MI AI API
1. OVERVIEW¶
1.1. Module Description¶
Audio Input (AI) is mainly used to configure and enable Audio Input devices, obtain Audio frame data, and perform acoustic algorithm processing. Acoustic algorithm processing mainly includes Sample Rate Conversion, Acoustic Echo Cancellation, Acoustic Noise Reduction, High-Pass Filtering, Equalizer, Automatic Gain Control, Sound Event Detection, Sound Source Location, Beamforming and so on. In 2.19 and later versions of the API, MI_AI no longer includes the associated algorithm functions.
1.2. Flow Block Diagram¶
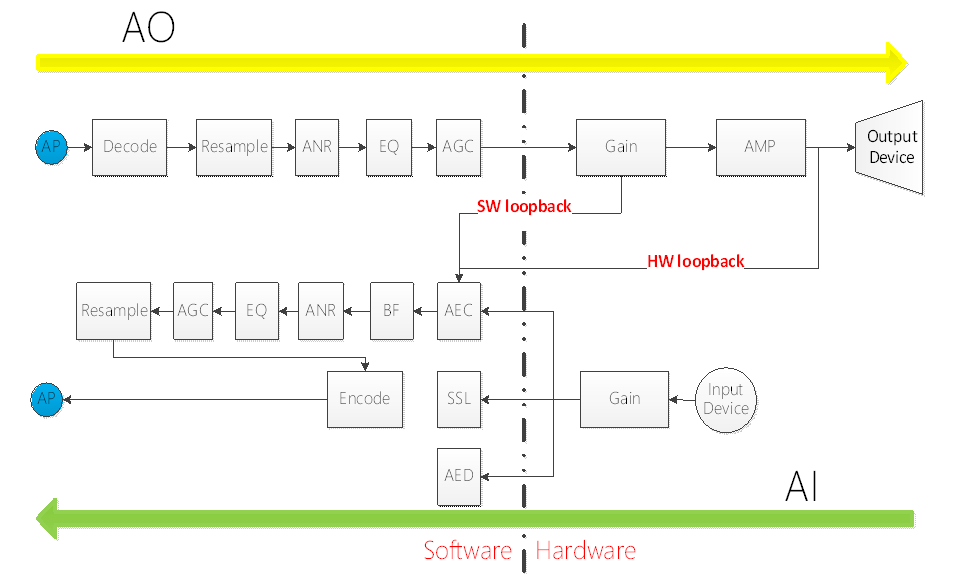
Figure1-1
In the 2.19 and later API versions, MI_AI/MI_AO no longer includes the related algorithm functions, and only the basic capture/playback functions are maintained.
1.3. Keyword Description¶
-
Device
Different from Device concepts of other modules, AI Device refers to different external input devices such as Amic/Dmic/I2S RX/Line in.
-
Channel
AI Channel refers to the number of tracks in the software concept.
-
SRC
SRC refers to Sample Rate Conversion.
-
AGC
AGC refers to Automatic Gain Control), and is used to control the output gain.
-
EQ
EQ refers to Equalizer, and is used to process specific frequencies.
-
ANR
ANR refers to Acoustic Noise Reduction, and is used to remove persistent, constant frequency noise in the environment.
-
BF
BF refers to beamforming, and is used in microphone arrays to enhance sound.
-
AEC
AEC refers to Acoustic Echo Cancellation.
-
SSL
SSL refers to Sound Source Localization, and is used in microphone arrays to identify the direction of sound.
-
AED
AED refers to Acoustic Event Detection. Currently, only baby cries and loud sound can be detected.
-
HPF
HPF refers to High-Pass Filtering.
2. API REFERENCE¶
2.1. Overview¶
Audio Input (AI) mainly implements functions such as configuring and enabling audio input devices and acquiring audio frame data
Table2-1 API List
| API Name | Features |
|---|---|
| MI_AI_SetPubAttr | Set AI device properties |
| MI_AI_GetPubAttr | Get AI device properties |
| MI_AI_Enable | Enable AI device |
| MI_AI_Disable | Disable AI device |
| MI_AI_EnableChn | Enable AI channel |
| MI_AI_DisableChn | Disable AI channel |
| MI_AI_GetFrame | Get audio frames |
| MI_AI_ReleaseFrame | Release audio frame |
| MI_AI_SetChnParam | Set AI channel parameters |
| MI_AI_GetChnParam | Get AI channel parameters |
| MI_AI_EnableReSmp | Enable AI channel resampling |
| MI_AI_DisableReSmp | Disable AI channel resampling. |
| MI_AI_SetVqeAttr | Set the sound quality enhancement related properties of AI channel |
| MI_AI_GetVqeAttr | Get the sound quality enhancement related properties of AI channel |
| MI_AI_EnableVqe | Enable the sound quality enhancements of AI channel |
| MI_AI_DisableVqe | Disable the sound quality enhancements of AI channel |
| MI_AI_ClrPubAttr | Clear AI device properties |
| MI_AI_SaveFile | Turn on audio input to save files |
| MI_AI_SetVqeVolume | Set the volume level of AI channel |
| MI_AI_GetVqeVolume | Get the volume level of AI channel |
| MI_AI_SetAencAttr | Set encoding function related properties of AI channel |
| MI_AI_GetAencAttr | Get encoding function related properties of AI channel |
| MI_AI_EnableAenc | Enable encoding of AI channel |
| MI_AI_DisableAenc | Disable encoding of AI channel |
| MI_AI_SetAedAttr | Set sound event detection function related properties of AI channel. |
| MI_AI_GetAedAttr | Get sound event detection function related properties of AI channel. |
| MI_AI_EnableAed | Enable sound event detection of AI channel. |
| MI_AI_DisableAed | Disable sound event detection of AI channel. |
| MI_AI_GetAedResult | Get the sound event detection result of AI channel. |
| MI_AI_SetExtAecChn | Set the external echo cancellation function reference AI channel |
| MI_AI_SetSslInitAttr | Set Sound source localization function initialized properties of AI channel |
| MI_AI_GetSslInitAttr | Get Sound source localization function initialized properties of AI channel |
| MI_AI_SetSslConfigAttr | Set Sound source localization function configured properties of AI channel |
| MI_AI_GetSslConfigAttr | Get Sound source localization function configured properties of AI channel |
| MI_AI_EnableSsl | Enable Sound source localization function of AI channel |
| MI_AI_DisableSsl | Disable Sound source localization function of AI channel |
| MI_AI_GetSslDoa | Get the Sound source localization result of AI channel |
| MI_AI_SetBfInitAttr | Set Beamforming function initialized properties of AI channel |
| MI_AI_GetBfInitAttr | Get Beamforming function initialized properties of AI channel |
| MI_AI_SetBfConfigAttr | Set Beamforming function configured properties of AI channel |
| MI_AI_GetBfConfigAttr | Get Beamforming function configured properties of AI channel |
| MI_AI_EnableBf | Enable Beamforming function of AI channel |
| MI_AI_DisableBf | Disable Beamforming function of AI channel |
| MI_AI_SetBfAngle | Set fixed Angle for Beamforming function of AI channel |
| MI_AI_SetMute | Set Mute status of channel |
| MI_AI_GetMute | Get Mute status of channel |
| MI_AI_InitDev | Initialize AI device |
| MI_AI_DeInitDev | De-initialize AI device |
| MI_AI_DupChn | Synchronize status of AI channel |
2.2. MI_AI_SetPubAttr¶
-
Features
Set the AI device properties.
-
Syntax
MI_S32 MI_AI_SetPubAttr(MI_AUDIO_DEV AiDevId,MI_AUDIO_Attr_t *pstAttr); -
Parameters
Table2-2
Parameter Name Description Input/Output AiDevId Audio device number Input pstAttr AI device property pointer Input -
Return value
-
Zero: Successful
-
Non-zero: Failed, see error code for details
-
-
Dependency
-
Header: mi_ai.h
-
Library: libmi_ai.a/libmi_ai.so
-
-
Note
Audio input device determines the format of input data attributes. The device attributes includes sampling rate, sampling precision, input operation mode, data format of channel, number of sampling points per frame channels, channel count of device, and configuration of I2S. When Codec is used, these attributes should be consistent with the requirements of the docking Codec configuration.
-
Sampling rate
The sampling rate refers to the number of sampling points in one second. The higher the sampling rate, the smaller the distortion, and the more data is processed. Generally speaking, 8k sampling rate is used for speech and 32k or more for audio. Currently, only 8/16/32/48KHz sampling rate is supported. When Codec is used, make sure whether the docked Audio Codec supports the sampling rate to be set.
-
Sampling accuracy
Sampling accuracy refers to the sampling point data width of a channel and determines the channel distribution of the entire device. The sampling accuracy supports 16 bits.
-
Operating mode
Audio input and output currently supports I2S master mode, I2S slave mode, Tdm master mode and Tdm slave mode, but the content supported by each audio device may be different.
-
Data format of channel
The data format indicates data arrangement in channel. Mono indicates that the data of AI channel is one physical data channel. Stereo indicates that the data of AI channel is two interlaced physical data channels. Queue indicates that multiple physical channels of data exist in one channel. When the algorithm is enabled in Queue mode, all channels use the same set of parameters.
-
Number of samples per frame
When the audio sampling rate is high, it is recommended to increase the number of sampling points per frame accordingly. If the sound is intermittent, you can increase the number of samples per frame and the buffer count as deemed necessary. It is recommended that the number of samples per frame be set at about 16 frames per second.
-
Number of channels
The number of channels refers to the number of channels in the software concept of the current input device. The number of channels, together with the data format of channel, determines how many physical channels to use.
-
Configuration of I2S
The configuration parameters of I2S specify the frequency of I2S MCLK, the data format of I2S transmission, and whether I2S uses 4-wire mode or 6-wire mode, the tdm slot number of I2S, the bit width of I2S.
-
-
Example
The following code shows how to implement the function of taking a data frame from the AI channel and releasing it.
MI_S32 ret; MI_AUDIO_Attr_t stAttr; MI_AUDIO_Dev AiDevId = 0; MI_AI_CHN AiChn = 0; MI_SYS_ChnPort_t stChnPort; MI_S32 s32Fd; fd_set readFdSet; struct timeval stTimeOut; MI_AUDIO_Frame_t stAiChFrame; MI_AUDIO_AecFrame_t stAecFrame; MI_SYS_ChnPort_t stAiChnOutputPort; MI_SYS_Init(); stAttr.eBitwidth = E_MI_AUDIO_BIT_WIDTH_16; stAttr.eSamplerate = E_MI_AUDIO_SAMPLE_RATE_8000; stAttr.eSoundmode = E_MI_AUDIO_SOUND_MODE_MONO; stAttr.eWorkmode = E_MI_AUDIO_MODE_I2S_SLAVE; stAttr.u32PtNumPerFrm = 160; stAttr.u32ChnCnt = 1; /* set public attribute of AI device */ ret = MI_AI_SetPubAttr(AiDevId, &stAttr); if (MI_SUCCESS != ret) { printf("set ai %d attr err:0x%x\n", AiDevId, ret); return ret; } /* get public attribute of AI device */ ret = MI_AI_GetPubAttr(AiDevId, &stAttr); if (MI_SUCCESS != ret) { printf("get ai %d attr err:0x%x\n", AiDevId, ret); return ret; } /* enable AI device */ ret = MI_AI_Enable(AiDevId); if (MI_SUCCESS != ret) { printf("enable ai %d err:0x%x\n", AiDevId, ret); return ret; } /* enable AI Channel */ ret = MI_AI_EnableChn(AiDevId, AiChn); if (MI_SUCCESS != ret) { printf("enable Dev%d Chn%d err:0x%x\n", AiDevId, AiChn, ret); return ret; } /* set buffer depth */ stAiChnOutputPort.eModId = E_MI_MODULE_ID_AI; stAiChnOutputPort.u32DevId = AiDevId; stAiChnOutputPort.u32ChnId = AiChn; stAiChnOutputPortu32PortId = 0; MI_SYS_SetChnOutputPortDepth(&stAiChnOutputPort, 1, 8); /* get port fd */ stChnPort.eModId = E_MI_MODULE_ID_AI; stChnPort.u32DevId = AiDevId; stChnPort.u32ChnId = AiChn; stChnPort.u32PortId = 0; ret = MI_SYS_GetFd(&stChnPort, &s32Fd); if (MI_SUCCESS != ret) { printf("Dev%d Chn%d failed to call MI_SYS_GetFd!!!\n", AiDevId, AiChn); return ret; } /* select 100ms */ FD_ZERO(&readFdSet); FD_SET(s32Fd, &readFdSet); stTimeOut.tv_sec = 0; stTimeOut.tv_usec = 100 * 1000; ret = select(s32Fd + 1, &readFdSet, NULL, NULL, &stTimeOut); if (FD_ISSET(s32Fd, &readFdSet)) { ret = MI_AI_GetFrame(AiDevId, AiChn, &stAiChFrame, &stAecFrame, 0); if (MI_SUCCESS == ret) { /* do something */ MI_AI_ReleaseFrame(AiDevId, AiChn, &stAiChFrame, &stAecFrame); } } /* disable AI Channel */ ret = MI_AI_DisableChn(AiDevId, AiChn); if (MI_SUCCESS != ret) { printf("disable Dev%d Chn%d err:0x%x\n", AiDevId, AiChn, ret); return ret; } /* disable AI Device */ ret = MI_AI_Disable(AiDevId); if (MI_SUCCESS != ret) { printf("disable ai %d err:0x%x\n", AiDevId, ret); return ret; } MI_SYS_Exit();
2.3. MI_AI_GetPubAttr¶
-
Features
Get the AI device properties.
-
Syntax
MI_S32 MI_AI_GetPubAttr(MI_AUDIO_DEV AiDevId, MI_AUDIO_Attr_t *pstAttr); -
Parameters
Table2-3
Parameter Name Description Input/Output AiDevId Audio device number Input pstAttr AI device property pointer Output -
Return value
-
Zero: Successful
-
Non-zero: Failed, see error code for details
-
-
Dependency
-
Header: mi_ai.h
-
Library: libmi_ai.a/libmi_ai.so
-
-
Note
-
The obtained property is the property of the previous configuration
-
If the property has never been configured, it returns a failure.
-
-
Example
Please refer to the MI_AI_SetPubAttr example section.
2.4. MI_AI_Enable¶
-
Features
Enable AI devices.
-
Syntax
MI_S32 MI_AI_Enable(MI_AUDIO_DEV AiDevId); -
Parameters
Table2-4
Parameter Name Description Input/Output AiDevId Audio device number Input -
Return value
-
Zero: Successful
-
Non-zero: Failed, see error code for details
-
-
Dependency
-
Header: mi_ai.h
-
Library: libmi_ai.a/libmi_ai.so
-
-
Note
-
The AI device attribute must be configured before enabling, otherwise the return attribute is not configured incorrectly.
-
If the AI device is already enabled, it will return Success directly.
-
-
Example
Please refer to the MI_AI_SetPubAttr example section.
2.5. MI_AI_Disable¶
-
Features
Disable AI device.
-
Syntax
MI_S32 MI_AI_Disable(MI_AUDIO_DEV AiDevId); -
Parameters
Table2-5
Parameter Name Description Input/Output AiDevId Audio device number Input -
Return value
-
Zero: Successful
-
Non-zero: Failed, see error code for details
-
-
Dependency
-
Header: mi_ai.h
-
Library: libmi_ai.a/libmi_ai.so
-
-
Note
-
If the AI device is already disabled, it will return Success directly.
-
All AI channels enabled under this device must be disabled before disabling the AI device.
-
-
Example
Please refer to the MI_AI_SetPubAttr example section.
2.6. MI_AI_EnableChn¶
-
Features
Enable AI channel.
-
Syntax
MI_S32 MI_AI_EnableChn(MI_AUDIO_DEV AiDevId, MI_AI_CHN AiChn); -
Parameters
Table2-6
Parameter Name Description Input/Output AiDevId Audio device number Input AiChn Audio input channel number.
The supported channel range is determined by the maximum number of channels in the AI device attribute u32ChnCnt.Input -
Return value
-
Zero: Successful
-
Non-zero: Failed, see error code for details
-
-
Dependency
-
Header: mi_ai.h
-
Library: libmi_ai.a/libmi_ai.so
-
-
Note
Before enabling the AI channel, you must first enable the AI device to which it belongs, otherwise it will return the error code that the device is not started.
-
Example
Please refer to the MI_AI_SetPubAttr example section.
2.7. MI_AI_DisableChn¶
-
Features
Disable AI channel.
-
Syntax
MI_S32 MI_AI_DisableChn( AiDevId, MI_AI_CHN AiChn); -
Parameters
Table2-7
Parameter Name Description Input/Output AiDevId Audio device number Input AiChn Audio input channel number.
The supported channel range is determined by the maximum number of channels in the AI device attribute u32ChnCnt.Input -
Return value
-
Zero: Successful
-
Non-zero: Failed, see error code for details
-
-
Dependency
-
Header: mi_ai.h
-
Library: libmi_ai.a/libmi_ai.so
-
-
Note
-
If the channel has already been disabled, success is returned.
-
All AI algorithms enabled under the channel must be disabled before disabling the AI channel.
-
-
Example
Please refer to the MI_AI_SetPubAttr example section.
2.8. MI_AI_GetFrame¶
-
Features
Get audio frames.
-
Syntax
MI_S32 MI_AI_GetFrame(MI_AUDIO_DEV AiDevId, MI_AI_CHN AiChn, MI_AUDIO_Frame_t *pstFrm, MI_AUDIO_AecFrame_t *pstAecFrm , MI_S32 s32MilliSec); -
Parameters
Table2-8
Parameter Name Description Input/Output AiDevId Audio device number Input AiChn Audio input channel number.
The supported channel range is determined by the maximum number of channels u32ChnCnt.Input pstFrm Audio frame structure pointer Output pstAecFrm The echo cancels the reference frame structure body pointer. Output s32MilliSec Timeout for getting data:
-1 indicates blocking mode, waiting for no data;
0 means non-blocking mode, when there is no data, it will return an error;
>0 means to block s32MilliSec milliseconds, and the timeout will return an error.Input -
Return value
-
Zero: Successful
-
Non-zero: Failed, see error code for details
-
-
Dependency
-
Header: mi_ai.h
-
Library: libmi_ai.a/libmi_ai.so
-
-
Note Before obtaining audio frame data, you must first enable the corresponding AI channel. If you need to obtain an echo cancellation reference frame, pstAecFrm cannot be a null pointer. If you do not want to get the echo cancellation reference frame pstAecFrm, you can set it to a null pointer. s32MilliSec value must be greater than equal to -1, -1 is equal to the data acquired using the blocking mode, the data acquired is equal to non-blocking mode 0, is greater than 0, the blocking s32MilliSec milliseconds, and no data timeout then return error. This interface supports select operations. It is recommended to use the select/poll operation instead of timeout parameter.
-
Example
Please refer to the MI_AI_SetPubAttr example section.
2.9. MI_AI_ReleaseFrame¶
-
Features
Release audio frame
-
Syntax
MI_S32 MI_AI_ReleaseFrame(MI_AUDIO_DEV AiDevId, MI_AI_CHN AiChn,MI_AUDIO_Frame_t *pstFrm, MI_AUDIO_AecFrame_t *pstAecFrm); -
Parameters
Table2-9
Parameter Name Description Input/Output AiDevId Audio device number Input AiChn Audio input channel number.
