependency
-
Head file: mi_sys_datatype.h, mi_sys.h
-
Library files: libmi_sys.a / libmi_sys.so
-
-
Note
Version 2.0 and above is not on by default, recommended MI_SYS_ConfigPrivateMMAPool.
2.5.6. MI_SYS_ReleaseGloPubPools¶
-
Function
Free the global public buffer pool.
-
Syntax
MI_S32 MI_VB_ ReleaseGloPubPools (void); -
Return
-
0 Successful.
-
!0 Failed, please refer to the error code.
-
-
Dependency
-
Head file: mi_sys_datatype.h, mi_sys.h
-
Library files: libmi_sys.a / libmi_sys.so
-
-
Sample
Version 2.0 and above is not on by default, recommended MI_SYS_ConfigPrivateMMAPool.
2.5.7. MI_SYS_MMA_Alloc¶
-
Function
Request the allocation of memory directly to the MMA Memory Manager.
-
Syntax
MI_S32 MI_SYS_MMA_Alloc(MI_U8 *pstMMAHeapName, MI_U32 u32BlkSize, MI_PHY *phyAddr); -
Parameters
Parameter Name Description Input/Output pstMMAHeapName Target MMA heapname Input u32BlkSize The size of the block byteto sedated Input phyAddr Physical address of memory block returned Output -
Return
-
0 Successful.
-
!0 Failed, please refer to the error code.
-
-
Dependency
-
Head file: mi_sys_datatype.h, mi_sys.h
-
Library files: libmi_sys.a / libmi_sys.so
-
-
Sample
MI_SYS_MMA_Alloc Sample
MI_PHY phySrcBufAddr = 0; void *pVirSrcBufAddr = NULL; MI_U32 srcBuffSize = 1920 * 1980 * 3 / 2; srcBuffSize = ALIGN_UP(srcBuffSize, 4096); ret = MI_SYS_MMA_Alloc(NULL, srcBuffSize, &phySrcBufAddr); if(ret != MI_SUCCESS) { printf("alloc src buff failed\n"); return -1; } ret = MI_SYS_Mmap(phySrcBufAddr, srcBuffSize, &pVirSrcBufAddr, TRUE); if(ret != MI_SUCCESS) { MI_SYS_MMA_Free(phySrcBufAddr); printf("mmap src buff failed\n"); return -1; } memset(pVirSrcBufAddr, 0, srcBuffSize); MI_SYS_FlushInvCache(pVirSrcBufAddr,srcBuffSize); MI_SYS_Munmap(pVirSrcBufAddr, srcBuffSize); MI_SYS_MMA_Free(phySrcBufAddr);
-
Related topics
2.5.8. MI_SYS_MMA_Free¶
-
Function
Memory allocated before being released directly to mmA Memory Manager.
-
Syntax
MI_S32 MI_SYS_MMA_Free(MI_U64 phyAddr); -
Parameters
Parameter Name Description Input/Output phyAddr Physical address of memory to be freed Input -
Return
-
0 Successful.
-
!0 Failed, please refer to the error code.
-
-
Dependency
-
Head file: mi_sys_datatype.h, mi_sys.h
-
Library files: libmi_sys.a / libmi_sys.so
-
-
Sample
Reference MI_SYS_MMA_Alloc Sample.
-
Related topics
2.5.9. MI_SYS_Mmap¶
-
Function
Mapping any physical memory to the CPU virtual address space for the current user-state process.
-
Syntax
MI_S32 MI_SYS_Mmap(MI_U64 u64PhyAddr, MI_U32 u32Size , void **ppVirtualAddress , MI_BOOL bCache);
-
Parameters
Parameter Name Description Input/Output u64PhyAddr Physical address to be mapped Input u32Size The length of the physical address to be mapped Input ppVirtualAddress Pointer to store the CPU virtual address pointer Output bCache Whether map into cache or un-cache Input -
Return
-
0 Successful.
-
!0 Failed, please refer to the error code.
-
-
Dependency
-
Head file: mi_sys_datatype.h, mi_sys.h
-
Library files: libmi_sys.a / libmi_sys.so
-
-
Note
-
The physical address must be 4KByte aligned.
-
The physical address is the SStar memory controller address, the non-CPU bridge address.
-
The physical address length must be 4KByte aligned.
-
Physical memory must fall completely outside the memory range managed by MMA or from the memory managed by linux kenrel
-
-
Sample
Reference MI_SYS_MMA_Alloc Sample.
-
Related topics
2.5.10. MI_SYS_FlushInvCache¶
-
Function
Flush cache.
-
Syntax
MI_S32 MI_SYS_FlushCache(MI_VOID *pVirtualAddress, MI_U32 u32Size); -
Parameters
Parameter Name Description Input/Output pVirtualAddress Previously MI_SYS_Mmap returned CPU virtual address Input u32Size The length of the cache to be flush Input -
Return
-
0 Successful.
-
!0 Failed, please refer to the error code.
-
-
Dependency
-
Head file: mi_sys_datatype.h, mi_sys.h
-
Library files: libmi_sys.a / libmi_sys.so
-
-
Note
-
The physical address to flush cache must be 4KByte aligned.
-
The mapping length to flush cache must be 4KByte aligned.
-
The map memory range to flush cache must be previously obtained through the MI_SYS_Mmap API.
-
The mapping memory for flush cache should be MI_SYS_Mmap in the way of cache, nocache way without flush cache.
-
-
Sample
Reference MI_SYS_MMA_Alloc Sample.
-
Related topics
2.5.11. MI_SYS_Munmap¶
-
Function
Cancel the mapping of physical memory to the virtual address..
-
Syntax
MI_S32 MI_SYS_Munmap(MI_VOID *pVirtualAddress, MI_U32 u32Size); -
Parameters
Parameter Name Description Input/Output pVirtualAddress Previously MI_SYS_Mmap returned CPU virtual address Input u32Size The length of the map to be unmapped Input -
Return
-
0 Successful.
-
!0 Failed, please refer to the error code.
-
-
Dependency
-
Head file: mi_sys_datatype.h, mi_sys.h
-
Library files: libmi_sys.a / libmi_sys.so
-
-
Note
-
The virtual address to be unmapped must be 4KByte aligned.
-
The mapping length to be unmapped must be 4KByte aligned
-
The range of mapped memory to be canceled must be previously obtained through the MI_SYS_Mmap API.
-
-
Sample
Reference MI_SYS_MMA_Alloc Sample.
-
Related topics
2.5.12. MI_SYS_MemsetPa¶
-
Function
Fill the entire physical memory with the DMA hardware module.
-
Syntax
MI_S32 MI_SYS_MemsetPa(MI_PHY phyPa, MI_U32 u32Val, MI_U32 u32Lenth); -
Parameters
Parameter Name Description Input/Output phyPa The physical address of the padding Input u32Val Fill value Input u32Lenth Fill size, in byte Input -
Return
-
0 Successful.
-
!0 Failed, please refer to the error code.
-
-
Dependency
-
Head file: mi_sys_datatype.h, mi_sys.h
-
Library files: libmi_sys.a / libmi_sys.so
-
-
Sample
MI_SYS_MemsetPa Sample
MI_PHY phySrcBufAddr = 0; MI_PHY phyDstBufAddr = 0; void *pVirSrcBufAddr = NULL; void *pVirDstBufAddr = NULL; MI_U32 buffSize = 1920 * 1980 * 3 / 2; buffSize = ALIGN_UP(buffSize, 4096); ret = MI_SYS_MMA_Alloc(NULL, buffSize, &phySrcBufAddr); if(ret != MI_SUCCESS) { printf("alloc src buff failed\n"); return -1; } ret = MI_SYS_MMA_Alloc(NULL, buffSize, &phyDstBufAddr); if(ret != MI_SUCCESS) { MI_SYS_MMA_Free(phySrcBufAddr); printf("alloc dts buff failed\n"); return -1; } MI_SYS_MemsetPa(phySrcBufAddr, 0xff, buffSize); MI_SYS_MemsetPa(phyDstBufAddr, 0x00, buffSize); MI_SYS_MemcpyPa(phyDstBufAddr, phySrcBufAddr, buffSize); MI_SYS_MMA_Free(phySrcBufAddr); MI_SYS_MMA_Free(phyDstBufAddr);
-
Related topics
2.5.13. MI_SYS_MemcpyPa¶
-
Function
Copy the source memory data to the target memory via the DMA hardware module.
-
Syntax
MI_S32 MI_SYS_MemcpyPa(MI_PHY phyDst, MI_PHY phySrc, MI_U32 u32Lenth); -
Parameters
Parameter Name Description Input/Output phyDst Destination physical address Input phySrc Source physical address Input u32Lenth Copy size, in byte Input -
Return
-
0 Successful.
-
!0 Failed, please refer to the error code.