The supported channel range is determined by the maximum number of channels in the AI device attribute u32ChnCnt.Input pstFrm Audio frame structure pointer Input pstAecFrm The echo cancels the reference frame structure body pointer. Input -
Return value
-
Zero: Successful
-
Non-zero: Failed, see error code for details
-
-
Dependency
-
Header: mi_ai.h
-
Library: libmi_ai.a/libmi_ai.so
-
-
Example
Please refer to the MI_AI_SetPubAttr example section.
2.10. MI_AI_SetChnParam¶
-
Features
Set AI channel parameters
-
Syntax
MI_S32 MI_AI_SetChnParam( AiDevId, MI_AI_CHN AiChn, MI_AI_ChnParam_t *pstChnParam); -
Parameters
Table2-10
Parameter Name Description Input/Output AiDevId Audio device number Input AiChn Audio input channel number.
The supported channel range is determined by the maximum number of channels u32ChnCnt.Input pstChnParam Audio parameter structure pointer. Input -
Return value
-
Zero: Successful
-
Non-zero: Failed, see error code for details
-
-
Dependency
-
Header: mi_ai.h
-
Library: libmi_ai.a/libmi_ai.so
-
-
Note
To set AI channel parameter, configure and enable AI device first.
-
Example
The following code shows how to configure and obtain AI channel parameters.
MI_S32 ret; MI_AUDIO_DEV AiDevId = 0; MI_AI_CHN AiChn = 0; MI_AUDIO_Attr_t stAttr; MI_AI_ChnParam_t stChnParam; MI_SYS_Init(); memset(&stAttr, 0x0, sizeof(MI_AUDIO_Attr_t)); stAttr.eBitwidth = E_MI_AUDIO_BIT_WIDTH_16; stAttr.eSamplerate = E_MI_AUDIO_SAMPLE_RATE_8000; stAttr.eSoundmode = E_MI_AUDIO_SOUND_MODE_MONO; stAttr.eWorkmode = E_MI_AUDIO_MODE_I2S_SLAVE; stAttr.u32PtNumPerFrm = 160; stAttr.u32ChnCnt = 1; /* set public attribute of AI device */ ret = MI_AI_SetPubAttr(AiDevId, &stAttr); if (MI_SUCCESS != ret) { printf("set Dev%d attr err:0x%x\n", AiDevId, ret); return ret; } /* enable AI device */ ret = MI_AI_Enable(AiDevId); if (MI_SUCCESS != ret) { printf("enable Dev%d err:0x%x\n", AiDevId, ret); return ret; } /* enable AI Channel */ ret = MI_AI_EnableChn(AiDevId, AiChn); if (MI_SUCCESS != ret) { printf("enable Dev%d Chn%d err:0x%x\n", AiDevId, AiChn, ret); return ret; } memset(&stChnParam, 0x0, sizeof(stChnParam)); stChnParam.stChnGain.bEnableGainSet = TRUE; stChnParam.stChnGain.s16FrontGain = 0; stChnParam.stChnGain.s16RearGain = 0; ret = MI_AI_SetChnParam(AiDevId, AiChn, &stChnParam); if (MI_SUCCESS != ret) { printf("set Dev%d Chn%d param err:0x%x\n", AiDevId, AiChn, ret); return ret; } /* get channel param */ ret = MI_AI_GetChnParam(AiDevId, AiChn, &stChnParam); if (MI_SUCCESS != ret) { printf("get Dev%d Chn%d param err:0x%x\n", AiDevId, AiChn, ret); return ret; } /* disable AI Channel */ ret = MI_AI_DisableChn(AiDevId, AiChn); if (MI_SUCCESS != ret) { printf("disable Dev%d Chn%d err:0x%x\n", AiDevId, AiChn, ret); return ret; } /* disable AI Device */ ret = MI_AI_Disable(AiDevId); if (MI_SUCCESS != ret) { printf("disable ai %d err:0x%x\n", AiDevId, ret); return ret; } MI_SYS_Exit();
2.11. MI_AI_GetChnParam¶
-
Features
Get AI channel parameters
-
Syntax
MI_S32 MI_AI_GetChnParam(MI_AUDIO_DEV AiDevId, MI_AI_CHN AiChn, MI_AI_ChnParam_t *pstChnParam); -
Parameters
Table2-11
Parameter Name Description Input/Output AiDevId Audio device number Input AiChn Audio input channel number.
The supported channel range is determined by the maximum number of channels in the AI device attribute u32ChnCnt.Input pstChnParam Audio parameter structure pointer.. Output -
Return value
-
Zero: Successful
-
Non-zero: Failed, see error code for details
-
-
Dependency
-
Header: mi_ai.h
-
Library: libmi_ai.a/libmi_ai.so
-
-
Example
Please refer to the MI_AI_SetChnParam example section.
2.12. MI_AI_EnableReSmp¶
-
Features
Enable resampling of AI channel.
-
Syntax
MI_S32 MI_AI_EnableReSmp(MI_AUDIO_DEV AiDevId, MI_AI_CHN AiChn, MI_AUDIO_SampleRate_e eOutSampleRate); -
Parameters
Table2-12
Parameter Name Description Input/Output AiDevId Audio device number Input AiChn Audio input channel number.
The supported channel range is determined by the maximum number of channels in the AI device attribute u32ChnCnt.Input eOutSampleRate Output sample rate for audio resampling. Input -
Return value
-
Zero: Successful
-
Non-zero: Failed, see error code for details
-
-
Dependency
-
Header: mi_ai.h
-
Library: libmi_ai.a/libmi_ai.so libSRC_LINUX.so
-
-
Note
After enabling the AI channels, call this interface to enable the resampling function. If enabling beamforming is required, resampling should be enabled after enabling beamforming. This interface is no longer supported in API version 2.19 and later.
-
Example
The following code shows how to implement AI resampling from 8K to 16K.
MI_S32 ret; MI_AUDIO_DEV AiDevId = 0; MI_AI_CHN AiChn = 0; MI_AUDIO_Attr_t stAttr; MI_SYS_Init(); memset(&stAttr, 0x0, sizeof(MI_AUDIO_Attr_t)); stAttr.eBitwidth = E_MI_AUDIO_BIT_WIDTH_16; stAttr.eSamplerate = E_MI_AUDIO_SAMPLE_RATE_8000; stAttr.eSoundmode = E_MI_AUDIO_SOUND_MODE_MONO; stAttr.eWorkmode = E_MI_AUDIO_MODE_I2S_SLAVE; stAttr.u32PtNumPerFrm = 160; stAttr.u32ChnCnt = 1; /* set public attribute of AI device */ ret = MI_AI_SetPubAttr(AiDevId, &stAttr); if (MI_SUCCESS != ret) { printf("set Dev%d attr err:0x%x\n", AiDevId, ret); return ret; } /* enable AI device */ ret = MI_AI_Enable(AiDevId); if (MI_SUCCESS != ret) { printf("enable Dev%d err:0x%x\n", AiDevId, ret); return ret; } /* enable AI Channel */ ret = MI_AI_EnableChn(AiDevId, AiChn); if (MI_SUCCESS != ret) { printf("enable Dev%d Chn%d err:0x%x\n", AiDevId, AiChn, ret); return ret; } ret = MI_AI_EnableReSmp(AiDevId, AiChn, E_MI_AUDIO_SAMPLE_RATE_16000); if (MI_SUCCESS != ret) { printf("resample Dev%d Chn%d err:0x%x\n", AiDevId, AiChn, ret); return ret; } ret = MI_AI_DisableReSmp(AiDevId, AiChn); if (MI_SUCCESS != ret) { printf("disable resample Dev%d Chn%d err:0x%x\n", AiDevId, AiChn, ret); return ret; } /* disable AI Channel */ ret = MI_AI_DisableChn(AiDevId, AiChn); if (MI_SUCCESS != ret) { printf("disable Dev%d Chn%d err:0x%x\n", AiDevId, AiChn, ret); return ret; } /* disable AI Device */ ret = MI_AI_Disable(AiDevId); if (MI_SUCCESS != ret) { printf("disable ai %d err:0x%x\n", AiDevId, ret); return ret; } MI_SYS_Exit();
2.13. MI_AI_DisableReSmp¶
-
Features
Disable resampling of AI channel.
-
Syntax
MI_S32 MI_AI_DisableReSmp( AiDevId, MI_AI_CHN AiChn); -
Parameters
Table2-13
Parameter Name Description Input/Output AiDevId Audio device number Input AiChn Audio input channel number.
The supported channel range is determined by the maximum number of channels in the AI device attribute u32ChnCnt.Input -
Return value
-
Zero: Successful
-
Non-zero: Failed, see error code for details
-
-
Dependency
-
Header: mi_ai.h
-
Library: libmi_ai.a/libmi_ai.so libSRC_LINUX.so
-
-
Note If you no longer use the AI resampling feature, you should call this interface to disable it. This interface is no longer supported in API version 2.19 and later.
-
Example
Please refer to the MI_AI_EnableReSmp example section.
2.14. MI_AI_SetVqeAttr¶
-
Features
Set the sound quality enhancement related properties of AI channel
-
Syntax
MI_S32 MI_AI_SetVqeAttr(MI_AUDIO_DEV AiDevId, MI_AI_CHN AiChn, MI_AUDIO_DEV AoDevId, MI_AO_CHN AoChn, MI_AI_VqeConfig_t *pstVqeConfig); -
Parameters
Table2-14
Parameter Name Description Input/Output AiDevId Audio device number Input AiChn Audio input channel number.
The supported channel range is determined by the maximum number of channels in the AI device attribute u32ChnCnt.Input AoDevId The AO device number used for echo cancellation. Input AoChn The AO channel number used for echo cancellation. The supported channel range is determined by the maximum number of channels u32ChnCnt of AO device. Input pstVqeConfig Audio input sound quality enhancement configuration structure pointer Input -
Return value
-
Zero: Successful
-
Non-zero: Failed, see error code for details
-
-
Dependency
-
Header: mi_ai.h
-
Library: libmi_ai.a/libmi_ai.so libAEC_LINUX.so libAPC_LINUX.so
-
-
Note
Before setting the AI sound quality enhancement function related properties, you must first enable the corresponding AI channel. All algorithms included in Vqe support 8/16k sampling rate, while only ANR/AGC/EQ support 48K. This interface is no longer supported in API version 2.19 and later.
-
Example
The following code shows how to enable and disable sound quality enhancement.
MI_S32 ret; MI_AUDIO_DEV AiDevId = 0; MI_AI_CHN AiChn = 0; MI_AUDIO_Attr_t stAttr; MI_AI_VqeConfig_t stVqeConfig; MI_U32 u32AecSupfreq[] = {4,6,36,49,50,51}; MI_U32 u32AecSupIntensity[] = {5,4,4,5,10,10,10}; MI_S16 s16Compression_ratio_input[] = {-80, -60, -40, -20, 0}; MI_S16 s16Compression_ratio_output[] = {-80, -60, -30, -15, -10}; MI_SYS_Init(); memset(&stAttr, 0x0, sizeof(MI_AUDIO_Attr_t)); stAttr.eBitwidth = E_MI_AUDIO_BIT_WIDTH_16; stAttr.eSamplerate = E_MI_AUDIO_SAMPLE_RATE_8000; stAttr.eSoundmode = E_MI_AUDIO_SOUND_MODE_MONO; stAttr.eWorkmode = E_MI_AUDIO_MODE_I2S_SLAVE; stAttr.u32PtNumPerFrm = 160; stAttr.u32ChnCnt = 1; /* set public attribute of AI device */ ret = MI_AI_SetPubAttr(AiDevId, &stAttr); if (MI_SUCCESS != ret) { printf("set Dev%d attr err:0x%xn", AiDevId, ret); return ret; } /* enable AI device */ ret = MI_AI_Enable(AiDevId); if (MI_SUCCESS != ret) { printf("enable Dev%d err:0x%xn", AiDevId, ret); return ret; } /* enable AI Channel */ ret = MI_AI_EnableChn(AiDevId, AiChn); if (MI_SUCCESS != ret) { printf("enable Dev%d Chn%d err:0x%xn", AiDevId, AiChn, ret); return ret; } /* set vqe attr */ memset(&stVqeConfig, 0x0, sizeof(stVqeConfig)); stVqeConfig.bHpfOpen = TRUE; stVqeConfig.bAecOpen = TRUE; stVqeConfig.bAnrOpen = TRUE; stVqeConfig.bAgcOpen = TRUE; stVqeConfig.bEqOpen = TRUE; stVqeConfig.u32ChnNum = 1; stVqeConfig.s32WorkSampleRate = 8000; stVqeConfig.s32FrameSample = 128; stVqeConfig.stHpfCfg.eMode = E_MI_AUDIO_ALGORITHM_MODE_USER; stVqeConfig.stHpfCfg.eHpfFreq = E_MI_AUDIO_HPF_FREQ_150; stVqeConfig.stAecCfg.bComfortNoiseEnable = TRUE; stVqeConfig.stAecCfg.s16DelaySample = 0; memcpy(stVqeConfig.stAecCfg.u32AecSupfreq, u32AecSupfreq, **sizeof**(u32AecSupfreq)); memcpy(stVqeConfig.stAecCfg.u32AecSupIntensity, u32AecSupIntensity, **sizeof**(u32AecSupIntensity)); stVqeConfig.stAnrCfg.eMode = E_MI_AUDIO_ALGORITHM_MODE_MUSIC; stVqeConfig.stAnrCfg.u32NrIntensity = 30; stVqeConfig.stAnrCfg.u32NrSmoothLevel = 10; stVqeConfig.stAnrCfg.eNrSpeed = E_MI_AUDIO_NR_SPEED_MID; stVqeConfig.stAgcCfg.eMode = E_MI_AUDIO_ALGORITHM_MODE_USER; stVqeConfig.stAgcCfg.stAgcGainInfo.s32GainMax = 15; stVqeConfig.stAgcCfg.stAgcGainInfo.s32GainMin = 0; stVqeConfig.stAgcCfg.stAgcGainInfo.s32GainInit = 0; stVqeConfig.stAgcCfg.u32DropGainMax = 55; stVqeConfig.stAgcCfg.u32AttackTime = 1; stVqeConfig.stAgcCfg.u32ReleaseTime = 6; memcpy(stVqeConfig.stAgcCfg.s16Compression_ratio_input, s16Compression_ratio_input, sizeof(s16Compression_ratio_input)); memcpy(stVqeConfig.stAgcCfg.s16Compression_ratio_output, s16Compression_ratio_output, sizeof(s16Compression_ratio_output)); stVqeConfig.stAgcCfg.s32TargetLevelDb = -3; stVqeConfig.stAgcCfg.s32NoiseGateDb = -80; stVqeConfig.stAgcCfg.u32NoiseGateAttenuationDb = 0; stVqeConfig.stEqCfg.eMode = E_MI_AUDIO_ALGORITHM_MODE_USER; ret = MI_AI_SetVqeAttr(AiDevId, AiChn, 0, 0, &stVqeConfig); if (MI_SUCCESS != ret) { printf("set vqe attr Dev%d Chn%d err:0x%x\n", AiDevId, AiChn, ret); return ret; } ret = MI_AI_GetVqeAttr(AiDevId, AiChn, 0, 0, &stVqeConfig); if (MI_SUCCESS != ret) { printf("get vqe attr Dev%d Chn%d err:0x%x\n", AiDevId, AiChn, ret); return ret; } /* enable vqe */ ret = MI_AI_EnableVqe(AiDevId, AiChn); if (MI_SUCCESS != ret) { printf("enable vqe Dev%d Chn%d err:0x%x\n", AiDevId, AiChn, ret); return ret; } /* disable vqe */ ret = MI_AI_DisableVqe(AiDevId, AiChn); if (MI_SUCCESS != ret) { printf("disable vqe Dev%d Chn%d err:0x%x\n", AiDevId, AiChn, ret); return ret; } /* disable AI Channel */ ret = MI_AI_DisableChn(AiDevId, AiChn); if (MI_SUCCESS != ret) { printf("disable Dev%d Chn%d err:0x%x\n", AiDevId, AiChn, ret); return ret; } /* disable AI Device */ ret = MI_AI_Disable(AiDevId); if (MI_SUCCESS != ret) { printf("disable ai %d err:0x%x\n", AiDevId, ret); return ret; } MI_SYS_Exit();
2.15. MI_AI_GetVqeAttr¶
-
Features
Get the sound quality enhancement related properties of AI channel.
-
Syntax
MI_S32 MI_AI_GetVqeAttr(MI_AUDIO_DEV AiDevId, MI_AI_CHN AiChn, MI_AI_VqeConfig_t *pstVqeConfig); -
Parameters
Table2-15
Parameter Name Description Input/Output AiDevId Audio device number Input AiChn Audio input channel number.
The supported channel range is determined by the maximum number of channels in the AI device attribute u32ChnCnt.Input pstVqeConfig Audio input sound quality enhancement configuration structure pointer Output -
Return value
-
Zero: Successful
-
Non-zero: Failed, see error code for details
-
-
Dependency
-
Header: mi_ai.h
-
Library: libmi_ai.a/libmi_ai.so libAEC_LINUX.so libAPC_LINUX.so
-
-
Note
- This interface is no longer supported in API version 2.19 and later.
-
Example
Please refer to the MI_AI_SetVqeAttr example section.
2.16. MI_AI_EnableVqe¶
-
Features
Enable sound quality enhancements of AI channel.
-
Syntax
MI_S32 MI_AI_EnableVqe(MI_AUDIO_DEV AiDevId, MI_AI_CHN AiChn); -
Parameters
Table2-16
Parameter Name Description Input/Output AiDevId Audio device number Input AiChn Audio input channel number.
The supported channel range is determined by the maximum number of channels in the AI device attribute u32ChnCnt.Input -
Return value
-
Zero: Successful
-
Non-zero: Failed, see error code for details
-
-
Dependency
-
Header: mi_ai.h
-
Library: libmi_ai.a/libmi_ai.so libAPC_LINUX.so libAEC_LINUX.so
-
-
Note
Before enabling the sound quality enhancement function, you must first enable the corresponding AI channel and set the relevant attributes of the sound quality enhancement function of the corresponding AI channel.
When the sound quality enhancement function of the same AI channel is enabled multiple times, the return is successful.
This interface is no longer supported in API version 2.19 and later.
-
Example
Please refer to the MI_AI_SetVqeAttr example section..
2.17. MI_AI_DisableVqe¶
-
Features
Disable sound quality enhancements of AI channel
-
Syntax
MI_S32 MI_AI_DisableVqe(MI_AUDIO_DEV AiDevId, MI_AI_CHN AiChn); -
Parameters
Table2-17
Parameter Name Description Input/Output AiDevId Audio device number Input AiChn Audio input channel number.
The supported channel range is determined by the maximum number of channels in the AI device attribute u32ChnCnt.Input -
Return value
-
Zero: Successful
-
Non-zero: Failed, see error code for details
-
-
Dependency
-
Header: mi_ai.h
-
Library: libmi_ai.a/libmi_ai.so libAPC_LINUX.so libAPC_LINUX.so
-
-
Note
When the AI sound quality enhancement is no longer used, this interface should be called to disable it.
The sound quality enhancement function of the same AI channel is disabled multiple times and the return is successful.
This interface is no longer supported in API version 2.19 and later.
-
Example
Please refer to the MI_AI_SetVqeAttr example section..
2.18. MI_AI_ClrPubAttr¶
-
Features
Clear AI device properties.
-
Syntax
MI_S32 MI_AI_ClrPubAttr(MI_AUDIO_DEV AiDevId); -
Parameters
Table2-18
Parameter Name Description Input/Output AiDevId Audio device number Input -
Return value
-
Zero: Successful
-
Non-zero: Failed, see error code for details
-
-
Dependency
-
Header: mi_ai.h
-
Library: libmi_ai.a/libmi_ai.so
-
-
Note
Before you can clear device properties, you need to stop the device first.
-
Example
The following code shows how to implement clearing device properties.
MI_S32 ret; MI_AUDIO_DEV AiDevId = 0; MI_AI_CHN AiChn = 0; MI_AUDIO_Attr_t stAttr; memset(&stAttr, 0x0, sizeof(MI_AUDIO_Attr_t)); stAttr.eBitwidth = E_MI_AUDIO_BIT_WIDTH_16; stAttr.eSamplerate = E_MI_AUDIO_SAMPLE_RATE_8000; stAttr.eSoundmode = E_MI_AUDIO_SOUND_MODE_MONO; stAttr.eWorkmode = E_MI_AUDIO_MODE_I2S_SLAVE; stAttr.u32PtNumPerFrm = 160; stAttr.u32ChnCnt = 1; /* set public attribute of AI device */ ret = MI_AI_SetPubAttr(AiDevId, &stAttr); if (MI_SUCCESS != ret) { printf("set Dev%d attr err:0x%x\n", AiDevId, ret); return ret; } /* clean public attr of AI device*/ ret = MI_AI_ClrPubAttr(AiDevId); if (MI_SUCCESS != ret) { printf("clean Dev%d attr err:0x%x\n", AiDevId, ret); return ret; }
2.19. MI_AI_SaveFile¶
-
Features
Turn on audio input to save files.
-
Syntax
MI_S32 MI_AI_SaveFile(MI_AUDIO_DEV AiDevId, MI_AI_CHN AiChn, MI_AUDIO_SaveFileInfo_t *pstSaveFileInfo); -
Parameters
Table2-19
Parameter Name Description Input/Output AiDevId Audio device number Input AiChn Audio input channel number.
The supported channel range is determined by the maximum number of channels u32ChnCnt.Input pstSaveFileInfo Audio save file attribute structure pointer. Input -
Return value
-
Zero: Successful
-
Non-zero: Failed, see error code for details
-
-
Dependency
-
Header: mi_ai.h
-
Library: libmi_ai.a/libmi_ai.so
-
-
Note
- This interface is no longer supported in API version 2.19 and later.
2.20. MI_AI_SetVqeVolume¶
-
Features
Set the volume level of AI channel.
-
Syntax
MI_S32 MI_AI_SetVqeVolume(MI_AUDIO_DEV AiDevId, MI_AI_CHN AiChn, MI_S32 s32VolumeDb); -
Parameters
Table2-20
Parameter Name Description Input/Output AiDevId Audio device number Input AiChn Audio input channel number.
The supported channel range is determined by the maximum number of channels in the AI device attribute u32ChnCnt.Input s32VolumeDb The volume level. Input -
Return value
-
Zero: Successful
-
Non-zero: Failed, see error code for details
-
-
Dependency
-
Header: mi_ai.h
-
Library: libmi_ai.a/libmi_ai.so
-
-
Note
The following table describes the corresponding gain (DB) of s32volumedb under each device. For Amic and Line in devices, s32volumedb represents the analog gain of the device. For macaron series, pudding series and Ispahan series chips, s32volumedb is the gain corresponding to Dmic.
Table2-21
s32VolumeDb Amic(dB) Line in(dB) Pretzel series
Taiyaki series
Takoyaki series
Tiramisu series
Ikayaki series
Dmic(dB)0 -6 -6 0 1 -3 -3 6 2 0 0 12 3 3 3 18 4 6 6 24 5 9 9 6 12 12 7 15 15 8 18 9 21 10 24 11 27 12 30 13 33 14 36 15 39 16 42 17 45 18 48 19 51 20 54 21 57 -
Example
The following code shows how to implement the function of setting and obtaining gain.
1. MI_S32 ret; 2. MI_AUDIO_DEV AiDevId = 0; 3. MI_AI_CHN AiChn = 0; 4. MI_AUDIO_Attr_t stAttr; 5. MI_S32 s32VolumeDb; 6. MI_SYS_Init(); 7. memset(&stAttr, 0x0, sizeof(MI_AUDIO_Attr_t)); 8. stAttr.eBitwidth = E_MI_AUDIO_BIT_WIDTH_16; 9. stAttr.eSamplerate = E_MI_AUDIO_SAMPLE_RATE_8000; 10. stAttr.eSoundmode = E_MI_AUDIO_SOUND_MODE_MONO; 11. stAttr.eWorkmode = E_MI_AUDIO_MODE_I2S_SLAVE; 12. stAttr.u32PtNumPerFrm = 160; 13. stAttr.u32ChnCnt = 1; 14. /* set public attribute of AI device */ 15. ret = MI_AI_SetPubAttr(AiDevId, &stAttr); 16. if (MI_SUCCESS != ret) 17. { 18. printf("set Dev%d attr err:0x%x\n", AiDevId, ret); 19. return ret; 20. } 21. /* enable AI device */ 22. ret = MI_AI_Enable(AiDevId); 23. if (MI_SUCCESS != ret) 24. { 25. printf("enable Dev%d err:0x%x\n", AiDevId, ret); 26. return ret; 27. } 28. /* enable AI Channel */ 29. ret = MI_AI_EnableChn(AiDevId, AiChn); 30. if (MI_SUCCESS != ret) 31. { 32. printf("enable Dev%d Chn%d err:0x%x\n", AiDevId, AiChn, ret); 33. return ret; 34. } 35. /* set channel volume */ 36. s32VolumeDb = 12; 37. ret = MI_AI_SetVqeVolume(AiDevId, AiChn, s32VolumeDb); 38. if (MI_SUCCESS != ret) 39. { 40. printf("set volume Dev%d Chn%d err:0x%x\n", AiDevId, AiChn, ret); 41. return ret; 42. } 43. /* get channel volume */ 44. ret = MI_AI_GetVqeVolume(AiDevId, AiChn, &s32VolumeDb); 45. if (MI_SUCCESS != ret) 46. { 47. printf("get volume Dev%d Chn%d err:0x%x\n", AiDevId, AiChn, ret); 48. return ret; 49. } 50. /* disable AI Channel */ 51. ret = MI_AI_DisableChn(AiDevId, AiChn); 52. if (MI_SUCCESS != ret) 53. { 54. printf("disable Dev%d Chn%d err:0x%x\n", AiDevId, AiChn, ret); 55. return ret; 56. } 57. /* disable AI Device */ 58. ret = MI_AI_Disable(AiDevId); 59. if (MI_SUCCESS != ret) 60. { 61. printf("disable ai %d err:0x%x\n", AiDevId, ret); 62. return ret; 63. } 64. MI_SYS_Exit();
2.21. MI_AI_GetVqeVolume¶
-
Features
Get the volume level of AI channel.
-
Syntax
MI_S32 MI_AI_GetVqeVolume(MI_AUDIO_DEV AiDevId, MI_AI_CHN AiChn, MI_S32 *ps32VolumeDb); -
Parameters
Table2-22
Parameter Name Description Input/Output AiDevId Audio device number Input AiChn Audio input channel number.
The supported channel range is determined by the maximum number of channels in the AI device attribute u32ChnCnt.Input ps32VolumeDb The volume level. Output -
Return value
-
Zero: Successful
-
Non-zero: Failed, see error code for details
-
-
Dependency
-
Header: mi_ai.h
-
Library: libmi_ai.a/libmi_ai.so
-
-
Example
Please refer to the MI_AI_SetVqeVolume example section.
2.22. MI_AI_SetAencAttr¶
-
Features
Set encoding function related properties of AI channel.
-
Syntax
MI_S32 MI_AI_SetAencAttr (MI_AUDIO_DEV AiDevId,MI_AI_CHN AiChn, MI_AI_AencConfig_t *pstAencConfig); -
Parameters
Table2-23
Parameter Name Description Input/Output AiDevId Audio device number Input AiChn Audio input channel number.
The supported channel range is determined by the maximum number of channels in the AI device attribute u32ChnCnt.Input pstAencConfig Audio coding configuration structure pointer Input -
Return value
-
Zero: Successful
-
Non-zero: Failed, see error code for details
-
-
Dependency
-
Header: mi_ai.h
-
Library: libmi_ai.a/libmi_ai.so libg711.so libg726.so
-
-
Note
-
To set the encoding function, enable the AI channel first.
-
This interface is no longer supported in API version 2.19 and later.
-
-
Example
The following code shows how to enable and disable the function of encoding parameters.
1. MI_S32 ret; 2. MI_AUDIO_DEV AiDevId = 0; 3. MI_AI_CHN AiChn = 0; 4. MI_AUDIO_Attr_t stAttr; 5. MI_AI_AencConfig_t stAiAencConfig; 6. MI_SYS_Init(); 7. memset(&stAttr, 0x0, sizeof(MI_AUDIO_Attr_t)); 8. stAttr.eBitwidth = E_MI_AUDIO_BIT_WIDTH_16; 9. stAttr.eSamplerate = E_MI_AUDIO_SAMPLE_RATE_8000; 10. stAttr.eSoundmode = E_MI_AUDIO_SOUND_MODE_MONO; 11. stAttr.eWorkmode = E_MI_AUDIO_MODE_I2S_SLAVE; 12. stAttr.u32PtNumPerFrm = 160; 13. stAttr.u32ChnCnt = 1; 14. /* set public attribute of AI device */ 15. ret = MI_AI_SetPubAttr(AiDevId, &stAttr); 16. if (MI_SUCCESS != ret) 17. { 18. printf("set Dev%d attr err:0x%x\n", AiDevId, ret); 19. return ret; 20. } 21. /* enable AI device */ 22. ret = MI_AI_Enable(AiDevId); 23. if (MI_SUCCESS != ret) 24. { 25. printf("enable Dev%d err:0x%x\n", AiDevId, ret); 26. return ret; 27. } 28. /* enable AI Channel */ 29. ret = MI_AI_EnableChn(AiDevId, AiChn); 30. if (MI_SUCCESS != ret) 31. { 32. printf("enable Dev%d Chn%d err:0x%x\n", AiDevId, AiChn, ret); 33. return ret; 34. } 35. /* set aenc attr */ 36. memset(&stAiAencConfig, 0x0, sizeof(stAiAencConfig)); 37. stAiAencConfig.eAencType = E_MI_AUDIO_AENC_TYPE_G711A; 38. ret = MI_AI_SetAencAttr(AiDevId, AiChn, &stAiAencConfig); 39. if (MI_SUCCESS != ret) 40. { 41. printf("set aenc attr Dev%d Chn%d err:0x%x\n", AiDevId, AiChn, ret); 42. return ret; 43. } 44. /* get aenc attr */ 45. memset(&stAiAencConfig, 0x0, sizeof(stAiAencConfig)); 46. ret = MI_AI_GetAencAttr(AiDevId, AiChn, &stAiAencConfig); 47. if (MI_SUCCESS != ret) 48. { 49. printf("get aenc attr Dev%d Chn%d err:0x%x\n", AiDevId, AiChn, ret); 50. return ret; 51. } 52. /* enable aenc */ 53. ret = MI_AI_EnableAenc(AiDevId, AiChn); 54. if (MI_SUCCESS != ret) 55. { 56. printf("enable aenc Dev%d Chn%d err:0x%x\n", AiDevId, AiChn, ret); 57. return ret; 58. } 59. /* disable aenc */ 60. ret = MI_AI_DisableAenc(AiDevId, AiChn); 61. if (MI_SUCCESS != ret) 62. { 63. printf("disable aenc Dev%d Chn%d err:0x%x\n", AiDevId, AiChn, ret); 64. return ret; 65. } 66. /* disable AI Channel */ 67. ret = MI_AI_DisableChn(AiDevId, AiChn); 68. if (MI_SUCCESS != ret) 69. { 70. printf("disable Dev%d Chn%d err:0x%x\n", AiDevId, AiChn, ret); 71. return ret; 72. } 73. /* disable AI Device */ 74. ret = MI_AI_Disable(AiDevId); 75. if (MI_SUCCESS != ret) 76. { 77. printf("disable ai %d err:0x%x\n", AiDevId, ret); 78. return ret; 79. } 80. MI_SYS_Exit();
2.23. MI_AI_GetAencAttr¶
-
Features
Get encoding function related properties of AI channel
-
Syntax
MI_S32 MI_AI_GetAencAttr (MI_AUDIO_DEV AiDevId, MI_AI_CHN AiChn, MI_AI_AencConfig_t *pstAencConfig); -
Parameters
Table2-24
Parameter Name Description Input/Output AiDevId Audio device number Input AiChn Audio input channel number.
The supported channel range is determined by the maximum number of channels in the AI device attribute u32ChnCnt.Input pstAencConfig Audio coding configuration structure pointer Output -
Return value
-
Zero: Successful
-
Non-zero: Failed, see error code for details
-
-
Dependency
-
Header: mi_ai.h
-
Library: libmi_ai.a/libmi_ai.so libg711.so libg726.so
-
-
Note
- This interface is no longer supported in API version 2.19 and later.
-
Example
Please refer to the MI_AI_SetAencAttr example section..
2.24. MI_AI_EnableAenc¶
-
Features
Enable encoding of AI channel.
-
Syntax
MI_S32 MI_AI_EnableAenc (MI_AUDIO_DEV AiDevId, MI_AI_CHN AiChn); -
Parameters
Table2-25
Parameter Name Description Input/Output AiDevId Audio device number Input AiChn Audio input channel number.
The supported channel range is determined by the maximum number of channels in the AI device attribute u32ChnCnt.Input -
Return value
-
Zero: Successful
-
Non-zero: Failed, see error code for details
-
-
Dependency
-
Header: mi_ai.h
-
Library: libmi_ai.a/libmi_ai.so libg711.so libg726.so
-
-
Note
-
Before enabling the coding function, you must enable the corresponding AI channel and set the encoding attributes.
-
This interface is no longer supported in API version 2.19 and later.
-
-
Example
Please refer to the MI_AI_SetAencAttr example section..
2.25. MI_AI_DisableAenc¶
-
Features
Disable encoding of AI channel.
-
Syntax
MI_S32 MI_AI_DisableAenc (MI_AUDIO_DEV AiDevId, MI_AI_CHN AiChn); -
Parameters
Table2-26
Parameter Name Description Input/Output AiDevId Audio device number Input AiChn Audio input channel number.
The supported channel range is determined by the maximum number of channels in the AI device attribute u32ChnCnt.Input -
Return value
-
Zero: Successful
-
Non-zero: Failed, see error code for details
-
-
Dependency
-
Header: mi_ai.h
-
Library: libmi_ai.a/libmi_ai.so libg711.so libg726.so
-
-
Note
- This interface is no longer supported in API version 2.19 and later.
-
Example
Please refer to the MI_AI_SetAencAttr example section..
2.26. MI_AI_SetAedAttr¶
-
Features
Set sound event detection function related properties of AI channel.
-
Syntax
MI_S32 MI_AI_SetAedAttr(MI_AUDIO_DEV AiDevId, MI_AI_CHN AiChn, MI_AI_AedConfig_t *pstAedConfig); -
Parameters
Table2-27
Parameter Name Description Input/Output AiDevId Audio device number Input AiChn Audio input channel number.
The supported channel range is determined by the maximum number of channels in the AI device attribute u32ChnCnt.Input pstAedConfig Sound event detecting configuration structure pointer Input -
Return value
-
Zero: Successful
-
Non-zero: Failed, see error code for details
-
-
Dependency
-
Header: mi_ai.h
-
Library: libmi_ai.a/libmi_ai.so libAED_LINUX.so
-
-
Note
-
To set the sound event detection function, enable the AI channel first.
-
This interface is no longer supported in API version 2.19 and later.
-
-
Example
The following code shows how to set sound event detection parameters, enable sound event detection, and obtain sound event detection results.
1. MI_S32 ret; 2. MI_AUDIO_Attr_t stAttr; 3. MI_AUDIO_Dev AiDevId = 0; 4. MI_AI_CHN AiChn = 0; 5. MI_SYS_ChnPort_t stChnPort; 6. MI_S32 s32Fd; 7. fd_set readFdSet; 8. struct timeval stTimeOut; 9. MI_AUDIO_Frame_t stAiChFrame; 10. MI_AUDIO_AecFrame_t stAecFrame; 11. MI_SYS_ChnPort_t stAiChnOutputPort; 12. MI_AI_AedConfig_t stAiAedConfig; 13. MI_AI_AedResult_t stAedResult; 14. MI_SYS_Init(); 15. stAttr.eBitwidth = E_MI_AUDIO_BIT_WIDTH_16; 16. stAttr.eSamplerate = E_MI_AUDIO_SAMPLE_RATE_8000; 17. stAttr.eSoundmode = E_MI_AUDIO_SOUND_MODE_MONO; 18. stAttr.eWorkmode = E_MI_AUDIO_MODE_I2S_SLAVE; 19. stAttr.u32PtNumPerFrm = 160; 20. stAttr.u32ChnCnt = 1; 21. /* set public attribute of AI device */ 22. ret = MI_AI_SetPubAttr(AiDevId, &stAttr); 23. if (MI_SUCCESS != ret) 24. { 25. printf("set ai %d attr err:0x%x\n", AiDevId, ret); 26. return ret; 27. } 28. /* get public attribute of AI device */ 29. ret = MI_AI_GetPubAttr(AiDevId, &stAttr); 30. if (MI_SUCCESS != ret) 31. { 32. printf("get ai %d attr err:0x%x\n", AiDevId, ret); 33. return ret; 34. } 35. /* enable AI device */ 36. ret = MI_AI_Enable(AiDevId); 37. if (MI_SUCCESS != ret) 38. { 39. printf("enable ai %d err:0x%x\n", AiDevId, ret); 40. return ret; 41. } 42. /* enable AI Channel */ 43. ret = MI_AI_EnableChn(AiDevId, AiChn); 44. if (MI_SUCCESS != ret) 45. { 46. printf("enable Dev%d Chn%d err:0x%x\n", AiDevId, AiChn, ret); 47. return ret; 48. } 49. memset(&stAiAedConfig, 0x0, sizeof(stAiAedConfig)); 50. stAiAedConfig.bEnableNr = TRUE; 51. stAiAedConfig.eSensitivity = E_MI_AUDIO_AED_SEN_HIGH; 52. stAiAedConfig.s32OperatingPoint = -5; 53. stAiAedConfig.s32VadThresholdDb = -40; 54. stAiAedConfig.s32LsdThresholdDb = -15; 55. /* set aed attr */ 56. ret = MI_AI_SetAedAttr(AiDevId, AiChn, &stAiAedConfig); 57. if (MI_SUCCESS != ret) 58. { 59. printf("set aed attr Dev%d Chn%d err:0x%x\n", AiDevId, AiChn, ret); 60. return ret; 61. } 62. /* get aed attr */ 63. ret = MI_AI_GetAedAttr(AiDevId, AiChn, &stAiAedConfig); 64. if (MI_SUCCESS != ret) 65. { 66. printf("get aed attr Dev%d Chn%d err:0x%x\n", AiDevId, AiChn, ret); 67. return ret; 68. } 69. /* enable aed */ 70. ret = MI_AI_EnableAed(AiDevId, AiChn); 71. if (MI_SUCCESS != ret) 72. { 73. printf("enable aed Dev%d Chn%d err:0x%x\n", AiDevId, AiChn, ret); 74. return ret; 75. } 76. /* set buffer depth */ 77. stAiChnOutputPort.eModId = E_MI_MODULE_ID_AI; 78. stAiChnOutputPort.u32DevId = AiDevId; 79. stAiChnOutputPort.u32ChnId = AiChn; 80. stAiChnOutputPortu32PortId = 0; 81. MI_SYS_SetChnOutputPortDepth(&stAiChnOutputPort, 1, 8); 82. /* get port fd */ 83. stChnPort.eModId = E_MI_MODULE_ID_AI; 84. stChnPort.u32DevId = AiDevId; 85. stChnPort.u32ChnId = AiChn; 86. stChnPort.u32PortId = 0; 87. ret = MI_SYS_GetFd(&stChnPort, &s32Fd); 88. if (MI_SUCCESS != ret) 89. { 90. printf("Dev%d Chn%d failed to call MI_SYS_GetFd!!!\n", AiDevId, AiChn); 91. return ret; 92. } 93. /* select 100ms */ 94. FD_ZERO(&readFdSet); 95. FD_SET(s32Fd, &readFdSet); 96. stTimeOut.tv_sec = 0; 97. stTimeOut.tv_usec = 100 * 1000; 98. ret = select(s32Fd + 1, &readFdSet, NULL, NULL, &stTimeOut); 99. if (FD_ISSET(s32Fd, &readFdSet)) 100. { 101. ret = MI_AI_GetFrame(AiDevId, AiChn, &stAiChFrame, &stAecFrame, 0); 102. if (MI_SUCCESS == ret) 103. { 104. /* get aed result */ 105. MI_AI_GetAedResult(AiDevId, AiChn, &stAedResult); 106. MI_AI_ReleaseFrame(AiDevId, AiChn, &stAiChFrame, &stAecFrame); 107. } 108. } 109. /* disable aed */ 110. ret = MI_AI_DisableAed(AiDevId, AiChn); 111. if (MI_SUCCESS != ret) 112. { 113. printf("disable aed Dev%d Chn%d err:0x%x\n", AiDevId, AiChn, ret); 114. return ret; 115. } 116. /* disable AI Channel */ 117. ret = MI_AI_DisableChn(AiDevId, AiChn); 118. if (MI_SUCCESS != ret) 119. { 120. printf("disable Dev%d Chn%d err:0x%x\n", AiDevId, AiChn, ret); 121. return ret; 122. } 123. /* disable AI Device */ 124. ret = MI_AI_Disable(AiDevId); 125. if (MI_SUCCESS != ret) 126. { 127. printf("disable ai %d err:0x%x\n", AiDevId, ret); 128. return ret; 129. } 130. MI_SYS_Exit();
2.27. MI_AI_GetAedAttr¶
-
Features
Get sound event detection function related properties of AI channel.