-
-
Dependency
-
Head file: mi_sys_datatype.h, mi_sys.h
-
Library files: libmi_sys.a / libmi_sys.so
-
-
Sample
Reference MI_SYS_MemsetPa Sample.
-
Related topics
2.5.14. MI_SYS_BufFillPa¶
-
Function
Fill some of the physical memory with the DMA hardware module.
-
Syntax
MI_S32 MI_SYS_BufFillPa(MI_SYS_FrameData_t *pstBuf, MI_U32 u32Val, MI_SYS_WindowRect_t *pstRect); -
Parameters
Parameter Name Description Input/Output pstBuf The structure of the filled frame data Description Input u32Val Fill value Input pstRect The extent of the data populated Input -
Return
-
0 Successful.
-
!0 Failed, please refer to the error code.
-
-
Dependency
-
Head file: mi_sys_datatype.h, mi_sys.h
-
Library files: libmi_sys.a / libmi_sys.so
-
-
Note
-
The pstRect data range is based on the first address of the pstBuf Description as the first address (0,0), and the width and height are partially filled with the ePixel Format in pstBuf to calculate the size of the memory data moved by each pixel.
-
PstBuf in u16Width, u16 Height, phyAddr, u32Stride, ePixelFormat is required, the rest of the value is meaningless.
-
-
Sample
MI_S32 ret = 0; MI_SYS_WindowRect_t rect; MI_SYS_FrameData_t stSysFrame; memcpy(&stSysFrame, &buf->stFrameData, sizeof(MI_SYS_FrameData_t)); if(pRect) { rect.u16X = pRect->left; rect.u16Y = pRect->top; rect.u16Height = pRect->bottom-pRect->top; rect.u16Width = pRect->right-pRect->left; } else { rect.u16X = 0; rect.u16Y = 0; rect.u16Height = stSysFrame.u16Height; rect.u16Width = stSysFrame.u16Width; } DBG_INFO("rect %d %d %d %d \n", rect.u16X, rect.u16Y , rect.u16Width, rect.u16Height); ret = MI_SYS_BufBlitPa(&stSysFrame, u32ColorVal, &rect); return ret;
-
Related topics
2.5.15. MI_SYS_BufBlitPa¶
-
Function
Copy parts of the source memory data to parts of the target memory through the DMA hardware module.
-
Syntax
MI_S32 MI_SYS_BufBlitPa(MI_SYS_FrameData_t *pstDstBuf, MI_SYS_WindowRect_t *pstDstRect, MI_SYS_FrameData_t *pstSrcBuf, MI_SYS_WindowRect_t *pstSrcRect);
-
Parameters
Parameter Name Description Input/Output pstDstBuf Target memory physical first address Input pstDstRect The area of the target memory copy Input pstSrcBuf Source memory physical first address Input pstSrcRect Area of the source memory copy Input -
Return
-
0 Successful.
-
!0 Failed, please refer to the error code.
-
-
Dependency
-
Head file: mi_sys_datatype.h, mi_sys.h
-
Library files: libmi_sys.a / libmi_sys.so
-
-
Note
-
The pstDStRect/pstSrcRect data range is based on the first address of pstDstBuf/pstSrcBuf Buf Description as the first address (0,0), and the width and height are partially populated with ePixelFormat to calculate the size of memory data moved by each pixel.
-
PstDdbuf/pstSrcBuf in u16Width, u16 Height, phyAddr, u32Stride, e32Cre, ePixelFormat is required, the rest of the value is meaningless.
-
The area portion of the source memory or target memory exceeds its original range and will only copy the data on which it is not exceeded.
-
-
Sample
MI_S32 ret = MI_SUCCESS; vdisp_copyinfo_plane_t *plane; MI_SYS_FrameData_t stSrcFrame, stDstFrame; MI_SYS_WindowRect_t stSrcRect, stDstRect; plane = ©info->plane[0]; stSrcFrame.ePixelFormat = E_MI_SYS_PIXEL_FRAME_I8; stSrcFrame.phyAddr[0] = plane->src_paddr; stSrcFrame.u16Width = plane->width; stSrcFrame.u16Height = plane->height; stSrcFrame.u32Stride[0] = plane->src_stride; stDstFrame.ePixelFormat = E_MI_SYS_PIXEL_FRAME_I8; stDstFrame.phyAddr[0] = plane->dst_paddr; stDstFrame.u16Width = plane->width; stDstFrame.u16Height = plane->height; stDstFrame.u32Stride[0] = plane->dst_stride; stSrcRect.u16X = 0; stSrcRect.u16Y = 0; stSrcRect.u16Height = stSrcFrame.u16Height; stSrcRect.u16Width = stSrcFrame.u16Width; stDstRect.u16X = 0; stDstRect.u16Y = 0; stDstRect.u16Height = stDstFrame.u16Height; stDstRect.u16Width = stDstFrame.u16Width; ret = MI_SYS_BufBlitPa(&stDstFrame, &stDstRect, &stSrcFrame, &stSrcRect); return ret;
-
Related topics
2.5.16. MI_SYS_ConfigPrivateMMAPool¶
-
Function
Configure private MMA Heap.
-
Syntax
MI_S32 MI_SYS_ConfigPrivateMMAPool(MI_SYS_GlobalPrivPoolConfig_t *pstGlobalPrivPoolConf);
-
Parameters
Parameter Name Description Input/Output pstGlobalPrivPoolConf Configure private MMA Heap for modules Input -
Return
-
0 Successful.
-
!0 Failed, please refer to the error code.
-
-
Dependency
-
Head file: mi_sys_datatype.h, mi_sys.h
-
Library files: libmi_sys.a / libmi_sys.so
-
-
Note
-
Device private MMA Heap and channel private MMA Heap cannot coexist.
-
It is recommended to create a private MMA heap for each module after MI_SYS_Init.
-
When pstGlobalPrivPoolConf-bCreate is TRUE, create a private POOL, destroy the private POOL when it is FALSE
-
Various eConfigType use scenarios are as follows:
eConfigType Applicable Scenario E_MI_SYS_VPE_TO_VENC_PRIVATE_RING_POOL Set up a private ring heap pool for vpe and venc ports bound to E_MI_SYS_BIND_TYPE_HW_RIN mode E_MI_SYS_PRE_CHN_PRIVATE_POOL Set up a private heap pool for the module channel E_MI_SYS_PRE_DEV_PRIVATE_POOL Set up a private heap pool for module devices E_MI_SYS_PER_CHN_PORT_OUTPUT_POOL Set heap pool for module output port, after which the ouput buf priority of the port port is assigned
-
-
Sample
Suppose the scene is: Two streams under IPC, one main Stream H265 maximum resolution 1920 x 1080, and all the way Sub Stream H264 max resolution is 720*576.