-
Syntax
MI_S32 MI_AI_GetAedAttr(MI_AUDIO_DEV AiDevId,MI_AI_CHN AiChn, MI_AI_AedConfig_t *pstAedConfig); -
Parameters
Table2-28
Parameter Name Description Input/Output AiDevId Audio device number Input AiChn Audio input channel number.
The supported channel range is determined by the maximum number of channels in the AI device attribute u32ChnCnt.Input pstAedConfig Sound event detecting configuration structure pointer Output -
Return value
-
Zero: Successful
-
Non-zero: Failed, see error code for details
-
-
Dependency
-
Header: mi_ai.h
-
Library: libmi_ai.a/libmi_ai.so libAED_LINUX.so
-
-
Note
- This interface is no longer supported in API version 2.19 and later.
-
Example
Please refer to the MI_AI_SetAedAttr example section.
2.28. MI_AI_EnableAed¶
-
Features
Enable sound event detection of AI channel.
-
Syntax
MI_S32 MI_AI_EnableAed(MI_AUDIO_DEV AiDevId, MI_AI_CHN AiChn); -
Parameters
Table2-29
Parameter Name Description Input/Output AiDevId Audio device number Input AiChn Audio input channel number.
The supported channel range is determined by the maximum number of channels in the AI device attribute u32ChnCnt.Input -
Return value
-
Zero: Successful
-
Non-zero: Failed, see error code for details
-
-
Dependency
-
Header: mi_ai.h
-
Library: libmi_ai.a/libmi_ai.so libAED_LINUX.so
-
-
Note
-
Before enabling the sound event detection function, the AI channel must be enabled and the sound event detection property must be set first.
-
This interface is no longer supported in API version 2.19 and later.
-
-
Example
Please refer to the MI_AI_SetAedAttr example section.
2.29. MI_AI_DisableAed¶
-
Features
Disable sound event detection of AI channel.
-
Syntax
MI_S32 MI_AI_DisableAed(MI_AUDIO_DEV AiDevId, MI_AI_CHN AiChn); -
Parameters
Table2-30
Parameter Name Description Input/Output AiDevId Audio device number Input AiChn Audio input channel number.
The supported channel range is determined by the maximum number of channels in the AI device attribute u32ChnCnt.Input -
Return value
-
Zero: Successful
-
Non-zero: Failed, see error code for details
-
-
Dependency
-
Header: mi_ai.h
-
Library: libmi_ai.a/libmi_ai.so libAED_LINUX.so
-
-
Note
- This interface is no longer supported in API version 2.19 and later.
-
Example
Please refer to the MI_AI_SetAedAttr example section.
2.30. MI_AI_GetAedResult¶
-
Features
Get the sound event detection result of AI channel.
-
Syntax
MI_S32 MI_AI_GetAedResult(MI_AUDIO_DEV AiDevId, MI_AI_CHN AiChn, MI_AI_AedResult_t *pstAedResult); -
Parameters
Table2-31
Parameter Name Description Input/Output AiDevId Audio device number Input AiChn Audio input channel number.
The supported channel range is determined by the maximum number of channels in the AI device attribute u32ChnCnt.Input pstAedResult Sound event detection result structure pointer. Output -
Return value
-
Zero: Successful
-
Non-zero: Failed, see error code for details
-
-
Dependency
-
Header: mi_ai.h
-
Library: libmi_ai.a/libmi_ai.so libAED_LINUX.so
-
-
Note
- This interface is no longer supported in API version 2.19 and later.
-
Example
Please refer to the MI_AI_SetAedAttr example section.
2.31. MI_AI_SetExtAecChn¶
-
Features
Set the external echo cancellation function reference AI channel.
-
Syntax
MI_S32 MI_AI_SetExtAecChn(MI_AUDIO_DEV AiDevId, MI_AI_CHN AiChn, MI_AI_CHN AiAECSndChn); -
Parameters
Table2-32
Parameter Name Description Input/Output AiDevId Audio device number Input AiChn Audio input channel number.
The supported channel range is determined by the maximum number of channels in the AI device attribute u32ChnCnt.Input AiAECSndChn The external echo cancellation function reference AI channel. Input -
Return value
-
Zero: Successful
-
Non-zero: Failed, see error code for details
-
-
Dependency
-
Header: mi_ai.h
-
Library: libmi_ai.a/libmi_ai.so
-
-
Note
- The external echo reference channel needs to be set before the channel is enabled. This interface is currently supported in Mono mode only.
-
Example
The following code shows how to set the external AEC reference channel.
1. MI_S32 ret; 2. MI_AUDIO_Attr_t stAttr; 3. MI_AUDIO_Dev AiDevId = 0; 4. MI_AI_CHN AiChn = 0; 5. MI_AI_CHN ExtAecChn = 0; 6. MI_SYS_Init(); 7. stAttr.eBitwidth = E_MI_AUDIO_BIT_WIDTH_16; 8. stAttr.eSamplerate = E_MI_AUDIO_SAMPLE_RATE_8000; 9. stAttr.eSoundmode = E_MI_AUDIO_SOUND_MODE_MONO; 10. stAttr.eWorkmode = E_MI_AUDIO_MODE_I2S_SLAVE; 11. stAttr.u32PtNumPerFrm = 160; 12. stAttr.u32ChnCnt = 1; 13. /* set public attribute of AI device */ 14. ret = MI_AI_SetPubAttr(AiDevId, &stAttr); 15. if (MI_SUCCESS != ret) 16. { 17. printf("set ai %d attr err:0x%x\n", AiDevId, ret); 18. return ret; 19. } 20. /* get public attribute of AI device */ 21. ret = MI_AI_GetPubAttr(AiDevId, &stAttr); 22. if (MI_SUCCESS != ret) 23. { 24. printf("get ai %d attr err:0x%x\n", AiDevId, ret); 25. return ret; 26. } 27. /* enable AI device */ 28. ret = MI_AI_Enable(AiDevId); 29. if (MI_SUCCESS != ret) 30. { 31. printf("enable ai %d err:0x%x\n", AiDevId, ret); 32. return ret; 33. } 34. /* set ext Aec Chn */ 35. ret = MI_AI_SetExtAecChn(AiDevId, AiChn, ExtAecChn); 36. if (MI_SUCCESS != ret) 37. { 38. printf("set ext aec chn Dev%d Chn%d err:0x%x\n", AiDevId, AiChn, ret); 39. return ret; 40. } 41. /* enable AI Channel */ 42. ret = MI_AI_EnableChn(AiDevId, AiChn); 43. if (MI_SUCCESS != ret) 44. { 45. printf("enable Dev%d Chn%d err:0x%x\n", AiDevId, AiChn, ret); 46. return ret; 47. } 48. /* disable AI Channel */ 49. ret = MI_AI_DisableChn(AiDevId, AiChn); 50. if (MI_SUCCESS != ret) 51. { 52. printf("disable Dev%d Chn%d err:0x%x\n", AiDevId, AiChn, ret); 53. return ret; 54. } 55. /* disable AI Device */ 56. ret = MI_AI_Disable(AiDevId); 57. if (MI_SUCCESS != ret) 58. { 59. printf("disable ai %d err:0x%x\n", AiDevId, ret); 60. return ret; 61. } 62. MI_SYS_Exit();
2.32. MI_AI_SetSslInitAttr¶
-
Features
Set Sound source localization function initialized properties of AI channel
-
Syntax
MI_S32 MI_AI_SetSslInitAttr(MI_AUDIO_DEV AiDevId, MI_AI_CHN AiChn, MI_AI_SslInitAttr_t * pstSslInitAttr); -
Parameters
Table2-33
Parameter Name Description Input/Output AiDevId Audio device number Input AiChn Audio input channel number.
The supported channel range is determined by the maximum number of channels in the AI device attribute u32ChnCnt.Input pstSslInitAttr Sound source localization function initialized structure pointer Input -
Return value
-
Zero: Successful
-
Non-zero: Failed, see error code for details
-
-
Dependency
-
Header: mi_ai.h
-
Library: libmi_ai.a/libmi_ai.so libSSL_LINUX.so
-
-
Note Initialization parameters for sound source location can only be set before enabling.
- This interface is no longer supported in API version 2.19 and later.
-
Example
The following code shows how to set the sound source location parameters to enable the sound source location and obtain the sound source location results.
1. MI_S32 ret; 2. MI_AUDIO_Attr_t stAttr; 3. MI_AUDIO_Dev AiDevId = 0; 4. MI_AI_CHN AiChn = 0; 5. MI_SYS_ChnPort_t stChnPort; 6. MI_S32 s32Fd; 7. fd_set readFdSet; 8. struct timeval stTimeOut; 9. MI_AUDIO_Frame_t stAiChFrame; 10. MI_AUDIO_AecFrame_t stAecFrame; 11. MI_SYS_ChnPort_t stAiChnOutputPort; 12. MI_S32 s32Doa; 13. MI_AI_SslInitAttr_t stSslInit = { 14. .bBfMode = FALSE, 15. .u32MicDistance = 3, 16. }; 17. MI_AI_SslConfigAttr_t stSslConfig = { 18. .s32Temperature = 25, 19. .s32NoiseGateDbfs = -40, 20. .s32DirectionFrameNum = 300, 21. }; 22. MI_AI_SslInitAttr_t stAiGetSslInitAttr; 23. MI_AI_SslConfigAttr_t stAiGetSslConfigAttr; 24. MI_SYS_Init(); 25. stAttr.eBitwidth = E_MI_AUDIO_BIT_WIDTH_16; 26. stAttr.eSamplerate = E_MI_AUDIO_SAMPLE_RATE_8000; 27. stAttr.eSoundmode = E_MI_AUDIO_SOUND_MODE_STEREO; 28. stAttr.eWorkmode = E_MI_AUDIO_MODE_I2S_SLAVE; 29. stAttr.u32PtNumPerFrm = 160; 30. stAttr.u32ChnCnt = 1; 31. /* set public attribute of AI device */ 32. ret = MI_AI_SetPubAttr(AiDevId, &stAttr); 33. if (MI_SUCCESS != ret) 34. { 35. printf("set ai %d attr err:0x%x\n", AiDevId, ret); 36. return ret; 37. } 38. /* get public attribute of AI device */ 39. ret = MI_AI_GetPubAttr(AiDevId, &stAttr); 40. if (MI_SUCCESS != ret) 41. { 42. printf("get ai %d attr err:0x%x\n", AiDevId, ret); 43. return ret; 44. } 45. /* enable AI device */ 46. ret = MI_AI_Enable(AiDevId); 47. if (MI_SUCCESS != ret) 48. { 49. printf("enable ai %d err:0x%x\n", AiDevId, ret); 50. return ret; 51. } 52. /* enable AI Channel */ 53. ret = MI_AI_EnableChn(AiDevId, AiChn); 54. if (MI_SUCCESS != ret) 55. { 56. printf("enable Dev%d Chn%d err:0x%x\n", AiDevId, AiChn, ret); 57. return ret; 58. } 59. /* set ssl init attr */ 60. ret = MI_AI_SetSslInitAttr(AiDevId, AiChn, &stSslInit); 61. if (MI_SUCCESS != ret) 62. { 63. printf("set ssl init attr Dev%d Chn%d err:0x%x\n", AiDevId, AiChn, ret); 64. return ret; 65. } 66. /* get ssl init attr */ 67. ret = MI_AI_GetSslInitAttr(AiDevId, AiChn, &stAiGetSslInitAttr); 68. if (MI_SUCCESS != ret) 69. { 70. printf("get ssl init attr Dev%d Chn%d err:0x%x\n", AiDevId, AiChn, ret); 71. return ret; 72. } 73. /* set ssl config attr */ 74. ret = MI_AI_SetSslConfigAttr(AiDevId, AiChn, &stSslConfig); 75. if (MI_SUCCESS != ret) 76. { 77. printf("set ssl config attr Dev%d Chn%d err:0x%x\n", AiDevId, AiChn, ret); 78. return ret; 79. } 80. /* get ssl config attr */ 81. ret = MI_AI_GetSslConfigAttr(AiDevId, AiChn, &stAiGetSslConfigAttr); 82. if (MI_SUCCESS != ret) 83. { 84. printf("get ssl config attr Dev%d Chn%d err:0x%x\n", AiDevId, AiChn, ret); 85. return ret; 86. } 87. /* enable ssl */ 88. ret = MI_AI_EnableSsl(AiDevId, AiChn); 89. **if** (MI_SUCCESS != ret) 90. { 91. printf("enable ssl Dev%d Chn%d err:0x%x\n", AiDevId, AiChn, ret); 92. return ret; 93. } 94. /* set buffer depth */ 95. stAiChnOutputPort.eModId = E_MI_MODULE_ID_AI; 96. stAiChnOutputPort.u32DevId = AiDevId; 97. stAiChnOutputPort.u32ChnId = AiChn; 98. stAiChnOutputPortu32PortId = 0; 99. MI_SYS_SetChnOutputPortDepth(&stAiChnOutputPort, 1, 8); 100. /* get port fd */ 101. stChnPort.eModId = E_MI_MODULE_ID_AI; 102. stChnPort.u32DevId = AiDevId; 103. stChnPort.u32ChnId = AiChn; 104. stChnPort.u32PortId = 0; 105. ret = MI_SYS_GetFd(&stChnPort, &s32Fd); 106. if (MI_SUCCESS != ret) 107. { 108. printf("Dev%d Chn%d failed to call MI_SYS_GetFd!!!\n", AiDevId, AiChn); 109. return ret; 110. } 111. /* select 100ms */ 112. FD_ZERO(&readFdSet); 113. FD_SET(s32Fd, &readFdSet); 114. stTimeOut.tv_sec = 0; 115. stTimeOut.tv_usec = 100 * 1000; 116. ret = select(s32Fd + 1, &readFdSet, NULL, NULL, &stTimeOut); 117. if (FD_ISSET(s32Fd, &readFdSet)) 118. { 119. ret = MI_AI_GetFrame(AiDevId, AiChn, &stAiChFrame, &stAecFrame, 0); 120. if (MI_SUCCESS == ret) 121. { 122. /* get ssl result */ 123. MI_AI_GetSslDoa(AiDevId, AiChn, &s32Doa); 124. MI_AI_ReleaseFrame(AiDevId, AiChn, &stAiChFrame, &stAecFrame); 125. } 126. } 127. /* disable ssl */ 128. ret = MI_AI_DiableSsl(AiDevId, AiChn); 129. if (MI_SUCCESS != ret) 130. { 131. printf("disable ssl Dev%d Chn%d err:0x%x\n", AiDevId, AiChn, ret); 132. return ret; 133. } 134. /* disable AI Channel */ 135. ret = MI_AI_DisableChn(AiDevId, AiChn); 136. if (MI_SUCCESS != ret) 137. { 138. printf("disable Dev%d Chn%d err:0x%x\n", AiDevId, AiChn, ret); 139. return ret; 140. } 141. /* disable AI Device */ 142. ret = MI_AI_Disable(AiDevId); 143. if (MI_SUCCESS != ret) 144. { 145. printf("disable ai %d err:0x%x\n", AiDevId, ret); 146. return ret; 147. } 148. MI_SYS_Exit();
2.33. MI_AI_GetSslInitAttr¶
-
Features
Get Sound source localization function initialized properties of AI channel
-
Syntax
MI_S32 MI_AI_GetSslInitAttr(MI_AUDIO_DEV AiDevId, MI_AI_CHN AiChn,MI_AI_SslInitAttr_t * pstSslInitAttr); -
Parameters
Table2-34
Parameter Name Description Input/Output AiDevId Audio device number Input AiChn Audio input channel number.
The supported channel range is determined by the maximum number of channels in the AI device attribute u32ChnCnt.Input pstSslInitAttr Sound source localization function initialized structure pointer Output -
Return value
-
Zero: Successful
-
Non-zero: Failed, see error code for details
-
-
Dependency
-
Header: mi_ai.h
-
Library: libmi_ai.a/libmi_ai.so libSSL_LINUX.so
-
-
Note
- This interface is no longer supported in API version 2.19 and later.
-
Example
Please refer to the MI_AI_SetSslInitAttr example section.
2.34. MI_AI_SetSslConfigAttr¶
-
Features
Set Sound source localization function configured properties of AI channel.
-
Syntax
MI_S32 MI_AI_SetSslConfigAttr(MI_AUDIO_DEV AiDevId, MI_AI_CHN AiChn,MI_AI_SslConfigAttr_t * pstSslConfigAttr); -
Parameters
Table2-35
Parameter Name Description Input/Output AiDevId Audio device number Input AiChn Audio input channel number.
The supported channel range is determined by the maximum number of channels in the AI device attribute u32ChnCnt.Input pstSslConfigAttr Sound source localization function configured structure pointer Input -
Return value
-
Zero: Successful
-
Non-zero: Failed, see error code for details
-
-
Dependency
-
Header: mi_ai.h
-
Library: libmi_ai.a/libmi_ai.so libSSL_LINUX.so
-
-
Note
-
You can set configured structure for each frame.
-
This interface is no longer supported in API version 2.19 and later.
-
-
Example
Please refer to the MI_AI_SetSslInitAttr example section.
2.35. MI_AI_GetSslConfigAttr¶
-
Features
Get Sound source localization function configured properties.
-
Syntax
MI_S32 MI_AI_GetSslConfigAttr(MI_AUDIO_DEV AiDevId, MI_AI_CHN AiChn,MI_AI_SslConfigAttr_t* pstSslConfigAttr); -
Parameters
Table2-36
Parameter Name Description Input/Output AiDevId Audio device number Input AiChn Audio input channel number.
The supported channel range is determined by the maximum number of channels in the AI device attribute u32ChnCnt.Input pstSslConfigAttr Sound source localization function configured structure pointer Output -
Return value
-
Zero: Successful
-
Non-zero: Failed, see error code for details
-
-
Dependency
-
Header: mi_ai.h
-
Library: libmi_ai.a/libmi_ai.so libSSL_LINUX.so
-
-
Note
- This interface is no longer supported in API version 2.19 and later.
-
Example
Please refer to the MI_AI_SetSslInitAttr example section.
2.36. MI_AI_EnableSsl¶
-
Features
Enable Sound source localization function.
-
Syntax
MI_S32 MI_AI_EnableSsl(MI_AUDIO_DEV AiDevId, MI_AI_CHN AiChn); -
Parameters
Table2-37
Parameter Name Description Input/Output AiDevId Audio device number Input AiChn Audio input channel number.
The supported channel range is determined by the maximum number of channels in the AI device attribute u32ChnCnt.Input -
Return value
-
Zero: Successful
-
Non-zero: Failed, see error code for details
-
-
Dependency
-
Header: mi_ai.h
-
Library: libmi_ai.a/libmi_ai.so libSSL_LINUX.so
-
-
Note Before enabling the sound source localization function, it is necessary to enable the AI channel and set the initialization parameters and configuration parameters of the sound source localization.
- This interface is no longer supported in API version 2.19 and later.
-
Example
Please refer to the MI_AI_SetSslInitAttr example section.
2.37. MI_AI_DisableSsl¶
-
Features
Disable Sound source localization function.
-
Syntax
MI_S32 MI_AI_DisableSsl(MI_AUDIO_DEV AiDevId, MI_AI_CHN AiChn); -
Parameters
Table2-38
Parameter Name Description Input/Output AiDevId Audio device number Input AiChn Audio input channel number.
The supported channel range is determined by the maximum number of channels in the AI device attribute u32ChnCnt.Input -
Return value
-
Zero: Successful
-
Non-zero: Failed, see error code for details
-
-
Dependency
-
Header: mi_ai.h
-
Library: libmi_ai.a/libmi_ai.so libSSL_LINUX.so
-
-
Note
- This interface is no longer supported in API version 2.19 and later.
-
Example
Please refer to the MI_AI_SetSslInitAttr example section.
2.38. MI_AI_GetSslDoa¶
-
Features
Get the Sound source localization result.
-
Syntax
MI_S32 MI_AI_GetSslDoa(MI_AUDIO_DEV AiDevId, MI_AI_CHN AiChn, MI_S32 *ps32SslDoa); -
Parameters
Table2-39
Parameter Name Description Input/Output AiDevId Audio device number Input AiChn Audio input channel number.
The supported channel range is determined by the maximum number of channels in the AI device attribute u32ChnCnt.Input ps32SslDoa Sound source localization result pointer Output -
Return value
-
Zero: Successful
-
Non-zero: Failed, see error code for details
-
-
Dependency
-
Header: mi_ai.h
-
Library: libmi_ai.a/libmi_ai.so libSSL_LINUX.so
-
-
Note
- This interface is no longer supported in API version 2.19 and later.
-
Example
Please refer to the MI_AI_SetSslInitAttr example section.
2.39. MI_AI_SetBfInitAttr¶
-
Features
Set Beamforming function initialized properties of AI channel.
-
Syntax
MI_S32 MI_AI_SetBfInitAttr(MI_AUDIO_DEV AiDevId, MI_AI_CHN AiChn, MI_AI_BfInitAttr_t* pstBfInitAttr); -
Parameters
Table2-40
Parameter Name Description Input/Output AiDevId Audio device number Input AiChn Audio input channel number.
The supported channel range is determined by the maximum number of channels in the AI device attribute u32ChnCnt.Input pstBfInitAttr Beamforming function initialized structure pointer Input -
Return value
-
Zero: Successful
-
Non-zero: Failed, see error code for details
-
-
Dependency
-
Header: mi_ai.h
-
Library: libmi_ai.so/libmi_ai.a libBF_LINUX.so
-
-
Note Initialization parameters for beamforming can only be set before enabling.
- This interface is no longer supported in API version 2.19 and later.
-
Example
The following code shows how to set the parameters of beamforming function and enable the beamforming function.
1. MI_S32 ret; 2. MI_AUDIO_Attr_t stAttr; 3. MI_AUDIO_Dev AiDevId = 0; 4. MI_AI_CHN AiChn = 0; 5. MI_AI_BfInitAttr_t stBfInit = { 6. .u32ChanCnt = 2, 7. .u32MicDistance = 3, 8. }; 9. MI_AI_BfConfigAttr_t stBfConfig = { 10. .s32Temperature = 25, 11. .s32NoiseGateDbfs = -40, 12. .s32NoiseSupressionMode = 8, 13. .s32NoiseEstimation = 1, 14. .outputGain = 0.7, 15. }; 16. MI_AI_BfInitAttr_t stAiGetBfInitAttr; 17. MI_AI_BfConfigAttr_t stAiGetBfConfigAttr; 18. MI_BOOL bAiSetBfDoa = TRUE; 19. MI_S32 s32AiBfDoa = 0; 20. MI_SYS_Init(); 21. stAttr.eBitwidth = E_MI_AUDIO_BIT_WIDTH_16; 22. stAttr.eSamplerate = E_MI_AUDIO_SAMPLE_RATE_8000; 23. stAttr.eSoundmode = E_MI_AUDIO_SOUND_MODE_STEREO; 24. stAttr.eWorkmode = E_MI_AUDIO_MODE_I2S_SLAVE; 25. stAttr.u32PtNumPerFrm = 160; 26. stAttr.u32ChnCnt = 1; 27. /* set public attribute of AI device */ 28. ret = MI_AI_SetPubAttr(AiDevId, &stAttr); 29. if (MI_SUCCESS != ret) 30. { 31. printf("set ai %d attr err:0x%x\n", AiDevId, ret); 32. return ret; 33. } 34. /* get public attribute of AI device */ 35. ret = MI_AI_GetPubAttr(AiDevId, &stAttr); 36. if (MI_SUCCESS != ret) 37. { 38. printf("get ai %d attr err:0x%x\n", AiDevId, ret); 39. return ret; 40. } 41. /* enable AI device */ 42. ret = MI_AI_Enable(AiDevId); 43. if (MI_SUCCESS != ret) 44. { 45. printf("enable ai %d err:0x%x\n", AiDevId, ret); 46. return ret; 47. } 48. /* enable AI Channel */ 49. ret = MI_AI_EnableChn(AiDevId, AiChn); 50. if (MI_SUCCESS != ret) 51. { 52. printf("enable Dev%d Chn%d err:0x%x\n", AiDevId, AiChn, ret); 53. return ret; 54. } 55. /* set bf init attr */ 56. ret = MI_AI_SetBfInitAttr(AiDevId, AiChn, &stBfInit); 57. if (MI_SUCCESS != ret) 58. { 59. printf("set bf init attr Dev%d Chn%d err:0x%x\n", AiDevId, AiChn, ret); 60. return ret; 61. } 62. /* get bf init attr */ 63. ret = MI_AI_GetBfInitAttr(AiDevId, AiChn, &stAiGetBfInitAttr); 64. if (MI_SUCCESS != ret) 65. { 66. printf("get bf init attr Dev%d Chn%d err:0x%x\n", AiDevId, AiChn, ret); 67. return ret; 68. } 69. /* set bf config attr */ 70. ret = MI_AI_SetBfConfigAttr(AiDevId, AiChn, &stBfConfig); 71. if (MI_SUCCESS != ret) 72. { 73. printf("set bf config attr Dev%d Chn%d err:0x%x\n", AiDevId, AiChn, ret); 74. return ret; 75. } 76. /* get bf config attr */ 77. ret = MI_AI_GetBfConfigAttr(AiDevId, AiChn, &stAiGetBfConfigAttr); 78. if (MI_SUCCESS != ret) 79. { 80. printf("get bf config attr Dev%d Chn%d err:0x%x\n", AiDevId, AiChn, ret); 81. return ret; 82. } 83. /* set bf angle */ 84. if (bAiSetBfDoa) 85. { 86. ret = MI_AI_SetBfAngle(AiDevId, AiChn, s32AiBfDoa); 87. if (MI_SUCCESS != ret) 88. { 89. printf("set bf doa Dev%d Chn%d err:0x%x\n", AiDevId, AiChn, ret); 90. return ret; 91. } 92. } 93. /* enable bf */ 94. ret = MI_AI_EnableBf(AiDevId, AiChn); 95. if (MI_SUCCESS != ret) 96. { 97. printf("enable bf Dev%d Chn%d err:0x%x\n", AiDevId, AiChn, ret); 98. return ret; 99. } 100. /* do something */ 101. /* enable bf */ 102. ret = MI_AI_DisableBf(AiDevId, AiChn); 103. if (MI_SUCCESS != ret) 104. { 105. printf("disable bf Dev%d Chn%d err:0x%x\n", AiDevId, AiChn, ret); 106. return ret; 107. } 108. /* disable AI Channel */ 109. ret = MI_AI_DisableChn(AiDevId, AiChn); 110. if (MI_SUCCESS != ret) 111. { 112. printf("disable Dev%d Chn%d err:0x%x\n", AiDevId, AiChn, ret); 113. return ret; 114. } 115. /* disable AI Device */ 116. ret = MI_AI_Disable(AiDevId); 117. if (MI_SUCCESS != ret) 118. { 119. printf("disable ai %d err:0x%x\n", AiDevId, ret); 120. return ret; 121. } 122. MI_SYS_Exit();
2.40. MI_AI_GetBfInitAttr¶
-
Features
Get Beamforming function initialized properties of AI channel.
-
Syntax
MI_S32 MI_AI_GetBfInitAttr(MI_AUDIO_DEV AiDevId, MI_AI_CHN AiChn, MI_AI_BfInitAttr_t *pstBfInitAttr); -
Parameters
Table2-41
Parameter Name Description Input/Output AiDevId Audio device number Input AiChn Audio input channel number.
The supported channel range is determined by the maximum number of channels in the AI device attribute u32ChnCnt.Input pstBfInitAttr Beamforming function initialized structure pointer Output -
Return value
-
Zero: Successful
-
Non-zero: Failed, see error code for details
-
-
Dependency
-
Header: mi_ai.h
-
Library: libmi_ai.so/libmi_ai.a libBF_LINUX.so
-
-
Note
- This interface is no longer supported in API version 2.19 and later.
-
Example
Please refer to the MI_AI_SetBfInitAttr example section..
2.41. MI_AI_SetBfConfigAttr¶
-
Features
Set Beamforming function configured properties of AI channel.
-
Syntax
MI_S32 MI_AI_SetBfConfigAttr(MI_AUDIO_DEV AiDevId,MI_AI_CHN AiChn, MI_AI_BfConfigAttr_t* pstBfConfigAttr); -
Parameters
Table2-42
Parameter Name Description Input/Output AiDevId Audio device number Input AiChn Audio input channel number.
The supported channel range is determined by the maximum number of channels in the AI device attribute u32ChnCnt.Input pstBfInitAttr Beamforming function configured structure pointer Input -
Return value
-
Zero: Successful
-
Non-zero: Failed, see error code for details
-
-
Dependency
-
Header: mi_ai.h
-
Library: libmi_ai.so/libmi_ai.a libBF_LINUX.so
-
-
Note
- This interface is no longer supported in API version 2.19 and later.
-
Example
Please refer to the MI_AI_SetBfInitAttr example section..
2.42. MI_AI_GetBfConfigAttr¶
-
Features
Get Beamforming function configured properties of AI channel.
-
Syntax
MI_S32 MI_AI_GetBfConfigAttr(MI_AUDIO_DEV AiDevId, MI_AI_CHN AiChn, MI_AI_BfConfigAttr_t* pstBfConfigAttr); -
Parameters
Table2-43
Parameter Name Description Input/Output AiDevId Audio device number Input AiChn Audio input channel number.
The supported channel range is determined by the maximum number of channels in the AI device attribute u32ChnCnt.Input pstBfConfigAttr Beamforming function configured structure pointer Output -
Return value
-
Zero: Successful
-
Non-zero: Failed, see error code for details
-
-
Dependency
-
Header: mi_ai.h
-
Library: libmi_ai.so/libmi_ai.a libBF_LINUX.so
-
-
Note
- This interface is no longer supported in API version 2.19 and later.
-
Example
Please refer to the MI_AI_SetBfInitAttr example section..
2.43. MI_AI_EnableBf¶
-
Features
Enable Beamforming function of AI channel.
-
Syntax
MI_S32 MI_AI_EnableBf(MI_AUDIO_DEV AiDevId, MI_AI_CHN AiChn); -
Parameters
Table2-44
Parameter Name Description Input/Output AiDevId Audio device number Input AiChn Audio input channel number.
The supported channel range is determined by the maximum number of channels in the AI device attribute u32ChnCnt.Input -
Return value
-
Zero: Successful
-
Non-zero: Failed, see error code for details
-
-
Dependency
-
Header: mi_ai.h
-
Library: libmi_ai.so/libmi_ai.a libBF_LINUX.so
-
-
Note
- This interface is no longer supported in API version 2.19 and later.
-
Example
Please refer to the MI_AI_SetBfInitAttr example section..
2.44. MI_AI_DisableBf¶
-
Features
Disable Beamforming function of AI channel.
-
Syntax
MI_S32 MI_AI_DisableBf(MI_AUDIO_DEV AiDevId, MI_AI_CHN AiChn); -
Parameters
Table2-45
Parameter Name Description Input/Output AiDevId Audio device number Input AiChn Audio input channel number.
The supported channel range is determined by the maximum number of channels in the AI device attribute u32ChnCnt.Input -
Return value
-
Zero: Successful
-
Non-zero: Failed, see error code for details
-
-
Dependency
-
Header: mi_ai.h
-
Library: libmi_ai.so/libmi_ai.a libBF_LINUX.so
-
-
Note
- This interface is no longer supported in API version 2.19 and later.
-
Example
Please refer to the MI_AI_SetBfInitAttr example section..
2.45. MI_AI_SetBfAngle¶
-
Features
Set fixed angle for Beamforming function of AI channel.
-
Syntax
MI_S32 MI_AI_SetBfAngle(MI_AUDIO_DEV AiDevId, MI_AI_CHN AiChn, MI_S32 s32BfAngle); -
Parameters
Table2-46
Parameter Name Description Input/Output AiDevId Audio device number Input AiChn Audio input channel number.
The supported channel range is determined by the maximum number of channels in the AI device attribute u32ChnCnt.Input s32BfAngle Fixed angel of Beamforming Input -
Return value
-
Zero: Successful
-
Non-zero: Failed, see error code for details
-
-
Dependency
-
Header: mi_ai.h
-
Library: libmi_ai.so/libmi_ai.a libBF_LINUX.so
-
-
Note
- This interface is no longer supported in API version 2.19 and later.
-
Example
Please refer to the MI_AI_SetBfInitAttr example section..
2.46. MI_AI_SetMute¶
-
Features
Set mute status of AI channel.
-
Syntax
MI_S32 MI_AI_SetMute(MI_AUDIO_DEV AiDevId, MI_AI_CHN AiChn, MI_BOOL bMute); -
Parameters
Table2-47
Parameter Name Description Input/Output AiDevId Audio device number Input AiChn Audio input channel number.
The supported channel range is determined by the maximum number of channels in the AI device attribute u32ChnCnt.Input bMute Mute status of AI channel Input -
Return value
-
Zero: Successful
-
Non-zero: Failed, see error code for details
-
-
Dependency
-
Header: mi_ai.h
-
Library: libmi_ai.so/libmi_ai.a
-
-
Example
The following code shows how to set/get mute status of AI channel.
1. MI_S32 ret; 2. MI_AUDIO_Attr_t stAttr; 3. MI_AUDIO_Dev AiDevId = 0; 4. MI_AI_CHN AiChn = 0; 5. MI_BOOL bMute = TRUE; 6. MI_SYS_Init(); 7. stAttr.eBitwidth = E_MI_AUDIO_BIT_WIDTH_16; 8. stAttr.eSamplerate = E_MI_AUDIO_SAMPLE_RATE_8000; 9. stAttr.eSoundmode = E_MI_AUDIO_SOUND_MODE_STEREO; 10. stAttr.eWorkmode = E_MI_AUDIO_MODE_I2S_SLAVE; 11. stAttr.u32PtNumPerFrm = 160; 12. stAttr.u32ChnCnt = 1; 13. /* set public attribute of AI device */ 14. ret = MI_AI_SetPubAttr(AiDevId, &stAttr); 15. if (MI_SUCCESS != ret) 16. { 17. printf("set ai %d attr err:0x%x\n", AiDevId, ret); 18. return ret; 19. } 20. /* get public attribute of AI device */ 21. ret = MI_AI_GetPubAttr(AiDevId, &stAttr); 22. if (MI_SUCCESS != ret) 23. { 24. printf("get ai %d attr err:0x%x\n", AiDevId, ret); 25. return ret; 26. } 27. /* enable AI device */ 28. ret = MI_AI_Enable(AiDevId); 29. if (MI_SUCCESS != ret) 30. { 31. printf("enable ai %d err:0x%x\n", AiDevId, ret); 32. return ret; 33. } 34. /* enable AI Channel */ 35. ret = MI_AI_EnableChn(AiDevId, AiChn); 36. if (MI_SUCCESS != ret) 37. { 38. printf("enable Dev%d Chn%d err:0x%x\n", AiDevId, AiChn, ret); 39. return ret; 40. } 41. /* set mute status */ 42. ret = MI_AI_SetMute(AiDevId, AiChn, bMute); 43. if (MI_SUCCESS != ret) 44. { 45. printf("set mute status Dev%d Chn%d err:0x%x\n", AiDevId, AiChn, ret); 46. return ret; 47. } 48. /* get mute status */ 49. ret = MI_AI_GetMute(AiDevId, AiChn, &bMute); 50. if (MI_SUCCESS != ret) 51. { 52. printf("get mute status Dev%d Chn%d err:0x%x\n", AiDevId, AiChn, ret); 53. return ret; 54. } 55. /* disable AI Channel */ 56. ret = MI_AI_DisableChn(AiDevId, AiChn); 57. if (MI_SUCCESS != ret) 58. { 59. printf("disable Dev%d Chn%d err:0x%x\n", AiDevId, AiChn, ret); 60. return ret; 61. } 62. /* disable AI Device */ 63. ret = MI_AI_Disable(AiDevId); 64. if (MI_SUCCESS != ret) 65. { 66. printf("disable ai %d err:0x%x\n", AiDevId, ret); 67. return ret; 68. } 69. MI_SYS_Exit();
2.47. MI_AI_GetMute¶
-
Features
Get mute status of AI channel.
-
Syntax
MI_S32 MI_AI_GetMute(MI_AUDIO_DEV AiDevId, MI_AI_CHN AiChn, MI_BOOL *pbMute); -
Parameters
Table2-48
Parameter Name Description Input/Output AiDevId Audio device number Input AiChn Audio input channel number.