VENC Creat MMA Heap:
//Main Sream: //Create private MMA heap with size of 38745760 for Channel 1 MI_SYS_GlobalPrivPoolConfig_t stConfig; memset(&stConfig , 0 ,sizeof(stConfig)); stConfig.eConfigType = E_MI_SYS_PER_CHN_PRIVATE_POOL; stConfig.bCreate = TRUE; stConfig.uConfig.stPreChnPrivPoolConfig.eModule = E_MI_MODULE_ID_VENC; stConfig.uConfig.stPreChnPrivPoolConfig.u32Devid = 0; stConfig.uConfig.stPreChnPrivPoolConfig.u32Channel= 1; stConfig.uConfig.stPreChnPrivPoolConfig.u32PrivateHeapSize = 38745760; MI_SYS_ConfigDevChnPrivateMMAHeap(&stConfig); //Sub Stream: // Create private MMA heap with size of 805152 for Channel 2 stConfig.eConfigType = E_MI_SYS_PER_CHN_PRIVATE_POOL; stConfig.bCreate = TRUE; stConfig.uConfig.stPreChnPrivPoolConfig.eModule = E_MI_MODULE_ID_VENC; stConfig.uConfig.stPreChnPrivPoolConfig.u32Devid = 0; stConfig.uConfig.stPreChnPrivPoolConfig.u32Channel= 2; stConfig.uConfig.stPreChnPrivPoolConfig.u32PrivateHeapSize = 805152; MI_SYS_ConfigDevChnPrivateMMAHeap(&stConfig);
VENC Destroyed MMA Heap:
//Main Sream: //Destroyed private MMA heap of Channel 1 stConfig.eConfigType = E_MI_SYS_PER_CHN_PRIVATE_POOL; stConfig.bCreate = FALSE; stConfig.uConfig.stPreChnPrivPoolConfig.eModule = E_MI_MODULE_ID_VENC; stConfig.uConfig.stPreChnPrivPoolConfig.u32Devid = 0; stConfig.uConfig.stPreChnPrivPoolConfig.u32Channel= 1; MI_SYS_ConfigDevChnPrivateMMAHeap(&stConfig); //Sub Stream: //Destroyed private MMA heap of Channel 2 stConfig.eConfigType = E_MI_SYS_PER_CHN_PRIVATE_POOL; stConfig.bCreate = FALSE; stConfig.uConfig.stPreChnPrivPoolConfig.eModule = E_MI_MODULE_ID_VENC; stConfig.uConfig.stPreChnPrivPoolConfig.u32Devid = 0; stConfig.uConfig.stPreChnPrivPoolConfig.u32Channel= 2; MI_SYS_ConfigDevChnPrivateMMAHeap(&stConfig);
VPE Creat MMA Heap:
//Creat private MMA Heap with size of 0x4f9200 for Device 0 stConfig.eConfigType = E_MI_SYS_PER_DEV_PRIVATE_POOL; stConfig.bCreate = TRUE; stConfig.uConfig.stPreDevPrivPoolConfig.eModule = E_MI_MODULE_ID_VPE; stConfig.uConfig.stPreDevPrivPoolConfig.u32Devid = 0; MI_SYS_ConfigDevChnPrivateMMAHeap(&stConfig);
VPE Destroyed MMA Heap:
//Destroyed private MMA Heap of Device 0 stConfig.eConfigType = E_MI_SYS_PER_DEV_PRIVATE_POOL; stConfig.bCreate = FALSE; stConfig.uConfig.stPreDevPrivPoolConfig.eModule = E_MI_MODULE_ID_VPE; stConfig.uConfig.stPreChnPrivPoolConfig.u32Devid = 0; MI_SYS_ConfigDevChnPrivateMMAHeap(&stConfig);
Creat VPE -> VENC ring MMA Heap:
stConfig.eConfigType = E_MI_SYS_VPE_TO_VENC_PRIVATE_RING_POOL; stConfig.bCreate = TRUE; stConfig.uConfig. stPreVpe2VencRingPrivPoolConfig.u32VencInputRingPoolStaticSize = 8*1024*1024; MI_SYS_ConfigDevChnPrivateMMAHeap(&stConfig);
Destroyed VPE -> VENC ring MMA Heap:
stConfig.eConfigType = E_MI_SYS_VPE_TO_VENC_PRIVATE_RING_POOL; stConfig.bCreate = FALSE; MI_SYS_ConfigDevChnPrivateMMAHeap(&stConfig); Different resolutions or turns on different Functionsize sizes are different, detailed parameters should be calculated according to the scene and specifications used.
-
Related topics
2.5.17. MI_SYS_PrivateDevChnHeapAlloc¶
-
Function
Request memory from module channel private MMA Pool.
-
Syntax
MI_S32 MI_SYS_PrivateDevChnHeapAlloc(MI_ModuleId_e eModule, MI_U32 u32Devid, MI_S32 s32ChnId, MI_U8 *pu8BufName, MI_U32 u32blkSize, MI_PHY *pphyAddr, MI_BOOL bTailAlloc);
-
Parameters
Parameter Name Description Input/Output eModule Module ID Input u32Devid The device ID of the module Input s32ChnId Channel ID of the module Input pu8BufName When applying for the name of private memory, pass null, use the "app-privAlloc" as the default name Input u32blkSize Request the size of private memory Input pphyAddr Physical address of allocated private memory Output bTailAlloc Whether to apply from the tail of the channel private pool Input -
Return
-
0 Successful.
-
!0 Failed, please refer to the error code.
-
-
Dependency
-
Head file: mi_sys_datatype.h, mi_sys.h
-
Library files: libmi_sys.a / libmi_sys.so
-
-
Note
When using this interface, make sure that you have applied E_MI_SYS_PRE_CHN_PRIVATE_POOL type of private memory pool using MI_SYS_ConfigPrivateMMAPool first.
-
Sample
MI_SYS_PrivateDevChnHeapAlloc Sample
MI_PHY *pphyAddr = NULL; MI_SYS_GlobalPrivPoolConfig_t stConfig; Memset(&stConfig , 0 ,sizeof(stConfig)); stConfig.eConfigType = E_MI_SYS_PER_CHN_PRIVATE_POOL; stConfig.bCreate = TRUE; stConfig.uConfig.stPreChnPrivPoolConfig. eModule = E_MI_MODULE_ID_VENC; stConfig.uConfig.stPreChnPrivPoolConfig. u32Devid = 0; stConfig.uConfig.stPreChnPrivPoolConfig. u32Channel= 1; stConfig.uConfig.stPreChnPrivPoolConfig. u32PrivateHeapSize = 38745760; MI_SYS_ConfigDevChnPrivateMMAHeap(&stConfig); ret = MI_SYS_PrivateDevChnHeapAlloc(E_MI_MODULE_ID_VENC, 0, 1, NULL, 4096, pphyAddr, FALSE); if(ret != MI_SUCCESS) { MI_SYS_ConfigDevChnPrivateMMAHeap(&stConfig); printf("alloc buff from chn private heap failed\n"); return -1; } //do something... MI_SYS_PrivateDevChnHeapFree(E_MI_MODULE_ID_VENC, 0, 1, *pphyAddr); MI_SYS_ConfigDevChnPrivateMMAHeap(&stConfig);
-
Related topics
2.5.18. MI_SYS_PrivateDevChnHeapFree¶
-
Function
Free memory from module channel private MMA Pool.
-
Syntax
MI_S32 MI_SYS_PrivateDevChnHeapFree(MI_ModuleId_e eModule, MI_U32 u32Devid, MI_S32 s32ChnId, MI_PHY phyAddr);
-
Parameters
Parameter Name Description Input/Output eModule Module ID Input u32Devid The device ID of the module Input s32ChnId Channel ID of the module Input phyAddr Physical address for memory that needs to be freed Input -
Return
-
0 Successful.
-
!0 Failed, please refer to the error code.
-
-
Dependency
-
Head file: mi_sys_datatype.h, mi_sys.h
-
Library files: libmi_sys.a / libmi_sys.so
-
-
Note
When using this interface, make sure that you have applied a private memory pool of E_MI_SYS_PRE_CHN_PRIVATE_POOL type using the MI_SYS_ConfigPrivateMMAPool first.
-
Sample
Reference MI_SYS_PrivateDevChnHeapAlloc Sample.
-
Related topics
2.5.19. MI_SYS_Va2Pa¶
-
Function
Turn CPU virtual address pointer to Physical address.
-
Syntax
MI_S32 MI_SYS_Va2Pa (void *pVirtualAddress, MI_PHY *pPhyAddr); -
Parameters
Parameter Name Description Input/Output pVirtualAddress CPU virtual address pointer Input pPhyAddr Pointer to store the physical address of the memory block Output -
Return
-
0 Successful.
-
!0 Failed, please refer to the error code.
-
-
Dependency
-
Head file: mi_sys_datatype.h, mi_sys.h
-
Library files: libmi_sys.a / libmi_sys.so
-
-
Note
When using the interface, make sure that the input CPU virtual address is valid and points to the address space allocated in MI.
-
Sample
MI_SYS_Va2Pa Sample
MI_PHY phySrcBufAddr = 0; MI_PHY phyAddrVa2Pa = 0; void *pVirSrcBufAddr = NULL; MI_U32 srcBuffSize = 1920 * 1980 * 3 / 2; srcBuffSize = ALIGN_UP(srcBuffSize, 4096); ret = MI_SYS_MMA_Alloc(NULL, srcBuffSize, &phySrcBufAddr); if(ret != MI_SUCCESS) { printf("alloc src buff failed\n"); return -1; } ret = MI_SYS_Mmap(phySrcBufAddr, srcBuffSize, &pVirSrcBufAddr, TRUE); if(ret != MI_SUCCESS) { MI_SYS_MMA_Free(phySrcBufAddr); printf("mmap src buff failed\n"); return -1; } MI_SYS_Va2Pa(pVirSrcBufAddr, &phyAddrVa2Pa); assert(phySrcBufAddr == phyAddrVa2Pa); memset(pVirSrcBufAddr, 0, srcBuffSize); MI_SYS_FlushInvCache(pVirSrcBufAddr,srcBuffSize); MI_SYS_Munmap(pVirSrcBufAddr, srcBuffSize); MI_SYS_MMA_Free(phySrcBufAddr);
-
Related topics
3. Data type¶
3.1. Description of data structure Description Format¶
This manual uses information about the five reference domain Description data types, which act as information about the reference domain Description data types, as shown in Table 3-1.