The supported channel range is determined by the maximum number of channels in the AI device attribute u32ChnCnt.Input pbMute Mute status pointer of AI channel Output -
Return value
-
Zero: Successful
-
Non-zero: Failed, see error code for details
-
-
Dependency
-
Header: mi_ai.h
-
Library: libmi_ai.so/libmi_ai.a
-
-
Example
Please refer to the MI_AI_SetMute example section..
2.48. MI_AI_InitDev¶
-
Features
Initialize AI device.
-
Syntax
MI_S32 MI_AI_InitDev(MI_AI_InitParam_t *pstInitParam); -
Parameters
Parameter Name Description Input/Output pstInitParam Initialization parameter of AI device Input -
Return value
-
Zero: Successful
-
Non-zero: Failed, see error code for details
-
-
Dependency
-
Header: mi_ai.h
-
Library: libmi_ai.so/libmi_ai.a
-
-
Note
This interface must be used in pair with MI_AI_DeInitDev and cannot be called separately; otherwise, it will return a failure.
This interface parameter setting only takes effect on SSC33X.
2.49. MI_AI_DeInitDev¶
-
Features
De-initialize AI device.
-
Syntax
MI_S32 MI_AI_DeInitDev(void); -
Return value
-
Zero: Successful
-
Non-zero: Failed, see error code for details
-
-
Dependency
-
Header: mi_ai.h
-
Library: libmi_ai.so/libmi_ai.a
-
-
Note
This function must be called after the device is initialized or it will return a failure. If the interface is not called before the app exits, the device will be automatically uninitialized internally.
This interface must be used in pair with MI_AI_InitDev and cannot be called separately; otherwise, it will return a failure.
This interface parameter setting only takes effect on SSC33X.
2.50. MI_AI_DupChn¶
-
Features
Synchronize status of AI channel
-
Syntax
MI_S32 MI_AI_DupChn(MI_AUDIO_DEV AiDevId, MI_AI_CHN AiChn) -
Parameters
Parameter Name Description Input/Output AiDevId Audio device number Input AiChn Audio input channel number. The supported channel range is determined by the maximum number of channels in the AI device attribute u32ChnCnt. Input -
Return value
-
Zero: Successful
-
Non-zero: Failed, see error code for details
-
-
Dependency
-
Header: mi_ai.h
-
Library: libmi_ai.so/libmi_ai.a
-
-
Note
- This interface applies only to dual OS environment.The AI channel is initialized in the rtos environment and used to synchronizethe status of the AI channel when switching to the Linux environment.
3. AI DATA TYPE¶
3.1. AI Module Related Data Types Definition¶
Table 3-1
| Data type | Definition |
|---|---|
| MI_AUDIO_DEV | Define the audio input / output device number |
| MI_AUDIO_MAX_CHN_NUM | Define the maximum number of channels for audio input / output devices |
| MI_AI_CHN | Define the audio input channel |
| MI_AUDIO_SampleRate_e | Define the audio sample rate |
| MI_AUDIO_Bitwidth_e | Define audio sampling accuracy |
| MI_AUDIO_Mode_e | Define the audio input and output working mode |
| MI_AUDIO_SoundMode_e | Define audio channel mode |
| MI_AUDIO_AencType_e | Define the audio encoding type. |
| MI_AUDIO_G726Mode_e | Define the G726 operating mode. |
| MI_AUDIO_I2sFmt_e | I2S format setting |
| MI_AUDIO_I2sMclk_e | I2S MCLK setting |
| MI_AUDIO_I2sConfig_t | Define the I2S attribute structure. |
| MI_AUDIO_Attr_t | Defining audio input/output device attribute structures |
| MI_AI_ChnParam_t | Define channel parameter structure |
| MI_AUDIO_Frame_t | Defining an audio frame data structure |
| MI_AUDIO_AecFrame_t | Defining echo cancellation reference frame information structure |
| MI_AUDIO_SaveFileInfo_t | Define audio save file function configuration information structure |
| MI_AI_VqeConfig_t | Defining audio input sound quality enhancement configuration information structure |
| MI_AUDIO_HpfConfig_t | Defining an audio high-pass filtering function configuration information structure |
| MI_AUDIO_HpfFreq_e | Define the audio high pass filter cutoff frequency |
| MI_AI_AecConfig_t | Defining an audio echo cancellation configuration information structure |
| MI_AUDIO_AnrConfig_t | Define audio voice noise reduction function configuration information structure |
| MI_AUDIO_NrSpeed_e | Define noise convergence speed |
| MI_AUDIO_AgcConfig_t | Defining an audio automatic gain control configuration information structure |
| AgcGainInfo_t | AGC gain value |
| MI_AUDIO_EqConfig_t | Define the audio equalizer function configuration information structure |
| MI_AI_AencGConfig_t | Defining an audio coding function configuration information structure |
| MI_AUDIO_AencG711Config_t | Define the audio encoding function configuration information structure. |
| MI_AUDIO_AencG726Config_t | Define the audio encoding function configuration information structure. |
| MI_AUDIO_AlgorithmMode_e | Define the operating mode of the audio algorithm. |
| MI_AI_AedConfig_t | Define the sound event detection function configuration information structure. |
| MI_AUDIO_AedSensitivity_e/MI_AUDIO_BabyCrySensitivity_e | Define the sensitivity of baby cry detection |
| MI_AI_AedResult_t | Define the sound event detection result structure. |
| MI_AI_ChnGainConfig_t | Define the AI channel gain setting structure |
| MI_AI_SslInitAttr_t | Define the Sound source localization initialized structure |
| MI_AI_SslConfigAttr_t | Define the Sound source localization configured structure |
| MI_AI_BfInitAttr_t | Define the Beamforming initialized structure |
| MI_AI_BfConfigAttr_t | Define the Beamforming configured structure |
| MI_AI_InitParam_t | Define the initialized parameter of audio input device |
| MI_AI_BabyCryConfig_t | Define the configured attribute structure of baby cry detection |
| MI_AI_LsdConfig_t | Define the configured attribute structure of loud sound detection |
3.2. MI_AUDIO_DEV¶
-
Description
Define the audio input / output device number.
-
Definition
typedef MI_S32 MI_AUDIO_DEV -
Note
The following table is a comparison table of AI Dev ID and physical device of chip.
Table3-2
0 1 2 3 4 5 Pretzel Amic Dmic I2s Rx Line in Macaron Amic Dmic I2s Rx Line in Taiyaki Amic Dmic I2s Rx Line in Takoyaki Amic Dmic I2s Rx Line in Amic + I2sRx Dmic + I2s Rx Pudding Amic Dmic I2s Rx Line in I2s Rx + Src Ispahan Amic Dmic I2s Rx Line in I2s Rx + Src Tiramisu AmicADC0/1 Dmic I2s Rx Line inADC0/1 AmicADC2/3 AmicADC0/1/2/3 Ikayaki AmicADC0/1 Dmic I2s Rx Line inADC0/1 AmicADC2 AmicADC0/1/2 The following table is the specifications of different series of chips.
Table3-3
Amic/Line in Dmic I2s Rx Pretzel Support 2 channels 8/16/32/48KHz sampling rate supporting 4 channels 8/16/32/48KHz sampling rate It supports standard I2S mode and TDM mode. TDM mode can be extended to 8 channels. It supports 4-wire and 6-wire modes and can provide MCLK. It supports 8/16/32/48KHz sampling rate. Macaron Support 2 channels 8/16/32/48KHz sampling rate supporting 2 channels 8/16/32KHz sampling rate Only standard I2S mode is supported and can only be used as master, only 4-wire mode is supported, MCLK is not available. Support 8/16/32/48KHz sampling rate. Taiyaki Support 1 channel 8/16/32/48KHz sampling rate supporting 4 channels 8/16/32/48KHz sampling rate Only standard I2S mode is supported and can only be used as master, only 4-wire mode is supported, MCLK is not available. Support 8/16/32/48KHz sampling rate. Takoyaki Support 1 channel 8/16/32/48KHz sampling rate supporting 4 channels 8/16/32/48KHz sampling rate Only standard I2S mode is supported and can only be used as master, only 4-wire mode is supported, MCLK is not available. Support 8/16/32/48KHz sampling rate. Pudding Support 2 channels 8/16/32/48KHz sampling rate supporting 2 channels 8/16/32KHz sampling rate It supports standard I2S mode and TDM mode. TDM mode can be extended to 8 channels. It supports 4-wire and 6-wire modes and can provide MCLK. It supports 8/16/32/48KHz sampling rate. Ispahan Support 2 channels 8/16/32/48KHz sampling rate supporting 2 channels 8/16/32KHz sampling rate Only standard I2S mode is supported and can only be used as master, only 4-wire mode is supported, MCLK is not available. Support 8/16/32/48KHz sampling rate. Tiramisu Support 4 channels 8/16/32/48KHz sampling rate supporting 4 channels 8/16/32/48KHz sampling rate It supports standard I2S mode and TDM mode. TDM mode can be extended to 8 channels. It supports 4-wire and 6-wire modes and can provide MCLK. It supports 8/16/32/48KHz sampling rate. Ikayaki Support 3 channels 8/16/32/48KHz sampling rate supporting 4 channels 8/16/32/48KHz sampling rate It supports standard I2S mode and TDM mode. TDM mode can be extended to 8 channels. It supports 4-wire and 6-wire modes and can provide MCLK. It supports 8/16/32/48KHz sampling rate.
3.3. MI_AUDIO_MAX_CHN_NUM¶
-
Description
Define the maximum number of channels for audio input / output devices.
-
Definition
#define MI_AUDIO_MAX_CHN_NUM 16
3.4. MI_AI_CHN¶
-
Description
Define the audio input channel.
-
Definition
typedef MI_S32 MI_AI_CHN
3.5. MI_AUDIO_SampleRate_e¶
-
Description
Define the audio sample rate.
-
Definition
typedef enum { E_MI_AUDIO_SAMPLE_RATE_8000 = 8000, /* 8kHz sampling rate */ E_MI_AUDIO_SAMPLE_RATE_11052 = 11025, /* 11.025kHz sampling rate */ E_MI_AUDIO_SAMPLE_RATE_12000 = 12000, /* 12kHz sampling rate */ E_MI_AUDIO_SAMPLE_RATE_16000 = 16000, /* 16kHz sampling rate */ E_MI_AUDIO_SAMPLE_RATE_22050 = 22050, /* 22.05kHz sampling rate */ E_MI_AUDIO_SAMPLE_RATE_24000 = 24000, /* 24kHz sampling rate */ E_MI_AUDIO_SAMPLE_RATE_32000 = 32000, /* 32kHz sampling rate */ E_MI_AUDIO_SAMPLE_RATE_44100 = 44100, /* 44.1kHz sampling rate */ E_MI_AUDIO_SAMPLE_RATE_48000 = 48000, /* 48kHz sampling rate */ E_MI_AUDIO_SAMPLE_RATE_96000 = 96000, /* 96kHz sampling rate */ E_MI_AUDIO_SAMPLE_RATE_INVALID, }MI_AUDIO_SampleRate_e;
-
Member
Table3-4
Member Name Description E_MI_AUDIO_SAMPLE_RATE_8000 8kHz sampling rate E_MI_AUDIO_SAMPLE_RATE_11025 11.025kHz sampling rate E_MI_AUDIO_SAMPLE_RATE_12000 12kHz sampling rate E_MI_AUDIO_SAMPLE_RATE_16000 16kHz sampling rate E_MI_AUDIO_SAMPLE_RATE_22050 22.05kHz sampling rate E_MI_AUDIO_SAMPLE_RATE_24000 24kHz sampling rate E_MI_AUDIO_SAMPLE_RATE_32000 32kHz sampling rate E_MI_AUDIO_SAMPLE_RATE_44100 44.1kHz sampling rate E_MI_AUDIO_SAMPLE_RATE_48000 48kHz sampling rate E_MI_AUDIO_SAMPLE_RATE_96000 96kHz sampling rate -
Note
-
The enumeration value here does not start at 0 but it is the same as the actual sample rate value.
-
Audio input only supports 8/16/32/48kHz sampling rate.
-
-
Related data types and interfaces
3.6. MI_AUDIO_Bitwidth_e¶
-
Description
Define audio sampling accuracy.
-
Definition
typedef enum { E_MI_AUDIO_BIT_WIDTH_16 =0, /* 16bit width */ E_MI_AUDIO_BIT_WIDTH_24 =1, /* 24bit width */ E_MI_AUDIO_BIT_WIDTH_32 =2, /* 32bit width */ E_MI_AUDIO_BIT_WIDTH_MAX, }MI_AUDIO_BitWidth_e;
-
Member
Table3-5
Member Name Description E_MI_AUDIO_BIT_WIDTH_16 Sampling accuracy is 16bit width E_MI_AUDIO_BIT_WIDTH_24 Sampling accuracy is 24 bit width E_MI_AUDIO_BIT_WIDTH_32 Sampling accuracy is 32 bit width -
Note
Currently the chip only supports 16bit bit width, but I2S of some chips can support 32 bits.
3.7. MI_AUDIO_Mode_e¶
-
Description
Define the audio input and output working mode
-
Definition
typedef enum { E_MI_AUDIO_MODE_I2S_MASTER, /* I2S master mode */ E_MI_AUDIO_MODE_I2S_SLAVE, /* I2S slave mode */ E_MI_AUDIO_MODE_TDM_MASTER, /* TDM master mode */ E_MI_AUDIO_MODE_TDM_SLAVE, /* TDM slave mode */ E_MI_AUDIO_MODE_MAX, }MI_AUDIO_Mode_e;
-
Member
Table3-6
Member Name Description E_MI_AUDIO_MODE_I2S_MASTER I2S master mode E_MI_AUDIO_MODE_I2S_SLAVE I2S slave mode E_MI_AUDIO_MODE_TDM_MASTER TDM master mode E_MI_AUDIO_MODE_TDM_SLAVE TDM slave mode -
Note
Whether the master mode and the slave mode is supported depends on the chip involved.
-
Related data types and interfaces
3.8. MI_AUDIO_SoundMode_e¶
-
Description
Define audio channel mode.
-
Definition
typedef enum { E_MI_AUDIO_SOUND_MODE_MONO =0, /* mono */ E_MI_AUDIO_SOUND_MODE_STEREO =1, /* stereo */ E_MI_AUDIO_SOUND_MODE_QUEUE =2, /*all data in One chn */ E_MI_AUDIO_SOUND_MODE_MAX, }MI_AUDIO_SoundMode_e
-
Member
Table3-7
Member Name Description E_MI_AUDIO_SOUND_MODE_MONO Mono E_MI_AUDIO_SOUND_MODE_STEREO Two channels. E_MI_AUDIO_SOUND_MODE_QUEUE All audio data is arranged in order in one channel for use in audio capture -
Note
When the sound mode is E_MI_AUDIO_SOUND_MODE_QUEUE, only channel 0 needs to be set as the parameter. Other channels will use the same parameter as channel 0, but the processing of each channel is independent of each other. At the same time, each channel gain is independent of each other, which needs to be set separately by the user. Suppose there are 4 channels at present, and the buffer size of the user is 4nByte, then the data size of each channel is 4n / 4 = nByte. The data are arranged as follows:
Ch0,Ch0,Ch0,Ch0,Ch0,Ch0,Ch0,Ch0……
Ch1,Ch1,Ch1,Ch1,Ch1,Ch1,Ch1,Ch1……
Ch2,Ch2,Ch2,Ch2,Ch2,Ch2,Ch2,Ch2……
Ch3,Ch3,Ch3,Ch3,Ch3,Ch3,Ch3,Ch3……
-
Related data types and interfaces
3.9. MI_AUDIO_AencType_e¶
-
Description
Define the audio encoding type.
-
Definition
typedef enum { E_MI_AUDIO_AENC_TYPE_G711A = 0, E_MI_AUDIO_AENC_TYPE_G711U, E_MI_AUDIO_AENC_TYPE_G726, E_MI_AUDIO_AENC_TYPE_INVALID, }MI_AUDIO_AencType_e;
-
Member
Table3-8
Member Name Description E_MI_AUDIO_AENC_TYPE_G711A G711A encoding E_MI_AUDIO_AENC_TYPE_G711U G711U encoding E_MI_AUDIO_AENC_TYPE_G726 G726 encoding -
Related data types and interfaces
3.10. MI_AUDIO_G726Mode_e¶
-
Description
Define the G726 operating mode.
-
Definition
typedef enum { E_MI_AUDIO_G726_MODE_16 = 0, E_MI_AUDIO_G726_MODE_24, E_MI_AUDIO_G726_MODE_32, E_MI_AUDIO_G726_MODE_40, E_MI_AUDIO_G726_MODE_INVALID, }MI_AUDIO_G726Mode_e;
-
Member
Table3-9
Member Name Description E_MI_AUDIO_G726_MODE_16 G726 16K bit rate mode. E_MI_AUDIO_G726_MODE_24 G726 24K bit rate mode. E_MI_AUDIO_G726_MODE_32 G726 32K bit rate mode. E_MI_AUDIO_G726_MODE_40 G726 40K bit rate mode. -
Related data types and interfaces
3.11. MI_AUDIO_I2sFmt_e¶
-
Description
I2S format setting.
-
Definition
typedef enum { E_MI_AUDIO_I2S_FMT_I2S_MSB, E_MI_AUDIO_I2S_FMT_LEFT_JUSTIFY_MSB, }MI_AUDIO_I2sFmt_e;
-
Member
Table3-10
Member Name Description E_MI_AUDIO_I2S_FMT_I2S_MSB I2S standard format, highest priority E_MI_AUDIO_I2S_FMT_LEFT_JUSTIFY_MSB I2S left-aligned format, highest priority -
Related data types and interfaces
3.12. MI_AUDIO_I2sMclk_e¶
-
Description
I2S MCLK setting
-
Definition
typedef enum{ E_MI_AUDIO_I2S_MCLK_0, E_MI_AUDIO_I2S_MCLK_12_288M, E_MI_AUDIO_I2S_MCLK_16_384M, E_MI_AUDIO_I2S_MCLK_18_432M, E_MI_AUDIO_I2S_MCLK_24_576M, E_MI_AUDIO_I2S_MCLK_24M, E_MI_AUDIO_I2S_MCLK_48M, }MI_AUDIO_I2sMclk_e;
-
Member
Table3-11
Member Name Description E_MI_AUDIO_I2S_MCLK_0 Turn off MCLK E_MI_AUDIO_I2S_MCLK_12_288M Set MCLK to 12.88M E_MI_AUDIO_I2S_MCLK_16_384M Set MCLK to 16.384M E_MI_AUDIO_I2S_MCLK_18_432M Set MCLK to 18.432M E_MI_AUDIO_I2S_MCLK_24_576M Set MCLK to 24.576M E_MI_AUDIO_I2S_MCLK_24M Set MCLK to 24M E_MI_AUDIO_I2S_MCLK_48M Set MCLK to 48M -
Related data types and interfaces
3.13. MI_AUDIO_I2sConfig_t¶
-
Description
Define the I2S attribute structure..
-
Definition
typedef struct MI_AUDIO_I2sConfig_s { MI_AUDIO_I2sFmt_e eFmt; MI_AUDIO_I2sMclk_e eMclk; MI_BOOL bSyncClock; }MI_AUDIO_I2sConfig_t;
-
Member
Table3-12
Member Name Description eFmt I2S format settings, static attribute. eMclk I2S MCLK clock setting, tatic attribute. bSyncClock The AI synchronizes the AO clock. Static attribute. -
Related data types and interfaces
3.14. MI_AUDIO_Attr_t¶
-
Description
Defining audio input/output device attribute structures.