Table 3‑1 : Data Structure Description Format Description
| Label | Function |
|---|---|
| Description | Brief Description data type of the main Function. |
| Define | Define statement slisting data types |
| Members | List the data structure of the Members and meaning. |
| Note | List things that should be in Note when using data types. |
| Related data types and interfaces | List the other data types and interfaces associated with this data type. |
3.2. List of data structures¶
Relevant data types and data structures are defined as follows:
Table 3‑2 : Summary of Data Structures
| Data Structures | definition |
|---|---|
| MI_ModuleId_e | Define module ID enumeration type |
| MI_SYS_PixelFormat_e | Define pixel enumeration type |
| MI_SYS_CompressMode_e | Define compression enumeration type |
| MI_SYS_FrameTileMode_e | Define Tile format enumeration type |
| MI_SYS_FieldType_e | Define Field Enumeration Type |
| MI_SYS_BufDataType_e | Define module ID enumeration type |
| MI_SYS_FrameIspInfoType_e | Types of ISP info enumerations carried by Define frame data |
| MI_SYS_ChnPort_t | Define module device channel structure |
| MI_SYS_MetaData_t | Structure of Define Stream MetaData |
| MI_SYS_RawData_t | Structure of Define Stream RawData |
| MI_SYS_WindowRect_t | Structure of Define Window coordinates |
| MI_SYS_FrameData_t | Structure of Define Stream FrameData |
| MI_SYS_BufInfo_t | Buf Information Structure |
| MI_SYS_FrameBufExtraConfig_t | Define Structure sits additionally configured by Stream Frame buffer |
| MI_SYS_BufFrameConfig_t | Frame buf configuration information structure |
| MI_SYS_BufRawConfig_t | Raw buf configuration information structure |
| MI_SYS_MetaDataConfig_t | Meta buf configuration information structure |
| MI_SYS_BufConf_t | Configure the Buf information structure |
| MI_SYS_Version_t | Sys version information structure |
| MI_VB_PoolListConf_t | Structure of DescribeVB Pool list information |
| MI_SYS_BindType_e | Enumeration type of Pre- and Post-Level Working Mode of Define |
| MI_SYS_FrameData_PhySignalType | Enumeration type of buffer type to which Describeframe data belongs |
| MI_SYS_InsidePrivatePoolType_e | Enumeration type of private MMA POOL type in Description Creat |
| MI_SYS_PerChnPrivHeapConf_t | Define Description Channel private MMA Pool structure |
| MI_SYS_PerDevPrivHeapConf_t | Define Description Structure of the device's private MMA Pool |
| MI_SYS_PerVpe2VencRingPoolConf_t | Define Description Structure of private Ring MMA Pool between VPE and VENC |
| MI_SYS_PerChnPortOutputPool_t | Define Describeouput port Structure of private MMA Pool |
| MI_SYS_GlobalPrivPoolConfig_t | Define Description Configure the structure of the private MMA Pool |
| MI_SYS_FrameIspInfo_t | Structure of ISP info in Define frame data |
| MI_SYS_InitParam_t | Define the initialized parameter of SYS device |
| MI_SYS_BufFrameMultiPlaneConfig_t | MultiPlane Frame buf configuration information structure |
| MI_SYS_FrameDataSubPlane_t | Structure of Define Stream SubPlane FrameData |
| MI_SYS_FrameDataMultiPlane_t | Structure of Define Stream MultiPlane FrameData |
| MI_SYS_GlobalFlagType_e | Define global Flag type |
| MI_SYS_GlobalFlagParam_t | Set global Flag parameter |
3.2.1. MI_ModuleId_e¶
-
Description
Define Module ID enumeration type.
-
Define
typedef enum { E_MI_MODULE_ID_IVE = 0, E_MI_MODULE_ID_VDF = 1, E_MI_MODULE_ID_VENC = 2, E_MI_MODULE_ID_RGN = 3, E_MI_MODULE_ID_AI = 4, E_MI_MODULE_ID_AO = 5, E_MI_MODULE_ID_VIF = 6, E_MI_MODULE_ID_VPE = 7, E_MI_MODULE_ID_VDEC = 8, E_MI_MODULE_ID_SYS = 9, E_MI_MODULE_ID_FB = 10, E_MI_MODULE_ID_HDMI = 11, E_MI_MODULE_ID_DIVP = 12, E_MI_MODULE_ID_GFX = 13, E_MI_MODULE_ID_VDISP = 14, E_MI_MODULE_ID_DISP = 15, E_MI_MODULE_ID_OS = 16, E_MI_MODULE_ID_IAE = 17, E_MI_MODULE_ID_MD = 18, E_MI_MODULE_ID_OD = 19, E_MI_MODULE_ID_SHADOW = 20, E_MI_MODULE_ID_WARP = 21, E_MI_MODULE_ID_UAC = 22, E_MI_MODULE_ID_LDC = 23, E_MI_MODULE_ID_SD = 24, E_MI_MODULE_ID_PANEL = 25, E_MI_MODULE_ID_CIPHER = 26, E_MI_MODULE_ID_SNR = 27, E_MI_MODULE_ID_WLAN =28, E_MI_MODULE_ID_IPU = 29, E_MI_MODULE_ID_MIPITX = 30, //E_MI_MODULE_ID_SED = 29, E_MI_MODULE_ID_MAX, } MI_ModuleId_e;
-
Members
Module ID Module ID HEX Value Members Name Module 0 0x00 E_MI_MODULE_ID_IVE Module ID for Image Intelligent Operator IVE 1 0x01 E_MI_MODULE_ID_VDF Module ID of Video Intelligent Algorithm Framework Module VDF 2 0x02 E_MI_MODULE_ID_VENC Module ID for video coding module VPE 3 0x03 E_MI_MODULE_ID_RGN MODULE ID FOR OSD OVERLAY AND MASKING MODULE REG 4 0x04 E_MI_MODULE_ID_AI Module ID for Audio Input Module AI 5 0x05 E_MI_MODULE_ID_AO Module ID for audio Output Module AO 6 0x06 E_MI_MODULE_ID_VIF Video InputVIF's Module ID 7 0x07 E_MI_MODULE_ID_VPE Module ID of the video image processing module VPE 8 0x08 E_MI_MODULE_ID_VDEC Module ID for video processing VPE 9 0x09 E_MI_MODULE_ID_SYS Module ID of System Module SYS 10 0x0A E_MI_MODULE_ID_FB SStar UI shows the module ID of the FrameBuffer Device module 11 0x0B E_MI_MODULE_ID_HDMI HMDI Module ID 12 0x0C E_MI_MODULE_ID_DIVP Module ID for video DI and post-processing module DIVP 13 0x0D E_MI_MODULE_ID_GFX Module ID of 2D Graphics Processing Acceleration Module GFX 14 0x0E E_MI_MODULE_ID_VDISP Image Puzzle Module VDISP Module ID 15 0x0F E_MI_MODULE_ID_DISP Video display module ID of module DISP 16 0x10 E_MI_MODULE_ID_OS RTOS System Module ID 17 0x11 E_MI_MODULE_ID_IAE Module ID for Audio Smart Operator IAE 18 0x12 E_MI_MODULE_ID_MD Module ID of the motion detection module MD 19 0x13 E_MI_MODULE_ID_OD Block ingesting module ID for the OD of the detection module 20 0x14 E_MI_MODULE_ID_SHADOW Module ID for virtual MI framework SHADOW 21 0x15 E_MI_MODULE_ID_WARP Module ID of the image malformation correction algorithm WARP 22 0x16 E_MI_MODULE_ID_UAC Module ID for USB Aduio Class-specific ALSA devices 23 0x17 E_MI_MODULE_ID_LDC Module ID of image malformation correction algorithm LDC 24 0x18 E_MI_MODULE_ID_SD Module ID for image zoom function 25 0x19 E_MI_MODULE_ID_PANEL The display of panel's module ID 26 0x1A E_MI_MODULE_ID_CIPHER Chip encrypts CIPHER's module ID 27 0x1B E_MI_MODULE_ID_SNR Sensor sensor module ID 28 0x1C E_MI_MODULE_ID_WLAN Module ID for wireless communication network Wi-Fi 29 0x1D E_MI_MODULE_ID_IPU Module ID for image recognition processing IPU 30 0x1E E_MI_MODULE_ID_MIPITX Send data module IDs using THE MIPI protocol
3.2.2. MI_SYS_PixelFormat_e¶
-
Description
Define Pixel enumeration type.
-
Define
typedef enum { E_MI_SYS_PIXEL_FRAME_YUV422_YUYV = 0, E_MI_SYS_PIXEL_FRAME_ARGB8888, E_MI_SYS_PIXEL_FRAME_ABGR8888, E_MI_SYS_PIXEL_FRAME_BGRA8888, E_MI_SYS_PIXEL_FRAME_RGB565, E_MI_SYS_PIXEL_FRAME_ARGB1555, E_MI_SYS_PIXEL_FRAME_ARGB4444, E_MI_SYS_PIXEL_FRAME_I2, E_MI_SYS_PIXEL_FRAME_I4, E_MI_SYS_PIXEL_FRAME_I8, E_MI_SYS_PIXEL_FRAME_YUV_SEMIPLANAR_422, E_MI_SYS_PIXEL_FRAME_YUV_SEMIPLANAR_420, E_MI_SYS_PIXEL_FRAME_YUV_SEMIPLANAR_420_NV21, E_MI_SYS_PIXEL_FRAME_YUV_TILE_420, E_MI_SYS_PIXEL_FRAME_YUV422_UYVY, E_MI_SYS_PIXEL_FRAME_YUV422_YVYU, E_MI_SYS_PIXEL_FRAME_YUV422_VYUY, E_MI_SYS_PIXEL_FRAME_YUV422_PLANAR, E_MI_SYS_PIXEL_FRAME_YUV420_PLANAR, E_MI_SYS_PIXEL_FRAME_FBC_420, E_MI_SYS_PIXEL_FRAME_RGB_BAYER_BASE, E_MI_SYS_PIXEL_FRAME_RGB_BAYER_NUM = E_MI_SYS_PIXEL_FRAME_RGB_BAYER_BASE + E_MI_SYS_DATA_PRECISION_MAX*E_MI_SYS_PIXEL_BAYERID_MAX-1, E_MI_SYS_PIXEL_FRAME_RGB888, E_MI_SYS_PIXEL_FRAME_BGR888,E_MI_SYS_PIXEL_FRAME_GRAY8, E_MI_SYS_PIXEL_FRAME_FORMAT_MAX, } MI_SYS_PixelFormat_e;
-
Members
Members Name Description E_MI_SYS_PIXEL_FRAME_YUV422_YUYV YUV422_YUYV format E_MI_SYS_PIXEL_FRAME_ARGB8888 ARGB8888 format E_MI_SYS_PIXEL_FRAME_ABGR8888 ABGR8888 format E_MI_SYS_PIXEL_FRAME_BGRA8888 BGRA8888 format E_MI_SYS_PIXEL_FRAME_RGB565 RGB565 format E_MI_SYS_PIXEL_FRAME_ARGB1555 ARGB1555 format E_MI_SYS_PIXEL_FRAME_ARGB4444 ARGB4444 format E_MI_SYS_PIXEL_FRAME_I2 2 bpp format E_MI_SYS_PIXEL_FRAME_I4 4 bpp format E_MI_SYS_PIXEL_FRAME_I8 8 bpp format E_MI_SYS_PIXEL_FRAME_YUV_SEMIPLANAR_422 YUV422 semi-planar format E_MI_SYS_PIXEL_FRAME_YUV_SEMIPLANAR_420 YUV420sp nv12 format E_MI_SYS_PIXEL_FRAME_YUV_SEMIPLANAR_420_NV21 YUV420sp nv21 format E_MI_SYS_PIXEL_FRAME_TILE_420 Internal custom TILE format E_MI_SYS_PIXEL_FRAME_YUV422_UYVY YUV422_UYVY format E_MI_SYS_PIXEL_FRAME_YUV422_YVYU YUV422_YVYU format E_MI_SYS_PIXEL_FRAME_YUV422_VYUY YUV422_VYUY format E_MI_SYS_PIXEL_FRAME_YUV422_PLANAR YUV422_PLANAR格式 E_MI_SYS_PIXEL_FRAME_YUV420_PLANAR YUV420_PLANAR格式 E_MI_SYS_PIXEL_FRAME_FBC_420 Internal customa format E_MI_SYS_PIXEL_FRAME_RGB_BAYER_BASE RGB raw data combined format base num value E_MI_SYS_PIXEL_FRAME_RGB_BAYER_NUM RGB raw data combined format max num value E_MI_SYS_PIXEL_FRAME_RGB888 RGB888 format E_MI_SYS_PIXEL_FRAME_BGR888 BGR888 format E_MI_SYS_PIXEL_FRAME_GRAY8 8bit gray format E_MI_SYS_PIXEL_FRAME_FORMAT_MAX Enum max value -
Note
E_MI_SYS_PIXEL_FRAME_RGB_BAYER_BASE, E_MI_SYS_PIXEL_FRAME_RGB_BAYER_NUM is available in the RGB raw data combination format. In this format, the bit bit ePixPrecision and the orderee eBayerId provided by the sensor generate an enum value in the RGB raw data combination format from a RGB_BAYER_PIXEL macro, with the following values ranging from: (E_MI_SYS_PIXEL_FRAME_RGB_BAYER_BASE, E_MI_SYS_PIXEL_FRAME_RGB_BAYER_ NUM)
A small example of the use is provided below, and for more detailed information, please refer to the API documentation for the corresponding module.
static MI_SYS_PixelFormat_e getVpeRawType(STUB_SensorType_e sensorType) { MI_SYS_PixelFormat_e eVpeRawType = E_MI_SYS_PIXEL_FRAME_RGB_BAYER_NUM; MI_SNR_PlaneInfo_t stSnrPlane0Info; memset(&stSnrPlane0Info, 0x0, sizeof(MI_SNR_PlaneInfo_t)); MI_SNR_GetPlaneInfo(E_MI_SNR_PAD_ID_0, 0, &stSnrPlane0Info); eVpeRawType = (MI_SYS_PixelFormat_e)RGB_BAYER_PIXEL(stSnrPlane0Info.ePixPrecision, stSnrPlane0Info.eBayerId); return eVpeRawType; }
3.2.3. MI_SYS_CompressMode_e¶
-
Description
Define Compression enumeration type.
-
Define
typedef enum { E_MI_SYS_COMPRESS_MODE_NONE,//no compress E_MI_SYS_COMPRESS_MODE_SEG,//compress unit is 256 bytes as a segment E_MI_SYS_COMPRESS_MODE_LINE,//compress unit is the whole line E_MI_SYS_COMPRESS_MODE_FRAME,//compress unit is the whole frame E_MI_SYS_COMPRESS_MODE_TO_8BIT, E_MI_SYS_COMPRESS_MODE_BUTT, //number }MI_SYS_CompressMode_e;
-
Members
Members Name Description E_MI_SYS_COMPRESS_MODE_NONE Uncompressed video formats E_MI_SYS_COMPRESS_MODE_SEG Segment compressed video format E_MI_SYS_COMPRESS_MODE_LINE Line-compressed video format, compressed by one segment of behavior E_MI_SYS_COMPRESS_MODE_FRAME Frame-compressed video format that compresses a frame of data E_MI_SYS_COMPRESS_MODE_TO_8BIT Compress pixel to 8-bit E_MI_SYS_COMPRESS_MODE_BUTT Number of video compression methods
3.2.4. MI_SYS_FrameTileMode_e¶
-
Description
Define Tile Format enumeration type.
-
Define
typedef enum { E_MI_SYS_FRAME_TILE_MODE_NONE = 0, E_MI_SYS_FRAME_TILE_MODE_16x16, // tile mode 16x16 E_MI_SYS_FRAME_TILE_MODE_16x32, // tile mode 16x32 E_MI_SYS_FRAME_TILE_MODE_32x16, // tile mode 32x16 E_MI_SYS_FRAME_TILE_MODE_32x32, // tile mode 32x32 E_MI_SYS_FRAME_TILE_MODE_MAX } MI_SYS_FrameTileMode_e;
-
Members
Members Name Description E_MI_SYS_FRAME_TILE_MODE_NONE None E_MI_SYS_FRAME_TILE_MODE_16x16 16x16 mode E_MI_SYS_FRAME_TILE_MODE_16x32 16x32 mode E_MI_SYS_FRAME_TILE_MODE_32x16 32x16 mode E_MI_SYS_FRAME_TILE_MODE_32x32 32x32 mode
3.2.5. MI_SYS_FieldType_e¶
-
Description
Define Enumeration type.