-
Definition
typedef struct MI_AUDIO_Attr_s { MI_AUDIO_SampleRate_e eSamplerate; /*sample rate*/ MI_AUDIO_BitWidth_e eBitwidth; /*bitwidth*/ MI_AUDIO_Mode_e eWorkmode; /*master or slave mode*/ MI_AUDIO_SoundMode_e eSoundmode; /*momo or stereo*/ MI_U32 u32FrmNum; /*frame num in buffer*/ MI_U32 u32PtNumPerFrm; /*number of samples*/ MI_U32 u32CodecChnCnt; /*channel number on Codec */ MI_U32 u32ChnCnt; union{ MI_AUDIO_I2sConfig_t stI2sConfig; }WorkModeSetting; }MI_AUDIO_Attr_t;
-
Member
Table3-13
Member Name Description eSamplerate Audio sample rate.
Static attribute.eBitwidth Audio sampling accuracy (in slave mode, this parameter must match the sampling accuracy of the audio AD/DA).
Static attribute.eWorkmode Audio input and output working mode.
Static attribute.eSoundmode Audio channel mode.
Static attribute.u32FrmNum The number of cached frames.
Reserved, unused.u32PtNumPerFrm The number of sampling points per frame.
The value ranges from: 128, 128*2, …, 128*N .
Static attribute.u32CodecChnCnt The number of channels supported codec.
Reserved, unused.u32ChnCnt The number of channels supported, the maximum number of channels that are actually enabled. (The input supports up to MI_AUDIO_MAX_CHN_NUM channels, and the output supports up to 2 channels) MI_AUDIO_I2sConfig_t stI2sConfig; Set I2S work properties -
Related data types and interfaces
3.15. MI_AI_ChnParam_t¶
-
Description
Define channel parameter structure.
-
Definition
typedef struct MI_AI_ChnParam_s { MI_AI_ChnGainConfig_t stChnGain; MI_U32 u32Reserved; } MI_AI_ChnParam_t
-
Member
Table3-14
Member Name Description stChnGain AI channel gain setting structure u32Reserved Reserved, not used. -
Related data types and interfaces
3.16. MI_AUDIO_Frame_t¶
-
Description
Define the audio frame structure.
-
Definition
MI_AO API Version <= 2.9: typedef struct MI_AUDIO_Frame_s { MI_AUDIO_BitWidth_e eBitwidth; MI_AUDIO_SoundMode_e eSoundmode; void *apVirAddr[MI_AUDIO_MAX_CHN_NUM]; MI_U64 u64TimeStamp; MI_U32 u32Seq; MI_U32 u32Len; MI_U32 au32PoolId[2]; }MI_AUDIO_Frame_t; MI_AO API Version 为 2.9 ~ 2.14: typedef struct MI_AUDIO_Frame_s { MI_AUDIO_BitWidth_e eBitwidth; MI_AUDIO_SoundMode_e eSoundmode; void *apVirAddr[MI_AUDIO_MAX_CHN_NUM]; MI_U64 u64TimeStamp; MI_U32 u32Seq; MI_U32 u32Len; MI_U32 au32PoolId[2]; void *apSrcPcmVirAddr[MI_AUDIO_MAX_CHN_NUM]; MI_U32 u32SrcPcmLen; }MI_AUDIO_Frame_t; MI_AO API Version >= 2.15: typedef struct MI_AUDIO_Frame_s { MI_AUDIO_BitWidth_e eBitwidth; MI_AUDIO_SoundMode_e eSoundmode; void *apVirAddr[MI_AUDIO_MAX_CHN_NUM]; MI_U64 u64TimeStamp; MI_U32 u32Seq; MI_U32 u32Len[MI_AUDIO_MAX_CHN_NUM]; MI_U32 au32PoolId[2]; void *apSrcPcmVirAddr[MI_AUDIO_MAX_CHN_NUM]; MI_U32 u32SrcPcmLen[MI_AUDIO_MAX_CHN_NUM]; }MI_AUDIO_Frame_t;
-
Member
Table3-15
Member Name Description eBitwidth Audio sampling accuracy eSoundmode Audio channel mode. apVirAddr Audio frame data virtual address. u64TimeStamp Audio frame timestamp. With µs unit. u32Seq Audio frame number. u32Len Audio frame length. In bytes. u32PoolId Audio frame buffer pool ID. apSrcPcmVirAddr Audio original pcm frame data virtual address. u32SrcPcmLen Audio original pcm frame length in bytes. -
Note
u32Len (audio frame length) refers to the data length of a whole buffer when the API version is less than or equal to 2.16. The data length of each channel is recording in u32Len[channel index] when the API version is greater than or equal to 2.17.
Mono data are directly stored, the number of sampling points is u32PtNumPerFrm, the length is u32Len; stereo data are stored by left and right channel interleaving storage method, with data format of L,R,L,R,L,R... , the sampling point of each channel is u32PtNumPerFrm, and the total length is u32Len. When sound mode is queue mode, data are stored in channel order. The data length of each channel is u32Len[channel index] , and the sampling points of each channel are u32PtNumPerFrm.
When no algorithm is turned on, pVirAddr is equivalent to apSrcPcmVirAddr, and u32Len is equivalent to u32SrcPcmLen. When the algorithm is turned on, pVirAddr returns the data processed by the algorithm, and apSrcPcmVirAddr returns the original PCM data collected by Audio input.
3.17. MI_AUDIO_AecFrame_t¶
-
Description
Define the audio echo cancellation reference frame information structure.
-
Definition
typedef struct MI_AUDIO_AecFrame_s { MI_AUDIO_Frame_t stRefFrame; /* aec reference audio frame */ MI_BOOL bValid; /* whether frame is valid */ }MI_AUDIO_AecFrame_t;
-
Member
Table3-16
Member Name Description stRefFrame The echo cancels the reference frame structure. bValid The reference frame is valid ranges:
TRUE: The reference frame is valid.
FALSE: The reference frame is invalid. If this is invalid, this reference frame cannot be used for echo cancellation.
3.18. MI_AUDIO_SaveFileInfo_t¶
-
Description
Define audio save file function configuration information structure.
-
Definition
typedef struct MI_AUDIO_SaveFileInfo_s { MI_BOOL bCfg; MI_U8 szFilePath[256]; MI_U32 u32FileSize; /*in KB*/ } MI_AUDIO_SaveFileInfo_t
-
Member
Table3-17
Member Name Description bCfg Configure the enable switch. szFilePath Audio file save path u32FileSize File size, ranging from [1,10240] KB . -
Related data types and interfaces
3.19. MI_AI_VqeConfig_t¶
-
Description
Defining audio input sound quality enhancement configuration information structure.
-
Definition
typedef struct MI_AI_VqeConfig_s { MI_BOOL bHpfOpen; MI_BOOL bAecOpen; MI_BOOL bAnrOpen; MI_BOOL bAgcOpen; MI_BOOL bEqOpen; MI_U32 u32ChnNum; MI_S32 s32WorkSampleRate; MI_S32 s32FrameSample; MI_AUDIO_HpfConfig_t stHpfCfg; MI_AI_AecConfig_t stAecCfg; MI_AUDIO_AnrConfig_t stAnrCfg; MI_AUDIO_AgcConfig_t stAgcCfg; MI_AUDIO_EqConfig_t stEqCfg; }MI_AI_VqeConfig_t;
-
Member
Table3-18
Member Name Description bHpfOpen Whether the high-pass filtering function is enabled or not. bAecOpen Whether the echo cancellation function enables the flag. bAnrOpen Whether the voice noise reduction function is enabled. bAgcOpen Whether the automatic gain control function enables the flag bEqOpen Whether the equalizer function is enabled u32ChnNum Channel number of data s32WorkSampleRate Working sampling frequency. This parameter is the working sampling rate of the internal function algorithm. Value range: 8KHz/16KHz. The default is 8KHz. s32FrameSample The frame length of VQE, that is, the number of sampling points. Only support 128. stHpfCfg High-pass filtering function related configuration information. stAecCfg Echo cancellation function related configuration information. stAnrCfg Configuration information related to the voice noise reduction function. stAgcCfg Automatic gain control related configuration information. stEqCfg Equalizer related configuration information.
3.20. MI_AUDIO_HpfConfig_t¶
-
Description
Defining an audio high-pass filtering function configuration information structure.
-
Definition
typedef struct MI_AUDIO_HpfConfig_s { MI_AUDIO_AlgorithmMode_e eMode; MI_AUDIO_HpfFreq_e eHpfFreq; /*freq to be processed*/ } MI_AUDIO_HpfConfig_t;
-
Member
Table3-19
Member Name Description eMode Audio algorithm operating mode. eHpfFreq High pass filter cutoff frequency selection.
80: The cutoff frequency is 80 Hz;
120: The cutoff frequency is 120 Hz;
150: The cutoff frequency is 150 Hz.
The default value is 150. -
Related data types and interfaces
3.21. MI_AUDIO_HpfFreq_e¶
-
Description
Define the audio high pass filter cutoff frequency.
-
Definition
typedef enum { E_MI_AUDIO_HPF_FREQ_80 = 80, /* 80Hz */ E_MI_AUDIO_HPF_FREQ_120 = 120, /* 120Hz */ E_MI_AUDIO_HPF_FREQ_150 = 150, /* 150Hz */ E_MI_AUDIO_HPF_FREQ_BUTT, } MI_AUDIO_HpfFreq_e;
-
Member
Table3-20
Member Name Description E_MI_AUDIO_HPF_FREQ_80 The cutoff frequency is 80 Hz. E_MI_AUDIO_HPF_FREQ_120 The cutoff frequency is 120 Hz. E_MI_AUDIO_HPF_FREQ_150 The cutoff frequency is 150 Hz. -
Note
The default configuration is 150Hz.
-
Related data types and interfaces
3.22. MI_AI_AecConfig_t¶
-
Description
Defining an audio echo cancellation configuration information structure.
-
Definition
MI_AI API Version <= 2.17: typedef struct MI_AI_AecConfig_s { MI_BOOL bComfortNoiseEnable; MI_S16 s16DelaySample; MI_U32 u32AecSupfreq[6]; MI_U32 u32AecSupIntensity[7]; MI_S32 s32Reserved; } MI_AI_AecConfig_t; MI_AI API Version >= 2.18: typedef struct MI_AI_AecConfig_s { MI_BOOL bComfortNoiseEnable; MI_S16 s16DelaySample; MI_U32 u32AecSupfreq[6]; MI_U32 u32AecSupIntensity[7]; MI_U32 u32AecRatioThreshold; MI_U32 u32AecDistortionTestFreq[2]; MI_S32 s32Reserved; } MI_AI_AecConfig_t;
-
Member
Table3-21
MI_AI API Version <= 2.17:
Member Name Description bComfortNoiseEnable add noise or not.
0: N
1: Y.s16DelaySample The number of samples at the sampling point is delayed.
Only valid when AEC is stereo processing, the default value is 0.u32AecSupfreq The acoustic echo cancellation protection frequency range, the latter data must be greater than or equal to the previous data.
For example: u32AecSupfreq [0] = 10, then: u32AecSupfreq [1] must be greater than or equal to 10.
The maximum frequency corresponding to the current sampling rate is divided into 128 copies on average, and u32AecSupfreq represents the number of copies constituting a frequency band.
For example, suppose the current sampling rate is 16K and the corresponding maximum frequency is 8K. Each copy is 63Hz (8000 / 128 ≈ 62.5Hz). In case we use the recommended values {4,6,36, 49,50,51}, the protection frequency range will be {0~4 * 62.5Hz, 4~6 * 62.5Hz, 6~36 * 62.5Hz, 36~49 * 62.5Hz, 49~50 * 62.5Hz, 50~51 * 62.5Hz, 51-127 * 62.5Hz} = {0~250Hz, 250~375Hz, 375~2250Hz, 2250~3062.5Hz, 3062.5~3125Hz, 3125~3178.5Hz, 3178.5Hz~8000Hz}.
Range [ 1,128 ]; step size 1
Recommended values: {4,6,36,49,50,51}u32AecSupIntensity Acoustic echo cancellation protection, the smaller the value, the stronger the protection effect. Correspond to secondary parameter u32AecSupfreq. u32AecSupIntensity [0] corresponds to 0 ~ u32AecSupfreq [0], u32AecSupIntensity [1] corresponds to u32AecSupfreq [0] ~ u32AecSupfreq [1], and so on.
Range [0,15]; step size 1
Recommended values {5,4,4,5,10,10,10}MI_AI API Version >= 2.18:
Member Name Description bComfortNoiseEnable add noise or not.
0: N
1: Y.s16DelaySample The number of samples at the sampling point is delayed.
Only valid when AEC is stereo processing, the default value is 0.u32AecSupfreq The echo cancellation protection frequency range, the latter data must be greater than or equal to the previous data.
For example: u32AecSupfreq [0] = 10, then: u32AecSupfreq [1] must be greater than or equal to 10.
The maximum frequency corresponding to the current sampling rate is divided into 128 copies on average, and u32AecSupfreq represents the number of copies constituting a frequency band.
For example, suppose the current sampling rate is 16K and the corresponding maximum frequency is 8K. Each copy is 63Hz (8000 / 128 ≈ 62.5Hz). In case we use the recommended values {4,6,36, 49,50,51}, the protection frequency range will be {0~4 * 62.5Hz, 4~6 * 62.5Hz, 6~36 * 62.5Hz, 36~49 * 62.5Hz, 49~50 * 62.5Hz, 50~51 * 62.5Hz, 51-127 * 62.5Hz} = {0~250Hz, 250~375Hz, 375~2250Hz, 2250~3062.5Hz, 3062.5~3125Hz, 3125~3178.5Hz, 3178.5Hz~8000Hz}.
Range [ 1,128 ]; step size 1
Recommended values: {4,6,36,49,50,51}u32AecSupIntensity Echo cancellation protection, the smaller the value, the stronger the protection effect. Correspond to secondary parameter u32AecSupfreq. u32AecSupIntensity [0] corresponds to 0 ~ u32AecSupfreq [0], u32AecSupIntensity [1] corresponds to u32AecSupfreq [0] ~ u32AecSupfreq [1], and so on.
Range [0,15]; step size 1
Recommended values {5,4,4,5,10,10,10}u32AecRatioThreshold The threshold condition for performing acoustic echo cancellation. The acoustic echo cancellation algorithm will always perform echo cancellation processing by default (that is, when u32AecRatioThreshold is 0). In some cases, when the energy ratio between the near end and the far end needs to be multiple, the echo cancellation processing is not performed directly.
Example: When it is hoped that the energy of the near end is n dB greater than that of the far end, no acoustic echo cancellation processing is performed, then u32AecRatioThreshold = 10^(n/10)u32AecDistortionTestFreq Acoustic echo cancellation distortion test frequency point. In some cases, it is desirable not to suppress a certain frequency point. When u32AecDistortionTest is 0, perform acoustic echo cancellation processing normally. -
Related data types and interfaces
3.23. MI_AUDIO_AnrConfig_t¶
-
Description
Define audio voice noise reduction function configuration information structure.
-
Definition
typedef struct MI_AUDIO_AnrConfig_s { MI_AUDIO_AlgorithmMode_e eMode; MI_U32 u32NrIntensity; MI_U32 u32NrSmoothLevel; MI_AUDIO_NrSpeed_e eNrSpeed; } MI_AUDIO_AnrConfig_t;
-
Member
Table3-22 APC API VERSION 1 (or without APIVERSION field)
Member Name Description eMode Audio algorithm operating mode. Note: ANR mode will affect the function of AGC to some extent. u32NrIntensity Noise reduction strength configuration. The larger the configuration value, the higher the noise reduction, but also the greater the loss/damage of the detail sound.
Range [0,30]; step size 1.
The default value is 20.u32NrSmoothLevel Smoothness. The larger the value, the smoother.
Range [0,10]; step size 1.
The default value is 10.eNrSpeed Noise convergence speed: low speed, medium speed, high speed.
The default value is medium speed. -
Note
In the case where both ANR and AGC are enabled, if ANR is set to user mode, AGC will process the audio data in frequency domain, and then evaluate the speech signal and make corresponding boost and cut. When ANR is set to default/music mode, AGC will process the audio data in time domain and boost and cut the data in full frequency band.
-
Related data types and interfaces
3.24. MI_AUDIO_NrSpeed_e¶
-
Description
Define noise convergence speed
-
Definition
typedef enum { E_MI_AUDIO_NR_SPEED_LOW, E_MI_AUDIO_NR_SPEED_MID, E_MI_AUDIO_NR_SPEED_HIGH }MI_AUDIO_NrSpeed_e;
-
Member
Table3-23
Member Name Description E_MI_AUDIO_NR_SPEED_LOW Low speed. E_MI_AUDIO_NR_SPEED_MID Medium speed. E_MI_AUDIO_NR_SPEED_HIGH High speed. -
Related data types and interfaces
3.25. MI_AUDIO_AgcConfig_t¶
-
Description
Defining an audio automatic gain control configuration information structure.
-
Definition
Because of the update of APC algorithm library, in order to be compatible with the old and new versions of algorithm library, the following description is given for different versions. (You can use the command ‘strings libAPC_LINUX.so | grep APCSET’ to get the version of APC algorithm library, where the APC API version will be recorded in the APIVERSION field.)
APC API VERSION 1 (or without APIVERSION field)
typedef struct MI_AUDIO_AgcConfig_s { MI_AUDIO_AlgorithmMode_e eMode; AgcGainInfo_t stAgcGainInfo; MI_U32 u32DropGainMax; MI_U32 u32AttackTime; MI_U32 u32ReleaseTime; MI_S16 s16Compression_ratio_input[5]; MI_S16 s16Compression_ratio_output[5]; MI_S32 s32TargetLevelDb; MI_S32 s32NoiseGateDb; MI_U32 u32NoiseGateAttenuationDb; } MI_AUDIO_AgcConfig_t;
APC API VERSION 2
typedef struct MI_AUDIO_AgcConfig_s { MI_AUDIO_AlgorithmMode_e eMode; AgcGainInfo_t stAgcGainInfo; MI_U32 u32DropGainMax; MI_U32 u32AttackTime; MI_U32 u32ReleaseTime; MI_S16 s16Compression_ratio_input[7]; MI_S16 s16Compression_ratio_output[7]; MI_S32 s32DropGainThreshold; MI_S32 s32NoiseGateDb; MI_U32 u32NoiseGateAttenuationDb; } MI_AUDIO_AgcConfig_t;
-
Member
Table 3-24
Member Name Description eMode Audio algorithm operating mode. stAgcGainInfo Define the maximum, minimum, and initial values of the AGC gain u32DropGainMax Maximum gain decrease, to prevent output saturation.
Range [0,60]; step size 1.
The default value is 55.
Note: This value only represents the range that can be reduced, but the minimum value of AGC gain shall be referred to for the specific value that can be reduced.u32AttackTime Gain fall time interval length, 1 unit in 16 milliseconds.
Range [1,20]; step size 1.
The default value is 0.u32ReleaseTime Gain rise time interval length, 1 unit in 16 milliseconds.
Range [1, 20]; step size 1.
The default value is 0.s16Compression_ratio_input Input RMS energy.
This parameter should be used together with the compression ratio output.
The gain curve consists of multiple turning points with different slopes.
Value range [-80,0]; step size 1.s16Compression_ratio_output Output target RMS energy related input energy.
The gain curve consists of multiple turning points with different slopes.
Value range [-80,0]; step size 1.s32TargetLevelDb Target level, processed maximum level threshold.
Range [-80,0] dB; step size 1.
The default value is 0.
Note: This value can only determine the maximum level that can be achieved, but whether it can be achieved or not depends on the setting of slope curve.s32NoiseGateDb Noise floor. When the signal is less than this value, it is treated as noise.