-
Define
typedef enum { E_MI_SYS_FIELDTYPE_NONE, //< no field. E_MI_SYS_FIELDTYPE_TOP, //< Top field only. E_MI_SYS_FIELDTYPE_BOTTOM, //< Bottom field only. E_MI_SYS_FIELDTYPE_BOTH, //< Both fields. E_MI_SYS_FIELDTYPE_NUM } MI_SYS_FieldType_e;
-
Members
Members Name Description E_MI_SYS_FIELDTYPE_NONE None E_MI_SYS_FIELDTYPE_TOP Top field only E_MI_SYS_FIELDTYPE_BOTTOM Bottom field only E_MI_SYS_FIELDTYPE_BOTH Both fields
3.2.6. MI_SYS_BufDataType_e¶
-
Description
Define Module ID enumeration type.
-
Define
typedef enum { E_MI_SYS_BUFDATA_RAW = 0, E_MI_SYS_BUFDATA_FRAME, E_MI_SYS_BUFDATA_META, E_MI_SYS_BUFDATA_MULTIPLANE } MI_SYS_BufDataType_e;
-
Members
Members Name Description E_MI_SYS_BUFDATA_RAW Raw data type E_MI_SYS_BUFDATA_FRAME Frame data type E_MI_SYS_BUFDATA_META Meta data type E_MI_SYS_BUFDATA_MULTIPLANE Multiplane data type
3.2.7. MI_SYS_FrameIspInfoType_e¶
-
Description
Types of ISP info enumerations carried by Define frame data.
-
Define
typedef enum { E_MI_SYS_FRAME_ISP_INFO_TYPE_NONE, E_MI_SYS_FRAME_ISP_INFO_TYPE_GLOBAL_GRADIENT }MI_SYS_FrameIspInfoType_e;
-
Members
Members Name Description E_MI_SYS_FRAME_ISP_INFO_TYPE_NONE NONE E_MI_SYS_FRAME_ISP_INFO_TYPE_GLOBAL_GRADIENT Global gradient data types for ISPs
3.2.8. MI_SYS_ChnPort_t¶
-
Description
Define Module equipment channel structure.
-
Define
typedef struct MI_SYS_ChnPort_s { MI_ModuleId_e eModId; MI_U32 u32DevId; MI_U32 u32ChnId; MI_U32 u32PortId; } MI_SYS_ChnPort_t;
-
Members
Members Name Description eModId Module No. u32DevId Device No. u32ChnId Channel No. u32PortId Port No.
3.2.9. MI_SYS_MetaData_t¶
-
Description
Define Structure of the Code Stream MetaData.
-
Define
typedef struct MI_SYS_MetaData_s { void* pVirAddr; MI_PHY phyAddr;//notice that this is miu bus addr,not cpu bus addr. MI_U32 u32Size; MI_U32 u32ExtraData; /*driver special flag*/ MI_ModuleId_e eDataFromModule; } MI_SYS_MetaData_t;
-
Members
Members Name Description pVirAddr Data storage virtual address. phyAddr Data storage physical address u32Size Data size u32ExtraData driver special flag eDataFromModule Data from which module
3.2.10. MI_SYS_RawData_t¶
-
Description
Define Structure of The Stream RawData.
-
Define
typedef struct MI_SYS_RawData_s { void* pVirAddr; MI_PHY phyAddr; //notice that this is miu bus addr,not cpu bus addr. MI_U32 u32BufSize; MI_U32 u32ContentSize; MI_BOOL bEndOfFrame; MI_U64 u64SeqNum; } MI_SYS_RawData_t;
-
Members
Members Name Description pVirAddr The address of the stream package. phyAddr The physical address of the stream package u32BufSize Buf size u32ContentSize Data actually takes up buf size bEndOfFrame Whether the current frame ends. (Reserved parameter) currently only supports frame-by-frame transmission in frame mode. u64SeqNum Frame number of the current frame -
Note
-
Currently only support the transmission of data by frame, each time need to transfer a complete frame of data.
-
When the stream frame data comes with PTS, the decoded Output data Output is the same PTS. When PTS is 1, do not refer to the system clock Output data frame.
-
3.2.11. MI_SYS_WindowRect_t¶
-
Description
Define window Structure of coordinates.
-
Define
typedef struct MI_SYS_WindowRect_s { MI_U16 u16X; MI_U16 u16Y; MI_U16 u16Width; MI_U16 u16Height; }MI_SYS_WindowRect_t;
-
Members
Members Name Description u16X The value of the horizontal direction of the window start position. u16Y The value of the vertical direction of the window start position. u16Width Window width. u16Height Window height.
3.2.12. MI_SYS_FrameData_t¶
-
Description
Define Structure of The Stream FrameData.
-
Define
//N.B. in MI_SYS_FrameData_t should never support u32Size, //for other values are enough,and not support u32Size is general standard method. typedef struct MI_SYS_FrameData_s { MI_SYS_FrameTileMode_e eTileMode; MI_SYS_PixelFormat_e ePixelFormat; MI_SYS_CompressMode_e eCompressMode; MI_SYS_FrameScanMode_e eFrameScanMode; MI_SYS_FieldType_e eFieldType; MI_SYS_FrameData_PhySignalType ePhylayoutType; MI_U16 u16Width; MI_U16 u16Height; //in case ePhylayoutType equal to REALTIME_FRAME_DATA, pVirAddr would be MI_SYS_REALTIME_MAGIC_PADDR and phyAddr would be MI_SYS_REALTIME_MAGIC_VADDR void* pVirAddr[3]; MI_PHY phyAddr[3]; //notice that this is miu bus addr,not cpu bus addr. MI_U32 u32Stride[3]; MI_U32 u32BufSize; //total size that allocated for this buffer,include consider alignment. MI_U16 u16RingBufStartLine; //Valid in case RINGBUF_FRAME_DATA, u16RingBufStartLine must be LGE than 0 and less than u16Height MI_U16 u16RingBufRealTotalHeight; ///Valid in case RINGBUF_FRAME_DATA, u16RingBufStartLine must be LGE than u16Height MI_SYS_FrameIspInfo_t stFrameIspInfo; //isp info of each frame MI_SYS_WindowRect_t stContentCropWindow; } MI_SYS_FrameData_t;
-
Members
Members Name Description eTileMode Tile mode ePixelFormat Pixel format eCompressMode Compressed format eFrameScanMode Frame scan module eFieldType File type ePhylayoutType The type of buffer that the frame belongs to u16Width Frame width u16Height Frame height pVirAddr Virtual address phyAddr Physical address u32Stride Number of bytes per row of pictures u32BufSize The actual buf size assigned by Sys to the current frame u16RingBufStartLine When ring mode, frame data starts with the number of rows of ring buffer u16RingBufRealTotalHeight The true height of frame data when ring mode stFrameIspInfo ISP info struct stContentCropWindow Crop info struct
3.2.13. MI_SYS_BufInfo_t¶
-
Description
Define Structure of code flow information.
-
Define
typedef struct MI_SYS_BufInfo_s { MI_U64 u64Pts; MI_U64 u64SidebandMsg; MI_SYS_BufDataType_e eBufType; MI_U32 bEndOfStream : 1; MI_U32 bUsrBuf : 1; MI_U32 bDrop : 1; MI_U32 u32IrFlag : 2; // For Window Hello Usage: 0x00/off, 0x01/on, 0x02/invalid MI_U32 u32Reserved : 27; MI_U32 u32SequenceNumber; union { MI_SYS_FrameData_t stFrameData; MI_SYS_RawData_t stRawData; MI_SYS_MetaData_t stMetaData; MI_SYS_FrameDataMultiPlane_t stFrameDataMultiPlane; }; } MI_SYS_BufInfo_t;
-
Members
Members Name Description eBufType Buf type u64Pts Time stamp bEndOfStream Whether all the information has been sent u32IrFlag Ir flag bit
3.2.14. MI_SYS_FrameBufExtraConfig_t¶
-
Description
Define Structure sits additionally configured by Stream Frame buffer.
-
Define
typedef struct MI_SYS_FrameBufExtraConfig_s { //Buf alignment requirement in horizontal MI_U16 u16BufHAlignment; //Buf alignment requirement in vertical MI_U16 u16BufVAlignment; //Buf alignment requirement in chroma MI_U16 u16BufChromaAlignment; //Clear padding flag MI_BOOL bClearPadding; }MI_SYS_FrameBufExtraConfig_t;
-
Members
Members Name Description u16BufHAlignment Horizontal alignment values u16BufVAlignment Vertical alignment values u16BufChromaAlignment Chroma buffer size alignment value bClearPadding Do you want to blacken the edges of the buffer?
3.2.15. MI_SYS_BufFrameConfig_t¶
-
Description
Define Structure of the Code Stream Frame buffer configuration.
-
Define
typedef struct MI_SYS_BufFrameConfig_s { MI_U16 u16Width; MI_U16 u16Height; MI_SYS_FrameScanMode_e eFrameScanMode;// MI_SYS_PixelFormat_e eFormat; MI_SYS_CompressMode_e eCompressMode; }MI_SYS_BufFrameConfig_t;
-
Members
Members Name Description u16Width Frame width u16Height Frame height eFrameScanMode Frame Scan Mode eFormat Frame pixel format eCompressMode Frame compress mode
3.2.16. MI_SYS_BufRawConfig_t¶
-
Description
Define Structure of the code flow raw buffer configuration.
-
Define
typedef struct MI_SYS_BufRawConfig_s { MI_U32 u32Size; }MI_SYS_BufRawConfig_t;
-
Members
Members Name Description u32Size Buf Size
3.2.17. MI_SYS_MetaDataConfig_t¶
-
Description
Define Structure of the code flow meta buffer configuration.
-
Define
typedef struct MI_SYS_MetaDataConfig_s { MI_U32 u32Size; }MI_SYS_MetaDataConfig_t;
-
Members
Members Name Description u32Size Buf Size
3.2.18. MI_SYS_BufConf_t¶
-
Description
Define Structure of the Flow Port Buf configuration.
-
Define
typedef struct MI_SYS_BufConf_s { MI_SYS_BufDataType_e eBufType; MI_U32 u32Flags; //0 or MI_SYS_MAP_VA MI_U64 u64TargetPts; union { MI_SYS_BufFrameConfig_t stFrameCfg; MI_SYS_BufRawConfig_t stRawCfg; MI_SYS_MetaDataConfig_t stMetaCfg; }; }MI_SYS_BufConf_t;
-
Members
Members Name Description eBufType Buf type u32Flags Buf is map kernel space va?
3.2.19. MI_SYS_Version_t¶
-
Description
Define Sys version structure information.
-
Define
typedef struct MI_SYS_Version_s { MI_U8 u8Version[128]; }MI_SYS_Version_t;
-
Members
Members Name Description u8Version[128] Describe sys version information string buf
3.2.20. MI_VB_PoolListConf_t¶
-
Description
Define DescribeVB Pool Structure of linked information.
-
Define
typedef struct MI_VB_PoolListConf_s { MI_U32 u32PoolListCnt; MI_VB_PoolConf_t stPoolConf[MI_VB_POOL_LIST_MAX_CNT]; } MI_VB_PoolListConf_t;
-
Members
Members Name Description u32PoolListCnt VB pool list number of Members stPoolConf VB pool linked table Members configuration information
3.2.21. MI_SYS_BindType_e¶
-
Description
Define Front and rear operating modes.
-
Define
typedef enum { E_MI_SYS_BIND_TYPE_FRAME_BASE = 0x00000001, E_MI_SYS_BIND_TYPE_SW_LOW_LATENCY = 0x00000002, E_MI_SYS_BIND_TYPE_REALTIME = 0x00000004, E_MI_SYS_BIND_TYPE_HW_AUTOSYNC = 0x00000008, E_MI_SYS_BIND_TYPE_HW_RING = 0x00000010 }MI_SYS_BindType_e;
-
Members
Members Name Description E_MI_SYS_BIND_TYPE_FRAME_BASE frame mode, default how to work E_MI_SYS_BIND_TYPE_SW_LOW_LATENCY Low latency working E_MI_SYS_BIND_TYPE_REALTIME How hardware is directly connected E_MI_SYS_BIND_TYPE_HW_AUTOSYNC Front and rear handshake level, buffer size consistent with image resolution E_MI_SYS_BIND_TYPE_HW_RING Front and rear handshake levels, ring buffer depth can be trated less than the image resolution is high -
Note
Older versions of MI SYS do not provide this function, if not found, do not have to set.
3.2.22. MI_SYS_FrameData_PhySignalType¶
-
Description
Describe frame data Enumerated types of buffer types that are affiliated.
-
Define
typedef enum { REALTIME_FRAME_DATA, RINGBUF_FRAME_DATA, NORMAL_FRAME_DATA, }MI_SYS_FrameData_PhySignalType;
-
Members
Members Name Description REALTIME_FRAME_DATA In E_MI_SYS_BIND_TYPE_REALTIME mode RINGBUF_FRAME_DATA The resulting frame data NORMAL_FRAME_DATA In E_MI_SYS_BIND_TYPE_HW_RING mode -
Note
Older versions of MI SYS do not provide this function, if not found, do not have to set.
3.2.23. MI_SYS_InsidePrivatePoolType_e¶
-
Description
Enumeration type of private MMA POOL type in Description Creat.
-
Define
typedef enum { E_MI_SYS_VPE_TO_VENC_PRIVATE_RING_POOL = 0, E_MI_SYS_PER_CHN_PRIVATE_POOL=1, E_MI_SYS_PER_DEV_PRIVATE_POOL=2, E_MI_SYS_PER_CHN_PORT_OUTPUT_POOL=3, }MI_SYS_InsidePrivatePoolType_e;
-
Members
Members Name Description E_MI_SYS_VPE_TO_VENC_PRIVATE_RING_POOL Private Ring Pool Type for VPE and VENC E_MI_SYS_PER_CHN_PRIVATE_POOL Channel Private Pool Type E_MI_SYS_PER_DEV_PRIVATE_POOL Device Private Pool Type E_MI_SYS_PER_CHN_PORT_OUTPUT_POOL Output Port Private Pool Type -
Note
Older versions of MI SYS do not provide this function, if not found, do not have to set.
3.2.24. MI_SYS_PerChnPrivHeapConf_t¶
-
Description
Define Description Channel private MMA Pool structure.
-
Define
typedef struct MI_PerChnPrivHeapConf_s { MI_ModuleId_e eModule; MI_U32 u32Devid; MI_U32 u32Channel; MI_U8 u8MMAHeapName[MI_MAX_MMA_HEAP_LENGTH]; MI_U32 u32PrivateHeapSize; }MI_SYS_PerChnPrivHeapConf_t;
-
Members
Members Name Description eModule Module ID u32Devid Device ID u32Channel Channel ID u8MMAHeapName Mma heap name u32PrivateHeapSize Private pool size
3.2.25. MI_SYS_PerDevPrivHeapConf_t¶
-
Description
Define Description Structure of the device's private MMA Pool.
-
Define
typedef struct MI_PerDevPrivHeapConf_s { MI_ModuleId_e eModule; MI_U32 u32Devid; MI_U32 u32Reserve; MI_U8 u8MMAHeapName[MI_MAX_MMA_HEAP_LENGTH]; MI_U32 u32PrivateHeapSize; }MI_SYS_PerDevPrivHeapConf_t;
-
Members
Members Name Description eModule Module ID u32Devid Device ID u32Reserve Reserved u8MMAHeapName Mma heap name u32PrivateHeapSize Private pool size
3.2.26. MI_SYS_PerVpe2VencRingPoolConf_t¶
-
Description
Define Description Structure of private Ring MMA Pool between VPE and VENC.
-
Define
typedef struct MI_SYS_PerVpe2VencRingPoolConf_s { MI_U32 u32VencInputRingPoolStaticSize; MI_U8 u8MMAHeapName[MI_MAX_MMA_HEAP_LENGTH]; }MI_SYS_PerVpe2VencRingPoolConf_t;
-
Members
Members Name Description u32VencInputRingPoolStaticSize Private pool size u8MMAHeapName Mma heap name
3.2.27. MI_SYS_PerChnPortOutputPool_t¶
-
Description
Define Describeouput port Structure of private MMA Pool.
-
Define
typedef struct MI_SYS_PerChnPortOutputPool_s { MI_ModuleId_e eModule; MI_U32 u32Devid; MI_U32 u32Channel; MI_U32 u32Port; MI_U8 u8MMAHeapName[MI_MAX_MMA_HEAP_LENGTH]; MI_U32 u32PrivateHeapSize; }MI_SYS_PerChnPortOutputPool_t;
-
Members
Members Name Description eModule Module ID u32Devid Device ID u32Channel Channel ID u32Port Port ID u8MMAHeapName Mma heap name u32PrivateHeapSize Private pool size
3.2.28. MI_SYS_GlobalPrivPoolConfig_t¶
-
Description
Define Description Configure the structure of the private MMA Pool.