Range [-80,0]; step size 1.
Note: When the value is -80, the noise floor will not work.
The default value is -55.u32NoiseGateAttenuationDb The percentage of attenuation of the input source when the noise floor value is effective.
Range [0,100]; step size 1.
The default value is 0.APC API VERSION 2
Member Name Description eMode Audio algorithm operating mode. stAgcGainInfo Define the maximum, minimum, and initial values of the AGC gain u32DropGainMax Maximum gain decrease, preventing output saturation Range [0,60]; step size 1 The default value is 55. Note: This value only represents the range that can be reduced, but the minimum value of AGC gain shall be referred to for the specific value that can be reduced. u32AttackTime Gain fall time interval length, 1 unit in 16 milliseconds Range [1,20]; step size 1 The default value is 0. u32ReleaseTime Gain rise time interval length, 1 unit in 16 milliseconds Range [ 1, 20 ] ; step size 1 The default value is 0. s16Compression_ratio_input Input RMS energy. This parameter should be used together with the compression ratio output. The gain curve consists of multiple turning points with different slopes. Value range [-80,0]; step size 1 s16Compression_ratio_output Output target RMS energy related input energy. The gain curve consists of multiple turning points with different slopes. Value range [-80,0]; step size 1 s32DropGainThreshold Dropping Gain threshold. When the signal amplitude exceeds this value, gain will slowly drop. Range [-80,0] dB; step size 1 The default value is 0. s32NoiseGateDb Noise floor. When the signal is less than this value, it is treated as noise. Range [-80,0]; step size 1 Note: When the value is -80, the noise floor will not work. The default value is -55. u32NoiseGateAttenuationDb The percentage of attenuation of the input source when the noise floor value is effective Range [0,100]; step size 1 The default value is 0. -
Note
In the case where both ANR and AGC are enabled, if ANR is set to user mode, AGC will process the audio data in frequency domain, and then evaluate the speech signal and make corresponding boost and cut. When ANR is set to default/music mode, AGC will process the audio data in time domain and boost and cut the data in full frequency band.
S16Compression_ratio_input and s16Compression_ratio_output should be set according to the desired gain curve.
As shown in the line graph below, the input gain of -80~0dB is divided into four (APIVERSION 1 or without APIVERSION field) or six (APIVERSION 2) slopes. The first section is -80db ~ -60db. The original gain is maintained within this range and the slope is 1. The second section is -60db ~ -40db, in which the gain needs to be slightly increased and the slope is 1.5. The third section is -40db ~ -20db and the slope in this range is 1.25. The fourth section is -20db ~0dB and the slope in this range is 0.25. Set s16Compression_ratio_input and s16Compression_ratio_output according to the turning point of the curve. If not so many sections of the curve are needed, then fill in 0 for the unwanted parts of the array.
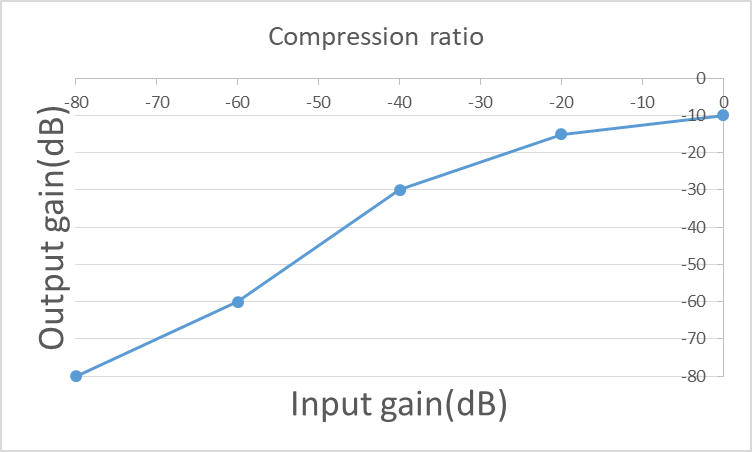
Figure3-1
-
Related data types and interfaces
3.26. AgcGainInfo_t¶
-
Description
AGC gain value.
-
Definition
typedef struct AgcGainInfo_s{ MI_S32 s32GainMax; MI_S32 S32GainMin; MI_S32 s32GainInit; }AgcGainInfo_t;
-
Member
Table3-25
Member Name Description s32GainMax Maximum gain
Range [0,60]; step size 1
The default value is 15.s32GainMin Minimum gain
Range [-20,30]; step size 1
The default value is 0.s32GainInit Initial gain
Range [-20,60]; step size 1
The default value is 0. -
Related data types and interfaces
3.27. MI_AUDIO_EqConfig_t¶
-
Description
Define the audio equalizer function configuration information structure.
-
Definition
typedef struct MI_AUDIO_EqConfig_s { MI_AUDIO_AlgorithmMode_e eMode; MI_S16 s16EqGainDb[129]; } MI_AUDIO_EqConfig_t;
-
Member
Table3-26
Member Name Description eMode Audio algorithm operating mode. s16EqGainDb[129] Equalizer gain adjustment value
It divides the frequency range of the current sampling rate into 129 parts for adjustment.
Range [-50,20]; step size 1
The default value is 0.
For example, if the current sampling rate is 16K and the corresponding maximum frequency is 8K, then the frequency range of a single adjustment is 62Hz (8000/129≈62Hz), and 0-8k is divided into {0-1 * 62Hz, 1-2 * 62Hz, 2-3 * 62Hz... , 128-129 * 62Hz} = {0-62Hz, 62-124Hz, 124-186Hz..., 7938-8000Hz}, each segment corresponding to a gain value. -
Related data types and interfaces
3.28. MI_AI_AencGConfig_t¶
-
Description
Defining an audio coding function configuration information structure.
-
Definition
typedef struct MI_AI_AencConfig_s { MI_AUDIO_AencType_e eAencType; union { MI_AUDIO_AencG711Config_t stAencG711Cfg; MI_AUDIO_AnecG726Config_t stAencG726Cfg; }; }MI_AI_AencConfig_t;
-
Member
Table3-27
Member Name Description eAencType Audio encoding type. stAencG711Cfg G711 code related configuration information. stAencG726Cfg G726 code related configuration information. -
Related data types and interfaces
3.29. MI_AUDIO_AencG711Config_t¶
-
Description
Define the audio encoding function configuration information structure.
-
Definition
typedef struct MI_AUDIO_AencG711Config_s { MI_AUDIO_SampleRate_e eSamplerate; MI_AUDIO_SoundMode_e eSoundmode; }MI_AUDIO_AencG711Config_t;
-
Member
Table3-28
Member Name Description eSamplerate Audio sample rate eSoundmode Audio channel mode. -
Related data types and interfaces
3.30. MI_AUDIO_AencG726Config_t¶
-
Description
Define the audio encoding function configuration information structure.
-
Definition
typedef struct MI_AUDIO_AencG726Config_s { MI_AUDIO_SampleRate_e eSamplerate; MI_AUDIO_SoundMode_e eSoundmode; MI_AUDIO_G726Mode_e eG726Mode; }MI_AUDIO_AencG726Config_t;
-
Member
Table3-29
Member Name Description eSamplerate Audio sample rate. eSoundmode Audio channel mode. eG726Mode G726 working mode. -
Related data types and interfaces
3.31. MI_AUDIO_AlgorithmMode_e¶
-
Description
Define the operating mode of the audio algorithm.
-
Definition
typedef enum { E_MI_AUDIO_ALGORITHM_MODE_DEFAULT, E_MI_AUDIO_ALGORITHM_MODE_USER, E_MI_AUDIO_ALGORITHM_MODE_MUSIC, E_MI_AUDIO_ALGORITHM_MODE_INVALID, }MI_AUDIO_AlgorithmMode_e;
-
Member
Table3-30
Member Name Description E_MI_AUDIO_ALGORITHM_MODE_DEFAULT Default mode. Note: When using this mode, the default parameters of the algorithm will be used E_MI_AUDIO_ALGORITHM_MODE_USER User mode. Note: When using this mode, the user needs to reset all parameters. E_MI_AUDIO_ALGORITHM_MODE_MUSIC Music mode. Note: Only ANR has this mode. When this mode is used, AGC does not perform speech enhancement processing. -
Note
In the case where both ANR and AGC are enabled, if ANR is set to user mode, AGC will process the audio data in frequency domain, and then evaluate the speech signal and make corresponding boost and cut. When ANR is set to default/music mode, AGC will process the audio data in time domain and boost and cut the data in full frequency band.
-
Related data types and interfaces
3.32. MI_AI_AedConfig_t¶
-
Description
Define the sound event detection function configuration information structure.
-
Definition
typedef struct MI_AI_AedConfig_s { MI_BOOL bEnableNr; MI_AUDIO_AedSensitivity_e eSensitivity; MI_S32 s32OperatingPoint; MI_S32 s32VadThresholdDb; MI_S32 s32LsdThresholdDb; }MI_AI_AedConfig_t;
-
Member
Table3-31
Member Name Description bEnableNr Whether to enable noise reduction function of baby cry detection eSensitivity Sensitivity of baby cry detection function s32OperatingPoint Operating Point
Range [ -10,10 ]; step size 1
The default value is 0.
Note:Increasing the operating point will reduce the false positive rate, and reducing the operating point will reduce the leak rate.s32VadThresholdDb Vad threshold Db
Range [ -80,0 ]; step size 1
The default value is -40.s32LsdThresholdDb Lsd threshold Db
Range [ -80,0 ]; step size 1
The default value is -15. -
Related data types and interfaces
3.33. MI_AUDIO_AedSensitivity_e/MI_AUDIO_BabyCrySensitivity_e¶
-
Description
Define the sensitivity of baby cry detection.
-
Definition
MI_AI API Version <= 2.15:
typedef enum { E_MI_AUDIO_AED_SEN_LOW, E_MI_AUDIO_AED_SEN_MID, E_MI_AUDIO_AED_SEN_HIGH, E_MI_AUDIO_AED_SEN_INVALID, }MI_AUDIO_AedSensitivity_e;
MI_AI API Version >= 2.16:
typedef enum { E_MI_AUDIO_BABYCRY_SEN_LOW, E_MI_AUDIO_BABYCRY_SEN_MID, E_MI_AUDIO_BABYCRY_SEN_HIGH, E_MI_AUDIO_BABYCRY_SEN_INVALID, } MI_AUDIO_BabyCrySensitivity_e;
-
Member
Table3-32
Member Name Description E_MI_AUDIO_AED_SEN_LOW/ E_MI_AUDIO_BABYCRY_SEN_LOW Low sensitivity E_MI_AUDIO_AED_SEN_MID/ E_MI_AUDIO_BABYCRY_SEN_MID Medium sensitivity E_MI_AUDIO_AED_SEN_HIGH/ E_MI_AUDIO_BABYCRY_SEN_HIGH High sensitivity -
Related data types and interfaces
3.34. MI_AI_AedResult_t¶
-
Description
Define the sound event detection result structure.
-
Definition
typedef struct MI_AI_AedResult_s { MI_BOOL bAcousticEventDetected; MI_BOOL bLoudSoundDetected; }MI_AI_AedResult_t;
-
Member
Table3-33
Member Name Description bAcousticEventDetected Whether an acoustic event is detected bLoudSoundDetected Whether a loud sound is detected -
Related data types and interfaces
3.35. MI_AI_ChnGainConfig_t¶
-
Description
Define the AI channel gain setting structure.
-
Definition
typedef struct MI_AI_ChnGainConfig_s { MI_BOOL bEnableGainSet; MI_S16 s16FrontGain; MI_S16 s16RearGain; }MI_AI_ChnGainConfig_t;
-
Member
Table3-34
Member Name Description bEnableGainSet Enable gain setting s16FrontGain Front Gain s16RearGain Rear Gain -
Note
The following table describes the definition of s16frontgain and s16reargain for each device.
Table3-35
AI Device ID s16FrontGain s16RearGain Amic Analog gain of Amic (0 - 21) Digital gain of Amic (-60 - 30) Dmic Gain of Dmic
Pretzel series(0 - 4)
Macaron series(-60 - 30)
Taiyaki series(0 - 4)
Takoyaki series(0 - 4)
Pudding series(-60 - 30)
Ispahan series(-60 - 30)
Tiramisu series(0 - 4)
Ikayaki series(0 - 4)No effect I2S RX No effect No effect Line in Analog gain of Line in (0 - 7) Digital gain of Line in (-60 - 30) -
Related data types and interfaces
3.36. MI_AI_SslInitAttr_t¶
-
Description
Define the Sound source localization initialized structure.
-
Definition
typedef struct MI_AI_SslInitAttr_s { MI_U32 u32MicDistance; MI_BOOL bBfMode; } MI_AI_SslInitAttr_t;
-
Member
Table3-36
Member Name Description u32MicDistance Microphone Distance (cm) bBfMode Whether to enable beamforming mode
Note:
FALSE: Mechanical rotation mode
TRUE: Beamforming mode -
Related data types and interfaces
3.37. MI_AI_SslConfigAttr_t¶
-
Description
Define the Sound source localization configured structure.
-
Definition
typedef struct MI_AI_SslConfigAttr_s { MI_S32 s32Temperature; MI_S32 s32NoiseGateDbfs; MI_S32 s32DirectionFrameNum; } MI_AI_SslConfigAttr_t;
-
Member
Table3-37
Member Name Description s32Temperature The temperature of environment (unit Celsius)
Celsius = (5/9) × (Fahrenheit-32)s32NoiseGateDbfs Noise gain threshold (dB)
Step size 1.
Note:
If power of any frame is smaller than this value, the SSL will return 0 as the direction immediately.
This value should be set to a negative value, because the unit is dbfs. The default setting is -80.s32DirectionFrameNum SSL direction frame number
Note:
It will determine the output one result every frame_num frames. It should be a multiple of 50. One frame of ssl has 128 sample points.
time of output a result = s32DirectionFrameNum * 128 / samplerate. -
Related data types and interfaces
3.38. MI_AI_BfInitAttr_t¶
-
Description
Define the Beamforming initialized structure.
-
Definition
typedef struct MI_AI_BfInitAttr_s { MI_U32 u32MicDistance; MI_U32 u32ChanCnt; } MI_AI_BfInitAttr_t;
-
Member
Table3-38
Member Name Description u32MicDistance Microphone Distance (cm) u32ChanCnt Channel Count. Note: must be 2 -
Related data types and interfaces
3.39. MI_AI_BfConfigAttr_t¶
-
Description
Define the Beamforming configured structure.
-
Definition
typedef struct MI_AI_BfConfigAttr_s { MI_S32 s32Temperature; MI_S32 s32NoiseGateDbfs; MI_S32 s32NoiseSupressionMode; MI_S32 s32NoiseEstimation; MI_FLOAT outputGain; } MI_AI_BfConfigAttr_t;
-
Member
Table3-39
Member Name Description s32Temperature The temperature of environment (unit Celsius)
Celsius = (5/9) × (Fahrenheit-32)s32NoiseGateDbfs If the power of signal is smaller than this setting, this frame will be taken as the noise part, and used to calculate some estimation.
Please be careful with the use of this parameter.
If set too high, it will cause speech distortion.
If set too small, it will cause BF result to be not good enough.
Recommended setting: -44.s32NoiseSupressionMode A bigger number will remove more noise (0~15).
Please be careful with the use of this parameter.
If set too high, it will cause speech distortion.
If set too small, it will cause BF result to be not good enough.
Recommended setting: 8.s32NoiseEstimation This setting could change the noise estimation method (0 or 1) for keyword spotting preprocessing.
0 for adaptation method.
1 for average method.
Recommended setting: 0
For acoustic communication, 1 is recommended.outputGain Output signal gain control (range: 0 ~ 1).
0.7 is the normal case.
Setting as 1 will add 4db.
Recommended setting: 0.7 (nothing changed). -
Related data types and interfaces
3.40. MI_AI_InitParam_t¶
-
Description
Define the initialized parameter of audio input device.
-
Definition
typedef struct MI_AI_InitParam_s { MI_U32 u32DevId; MI_U8 *u8Data; } MI_AI_InitParam_t;
-
Member
Table3-40
Member Name Description u32DevId Audio device number u8Data Initialization parameter pointer (reserved) -
Related data types and interfaces
3.41. MI_AI_BabyCryConfig_t¶
-
Description
Define the configured attribute structure of baby cry detection.
-
Definition
typedef struct MI_AI_BabyCryConfig_s { MI_BOOL bEnableNr; MI_AUDIO_BabyCrySensitivity_e eSensitivity; MI_S32 s32OperatingPoint; MI_S32 s32VadThresholdDb; } MI_AI_BabyCryConfig_t;
-
Member
Table3-41
Member Name Description bEnableNr Whether to enable noise reduction function of baby cry detection eSensitivity Sensitivity of baby cry detection function s32OperatingPoint Operating Point
Range [ -10,10 ]; step size 1
The default value is 0.
Note:Increasing the operating point will reduce the false positive rate, and reducing the operating point will reduce the leak rate.s32VadThresholdDb Vad threshold Db
Range [ -80,0 ]; step size 1
The default value is -40. -
Related data types and interfaces
3.42. MI_AI_LsdConfig_t¶
-
Description
Define the configured attribute structure of loud sound detection.
-
Definition
typedef struct MI_AI_LsdConfig_s { MI_S32 s32LsdThresholdDb; } MI_AI_LsdConfig_t;
-
Member
Table3-42
Member Name Description s32LsdThresholdDb Lsd threshold Db
Range [ -80,0 ]; step size 1
The default value is -15. -
Related data types and interfaces
4. Error Code¶
The AI API error codes are shown in the table below.
| Error Code | Definition | Description |
|---|---|---|
| 0xA0042001 | MI_AI_ERR_INVALID_DEVID | Invalid audio input device number |
| 0xA0042002 | MI_AI_ERR_INVALID_CHNID | Invalid audio input channel number |
| 0xA0042003 | MI_AI_ERR_ILLEGAL_PARAM | Invalid audio input parameter setting |
| 0xA0042006 | MI_AI_ERR_NULL_PTR | Input parameter empty indicator error |
| 0xA0042007 | MI_AI_ERR_NOT_CONFIG | Audio input device properties are not set |
| 0xA0042008 | MI_AI_ERR_NOT_SUPPORT | Operation is not supported |
| 0xA0042009 | MI_AI_ERR_NOT_PERM | Operation not allowed |
| 0xA004200C | MI_AI_ERR_NOMEM | Failed to allocate memory |
| 0xA004200D | MI_AI_ERR_NOBUF | Insufficient audio input buffer |
| 0xA004200E | MI_AI_ERR_BUF_EMPTY | Audio input buffer is empty |
| 0xA004200F | MI_AI_ERR_BUF_FULL | Audio input buffer is full |
| 0xA0042010 | MI_AI_ERR_SYS_NOTREADY | Audio input system is not initialized |
| 0xA0042012 | MI_AI_ERR_BUSY | Audio input system is busy |
| 0xA0042017 | MI_AI_ERR_NOT_ENABLED | Audio input device or channel is not enabled |
| 0xA0042100 | MI_AI_ERR_VQE_ERR | Audio input VQE algorithm failed to process |
| 0xA0042101 | MI_AI_ERR_AENC_ERR | Audio input encoding algorithm failed to process |
| 0xA0042102 | MI_AI_ERR_AED_ERR | Audio input AED algorithm failed to process |
| 0xA0042103 | MI_AI_ERR_SSL_ERR | Audio input SSL algorithm failed to process |
| 0xA0042104 | MI_AI_ERR_BF_ERR | Audio input BF algorithm failed to process |