-
Define
typedef struct MI_SYS_GlobalPrivPoolConfig_s { MI_SYS_InsidePrivatePoolType_e eConfigType; MI_BOOL bCreate; union { MI_SYS_PerChnPrivHeapConf_t stPreChnPrivPoolConfig; MI_SYS_PerDevPrivHeapConf_t stPreDevPrivPoolConfig; MI_SYS_PerVpe2VencRingPoolConf_t stPreVpe2VencRingPrivPoolConfig; MI_SYS_PerChnPortOutputPool_t stPreChnPortOutputPrivPool; }uConfig; }MI_SYS_GlobalPrivPoolConfig_t;
-
Members
Members Name Description eConfigType Private pool type bCreate Whether Create PrivatePool.true: Creat false: Destroyed uConfig Structures of different types of private pool
3.2.29. MI_SYS_FrameIspInfo_t¶
-
Description
Structure of ISP info in Define frame data.
-
Define
typedef struct MI_SYS_FrameIspInfo_s { MI_SYS_FrameIspInfoType_e eType; union { MI_U32 u32GlobalGradient; }uIspInfo; }MI_SYS_FrameIspInfo_t;
-
Members
Members Name Description eType ISP info type uIspInfo ISP info union
3.2.30. MI_SYS_InitParam_t¶
-
Description
SYS device initialization parameter.
-
Define
typedef struct MI_SYS_InitParam_s { MI_U32 u32DevId; MI_U8 *u8Data; } MI_SYS_InitParam_t;
-
Members
Members Name Description u32DevId Device ID u8Data Data pointer buffer -
Related data types and interfaces
3.2.31. MI_SYS_BufFrameMultiPlaneConfig_t¶
-
Description
Define Structure of the code flow multiplane buffer configuration.
-
Define
typedef struct MI_SYS_BufFrameMultiPlaneConfig_s { MI_U8 u8SubPlaneNum; MI_SYS_BufFrameConfig_t stFrameCfg; }MI_SYS_BufFrameMultiPlaneConfig_t;
-
Members
Members Name Description u8SubPlaneNum Buf count stFrameCfg Define Structure of the code flow frame buffer configuration.
3.2.32. MI_SYS_FrameDataSubPlane_t¶
-
Description
Define Structure of The Stream SubPlane FrameData.
-
Define
typedef struct MI_SYS_FrameDataSubPlane_s { MI_SYS_PixelFormat_e ePixelFormat; MI_SYS_CompressMode_e eCompressMode; MI_U64 u64FrameId; MI_U16 u16Width; MI_U16 u16Height; void* pVirAddr[2]; MI_PHY phyAddr[2]; MI_U16 u16Stride[2]; MI_U32 u32BufSize; } MI_SYS_FrameDataSubPlane_t;
-
Members
Members Name Description ePixelFormat Pixel format eCompressMode Compressed format u64FrameId Frame id u16Width Frame width u16Height Frame height pVirAddr Virtual address phyAddr Physical address u16Stride Number of bytes per row of pictures u32BufSize The actual buf size assigned by Sys to the current frame
3.2.33. MI_SYS_FrameDataMultiPlane_t¶
-
Description
Define Structure of the Stream MutiPlane FrameData.
-
Define
typedef struct MI_SYS_FrameDataMultiPlane_s { MI_U8 u8SubPlaneNum; MI_SYS_FrameDataSubPlane_t stSubPlanes[MI_SYS_MAX_SUB_PLANE_CNT]; } MI_SYS_FrameDataMultiPlane_t;
-
Members
Members Name Description u8SubPlaneNum Buf count stSubPlanes Define Structure of the code flow MultiPlane buffer configuration.
3.2.34. MI_SYS_GlobalFlagType_e¶
-
Description
Define global Flag type.
-
Define
typedef enum { E_MI_SYS_GLOBALFLAG_IR, E_MI_SYS_GLOBALFLAG_NUM, } MI_SYS_GlobalFlagType_e;
-
Members
Members Name Description E_MI_SYS_GLOBALFLAG_IR IR global Flag
3.2.35. MI_SYS_GlobalFlagParam_t¶
-
Description
Set global Flag parameter.
-
Define
typedef struct MI_SYS_GlobalFlagParam_s { MI_SYS_GlobalFlagType_e eFlagType; MI_BOOL bIsr; MI_U32 u32Value; } MI_SYS_GlobalFlagParam_t;
-
Members
Members Name Description eFlagType Set Flag type bIsr Whether the Flag setting will be executed in the interrupt request u32FlagNew Set new Flag value -
Note
When setting the IR global Flag, u32FlagNew=0, it means OFF, u32FlagNew=1, it means ON.
4. Error Code¶
4.1. The composition of the error code¶
Mi returns the error code for 4 bytes, a total of 32bits, consisting of five parts as shown in Table 4-1:
Table 4‑1: The composition of the error code
| Position | Bits | Description |
|---|---|---|
| BIT [0-11] | 12bits | The error type that indicates the specific error meaning of the error code. |
| BIT [12-15] | 4bits | Error level, fixed return 2. |
| BIT [16-23] | 8bits | Module ID, which module the error code belongs to. |
| BIT [24-31] | 8bits | Fixed to 0xA0. |
Tips:
We can simply think of the error code as two double bytes (16bits) for quick interpretation, in the case of the error code 0xA0092001:
"A009": Indicates that the error occurred in a module with module ID 9, which can be seen as a MI_SYS module by looking at the “MI_ModuleId_e”Define.
"2001": The error type that indicates the error is 1, i.e. "Device ID is out of legal range".
4.2. The error code list for MI_SYS API¶
MI_SYS module all APIs return a value of 4 bytes, 0 indicates execution success, other values indicate execution failure, the need for Note is that all! 0 Return should be listed in Table 4-2, otherwise it is illegal.
Table 4‑2: MI_SYS Module sier ingo code
| Error Code | Definition | Description |
|---|---|---|
| 0xA0092001 | MI_ERR_SYS_INVALID_DEVID | Device ID out of legal range |
| 0xA0092002 | MI_ERR_SYS_INVALID_CHNID | Channel group number error or invalid area handle |
| 0xA0092003 | MI_ERR_SYS_ILLEGAL_PARAM | Argument out of legal range |
| 0xA0092004 | MI_ERR_SYS_EXIST | Repeat a device, channel, or resource that already exists in Creat |
| 0xA0092005 | MI_ERR_SYS_UNEXIST | Trying to use a setting that does not exist in Destroyed |
| 0xA0092006 | MI_ERR_SYS_NULL_PTR | access, channel, or resource |
| 0xA0092007 | MI_ERR_SYS_NOT_CONFIG | There are empty pointers in the function arguments |
| 0xA0092008 | MI_ERR_SYS_NOT_SUPPORT | The module is not configured |
| 0xA0092009 | MI_ERR_SYS_NOT_PERM | Unsupported parameters or Function |
| 0xA009200C | MI_ERR_SYS_NOMEM | This operation is not allowed, such as an attempt to modify static configuration parameters |
| 0xA009200D | MI_ERR_SYS_NOBUF | Failed to allocate memory, such as insufficient system memory |
| 0xA009200E | MI_ERR_SYS_BUF_EMPTY | Allocation cache failed, such as the requested data buffer is too large |
| 0xA009200F | MI_ERR_SYS_BUF_FULL | No data in the buffer |
| 0xA0092010 | MI_ERR_SYS_NOTREADY | Full data in buffer |
| 0xA0092011 | MI_ERR_SYS_BADADDR | The system did not initialize or load the module |
| 0xA0092012 | MI_ERR_SYS_BUSY | The address's illegal |
| 0xA0092013 | MI_ERR_SYS_CHN_NOT_STARTED | The system is busy |
| 0xA0092014 | MI_ERR_SYS_CHN_NOT_STOPED | The channel didn't start. |
| 0xA0092015 | MI_ERR_SYS_NOT_INIT | The channel has not stopped. |
| 0xA0092016 | MI_ERR_SYS_INITED | The module is not initialized |
| 0xA0092017 | MI_ERR_SYS_NOT_ENABLE | Module has been initialized |
| 0xA0092018 | MI_ERR_SYS_NOT_DISABLE | Channel or port does not have ENABLE |
| 0xA0092019 | MI_ERR_SYS_TIMEOUT | Channel or port does not have DISABLE |
| 0xA009201A | MI_ERR_SYS_DEV_NOT_STARTED | Timeout |
| 0xA009201B | MI_ERR_SYS_DEV_NOT_STOPED | The device didn't start |
| 0xA009201C | MI_ERR_SYS_CHN_NO_CONTENT | The device is not stopped |
| 0xA009201D | MI_ERR_SYS_NOVASAPCE | There's no information in the channel. |
| 0xA009201E | MI_ERR_SYS_NOITEM | Failed to map virtual address |
| 0xA009201F | MI_ERR_SYS_FAILED | There's no record in RingPool. |